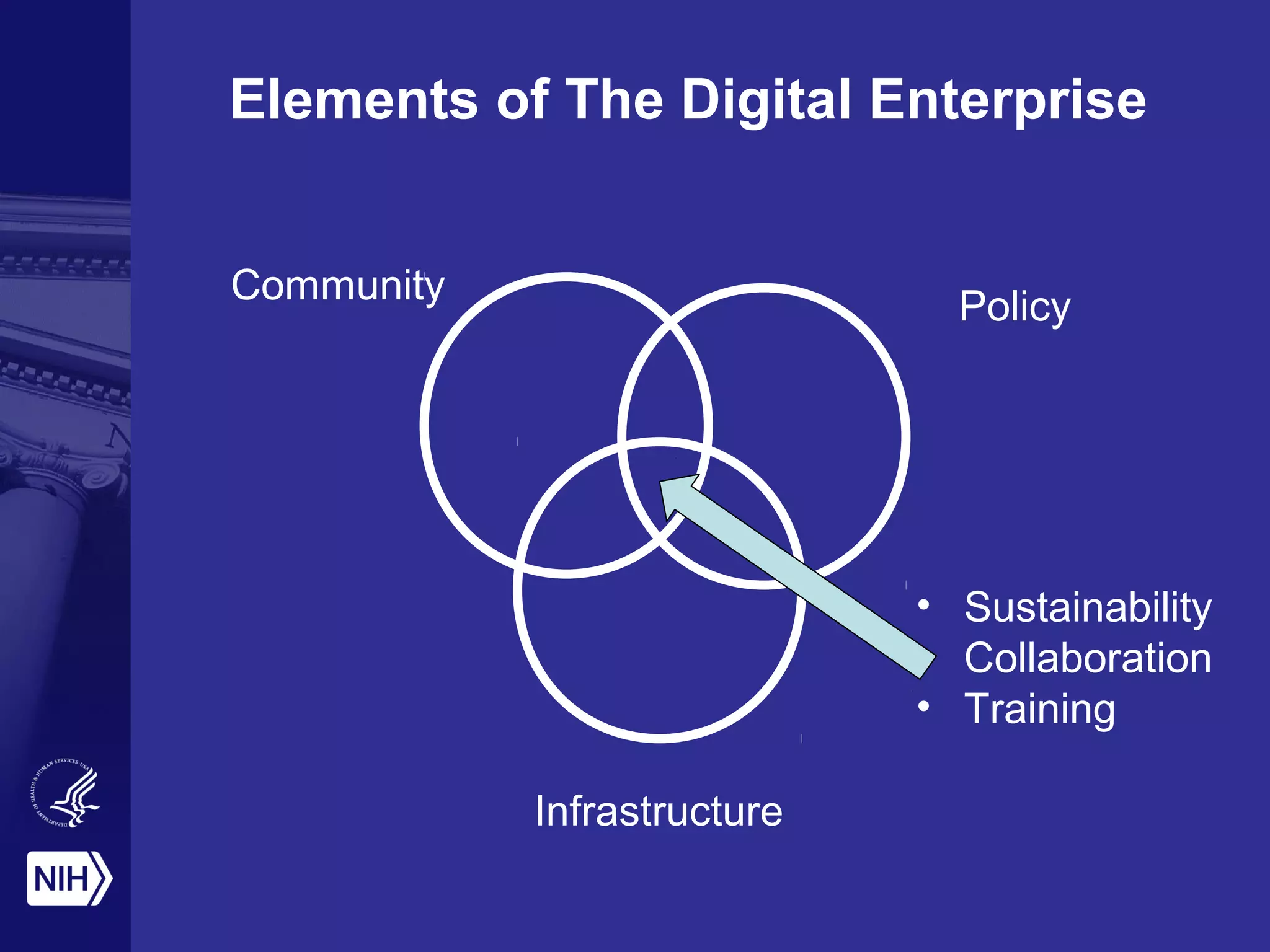
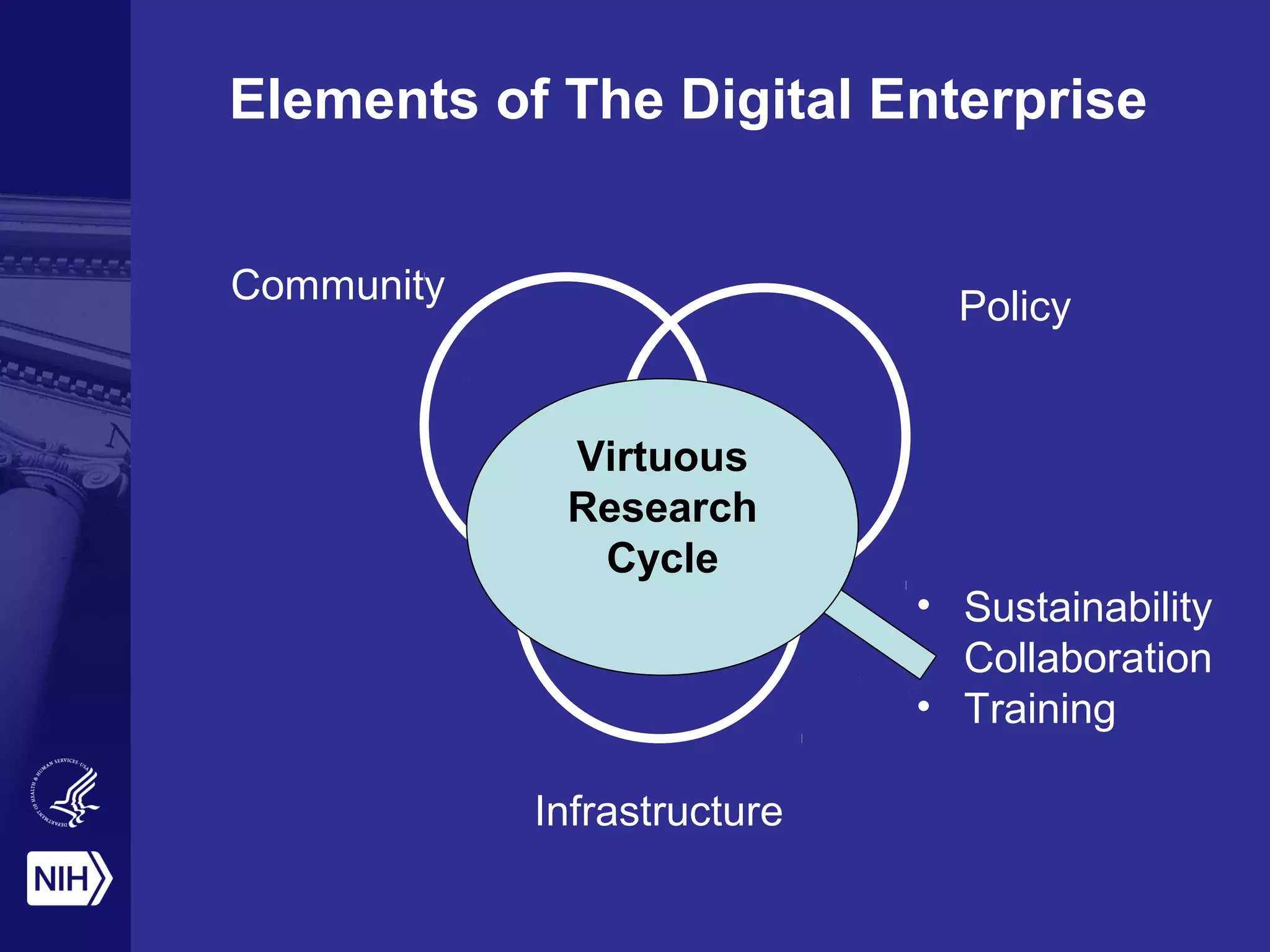
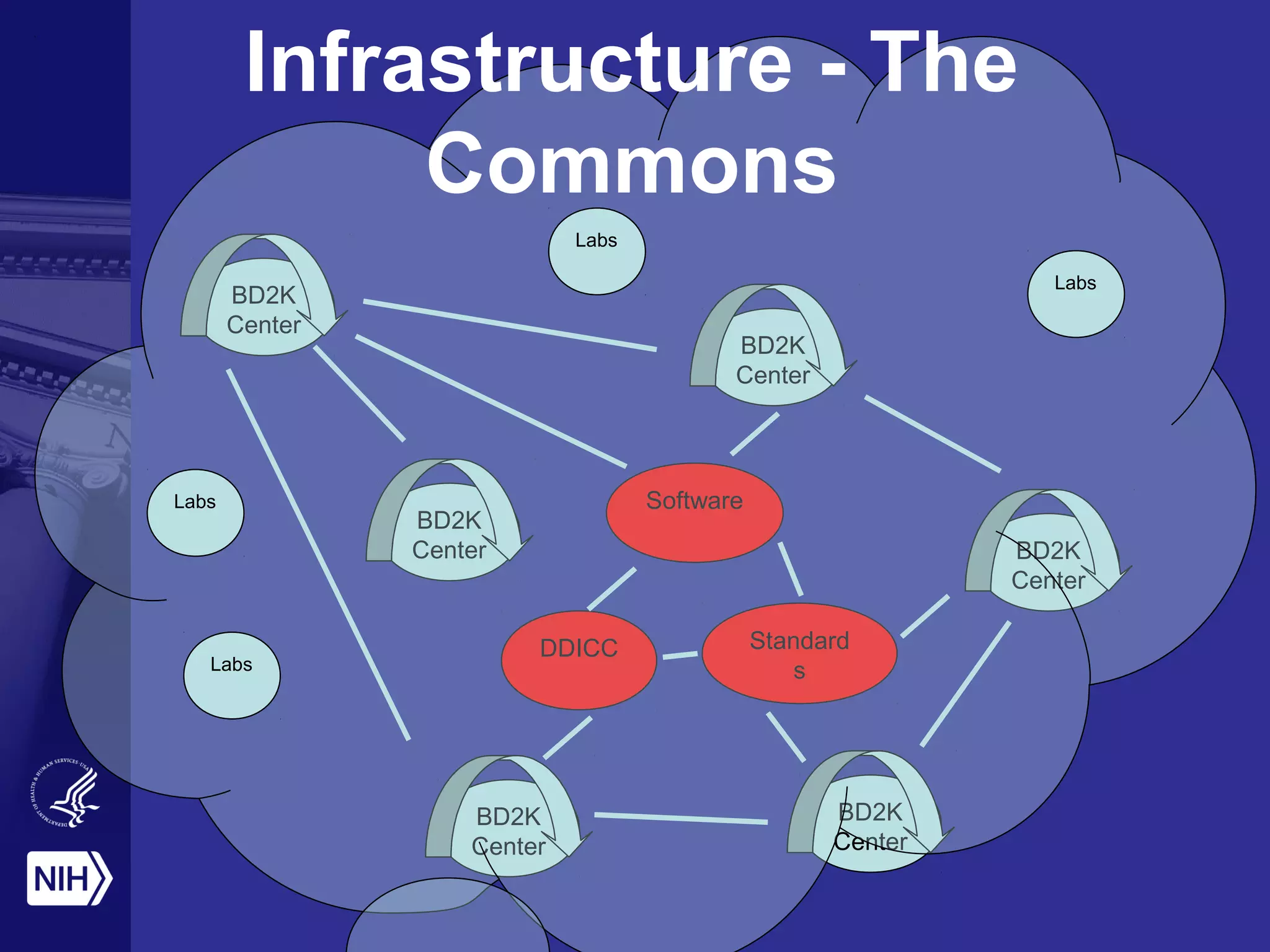
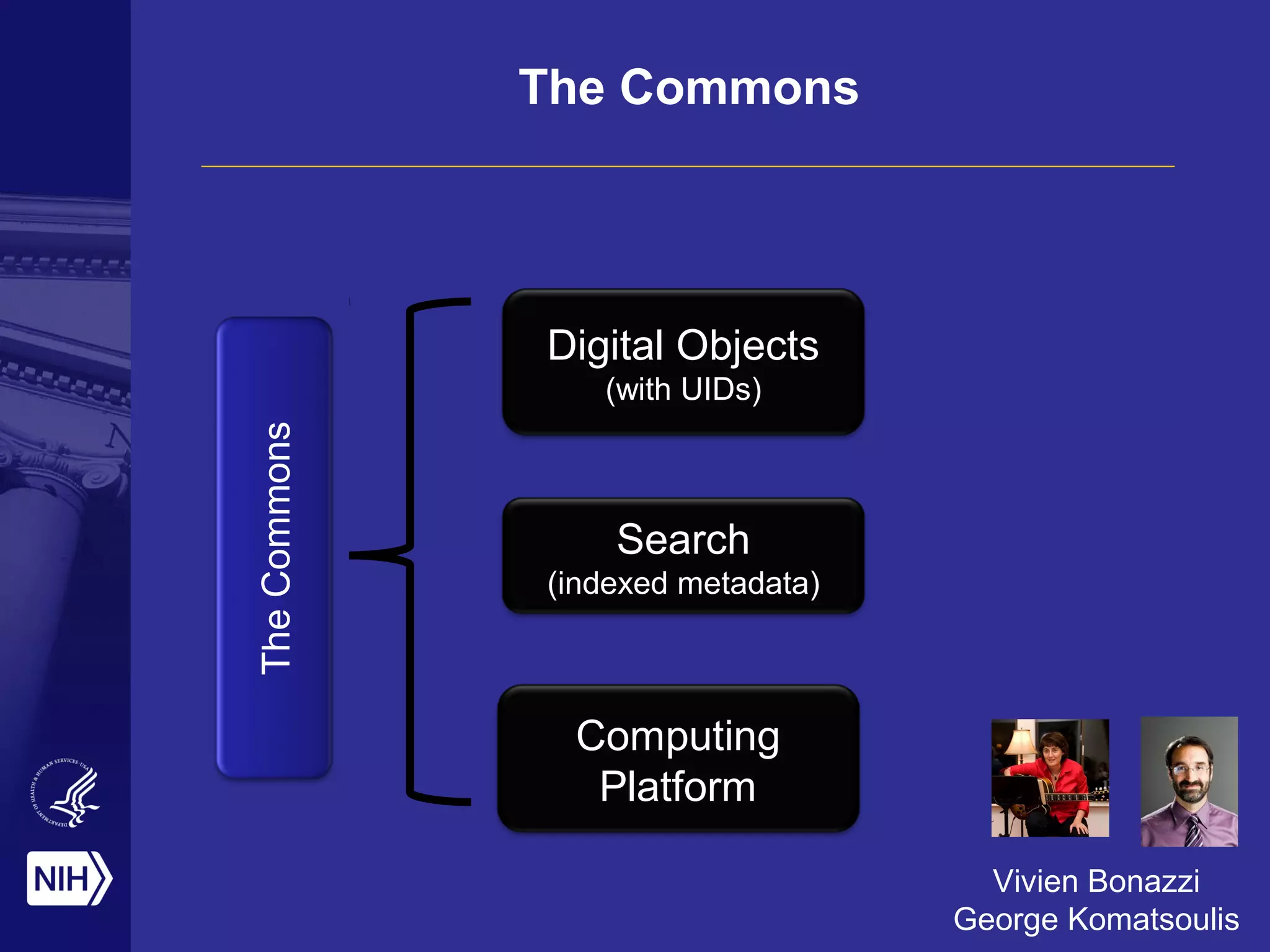
The document discusses the NIH's vision of becoming a digital enterprise to enhance biomedical research. It outlines how research is becoming more digital and data-driven. The NIH aims to foster open sharing of data and tools through its Commons platform to facilitate collaboration and reproducibility. It also stresses the importance of training the next generation of data scientists to enable the digital enterprise. The end goal is to accelerate discovery and improve health outcomes through more integrated and data-driven research.






![47/53 “landmark” publications
could not be replicated
[Begley, Ellis Nature,
483, 2012] [Carole Goble]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pag011114-150111124237-conversion-gate02/75/The-NIH-as-a-Digital-Enterprise-Implications-for-PAG-10-2048.jpg)






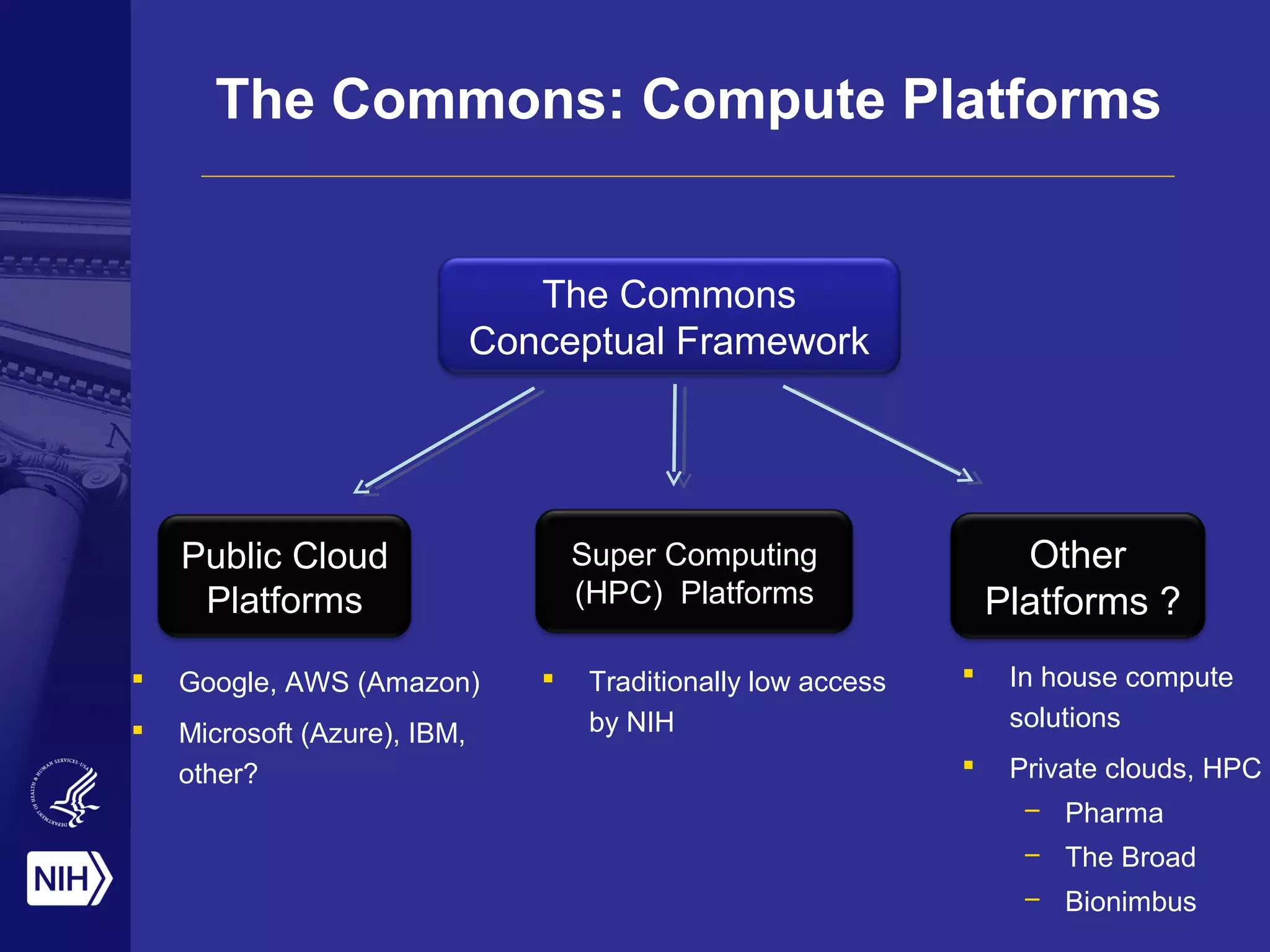
![The Commons:
Business Model
[George Komatsoulis]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pag011114-150111124237-conversion-gate02/75/The-NIH-as-a-Digital-Enterprise-Implications-for-PAG-23-2048.jpg)






