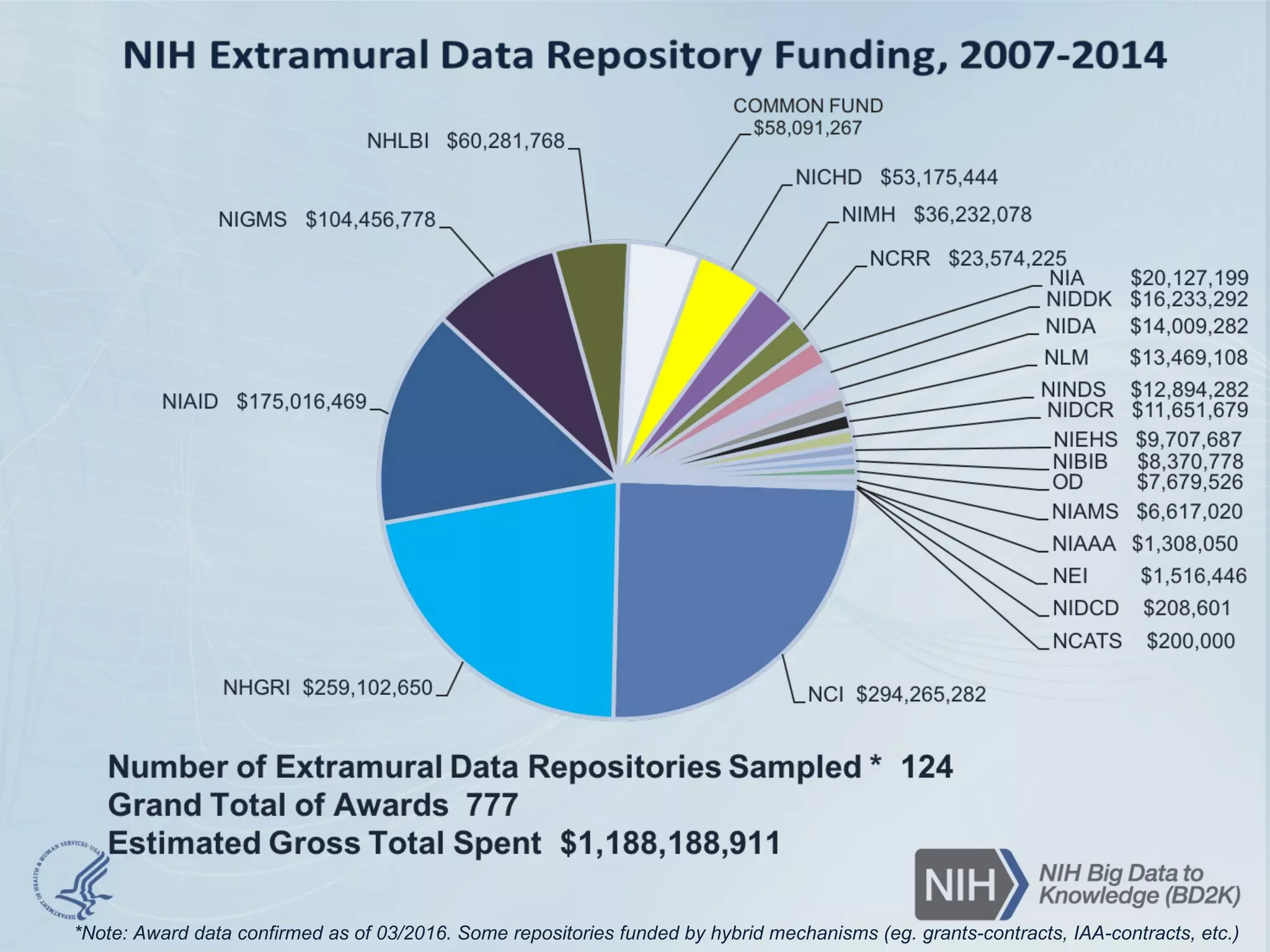
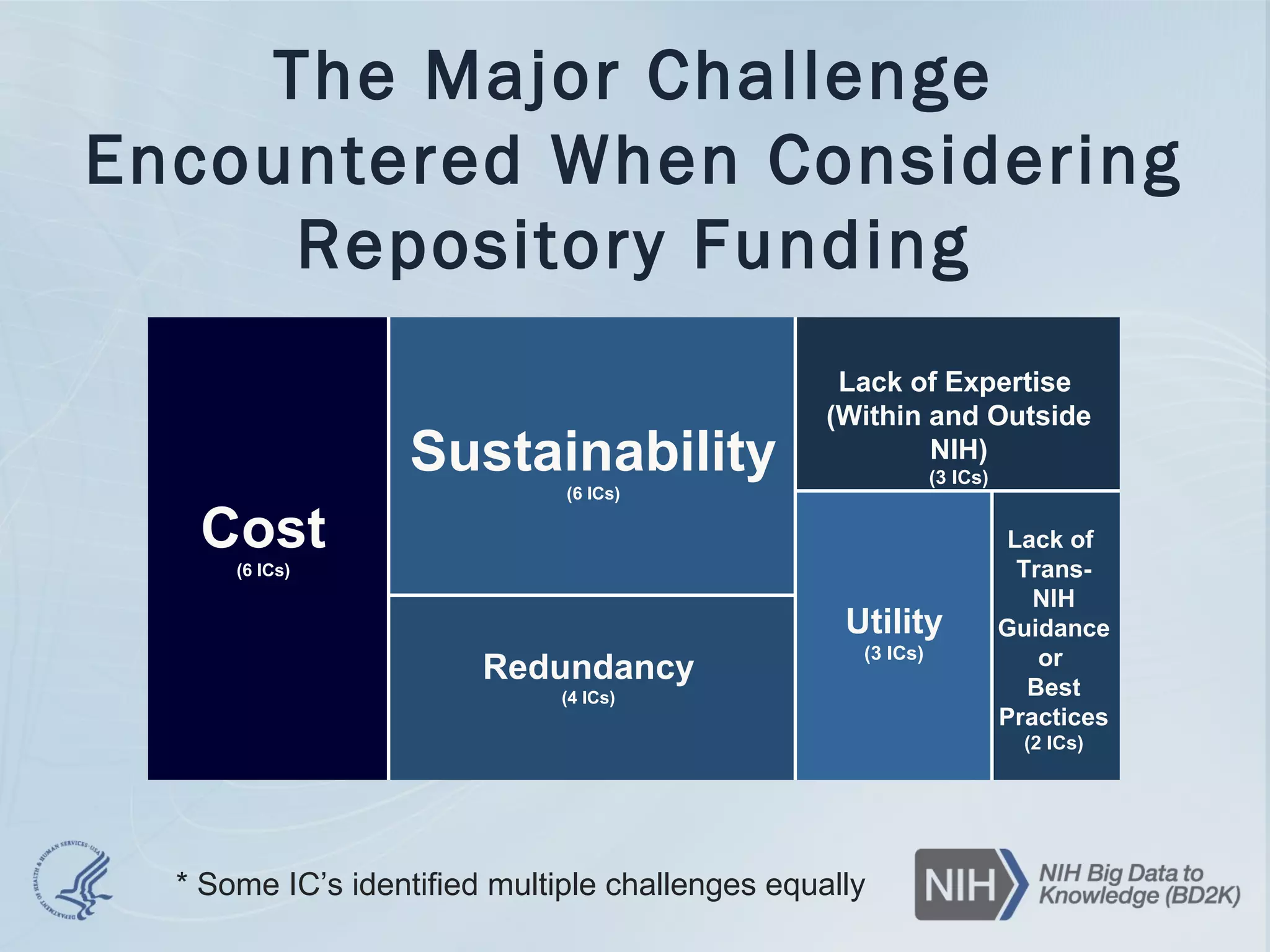
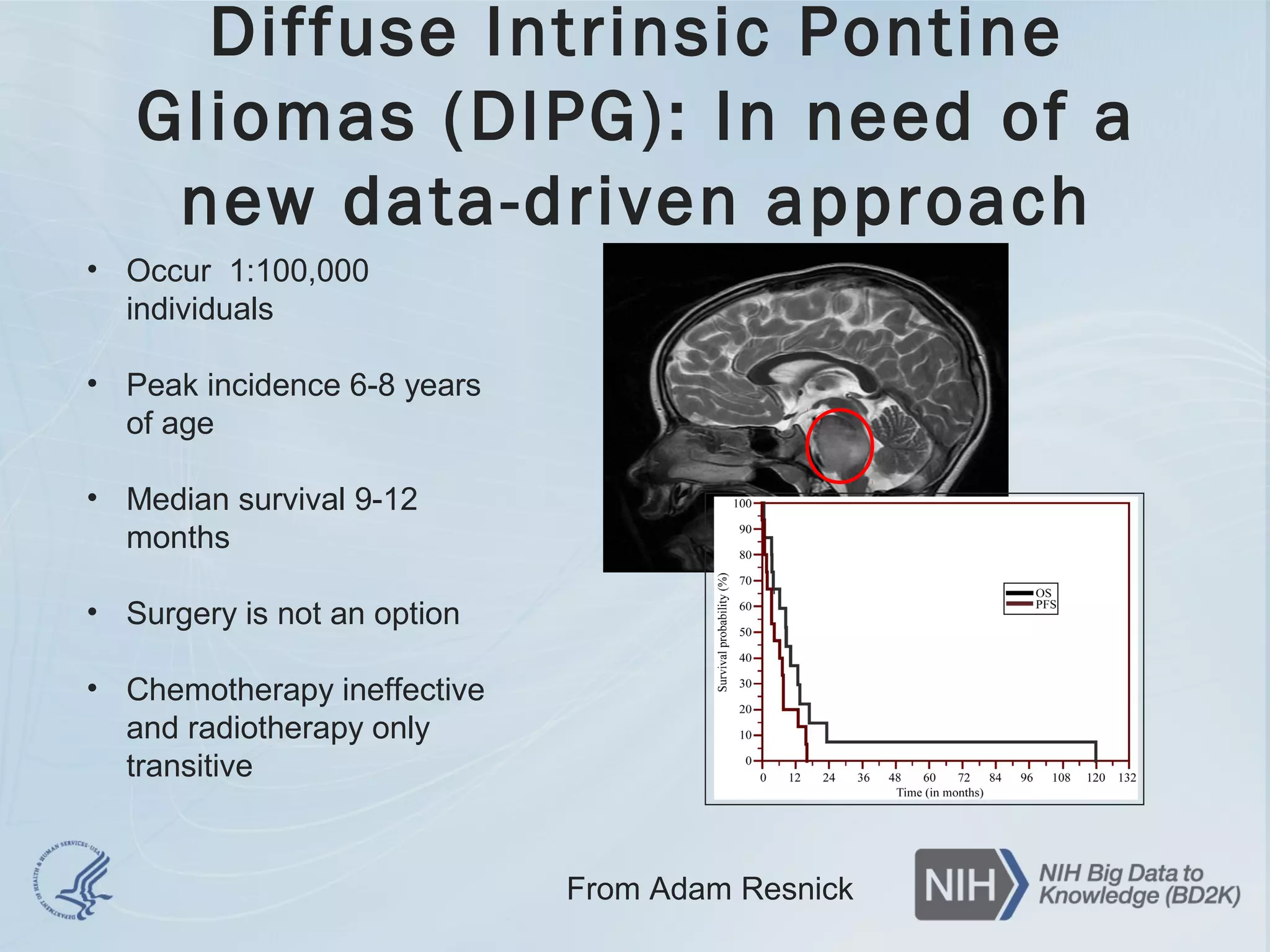
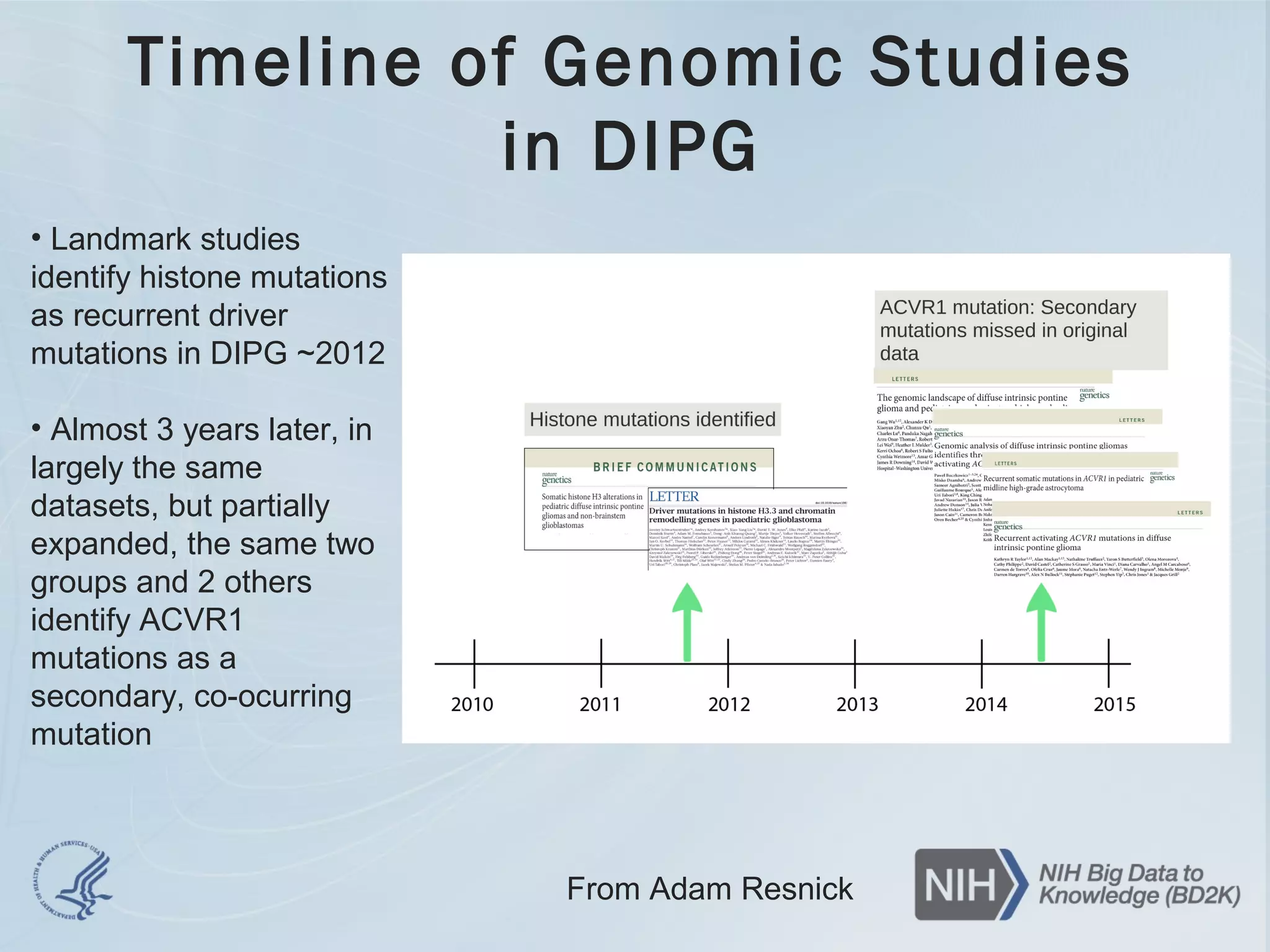
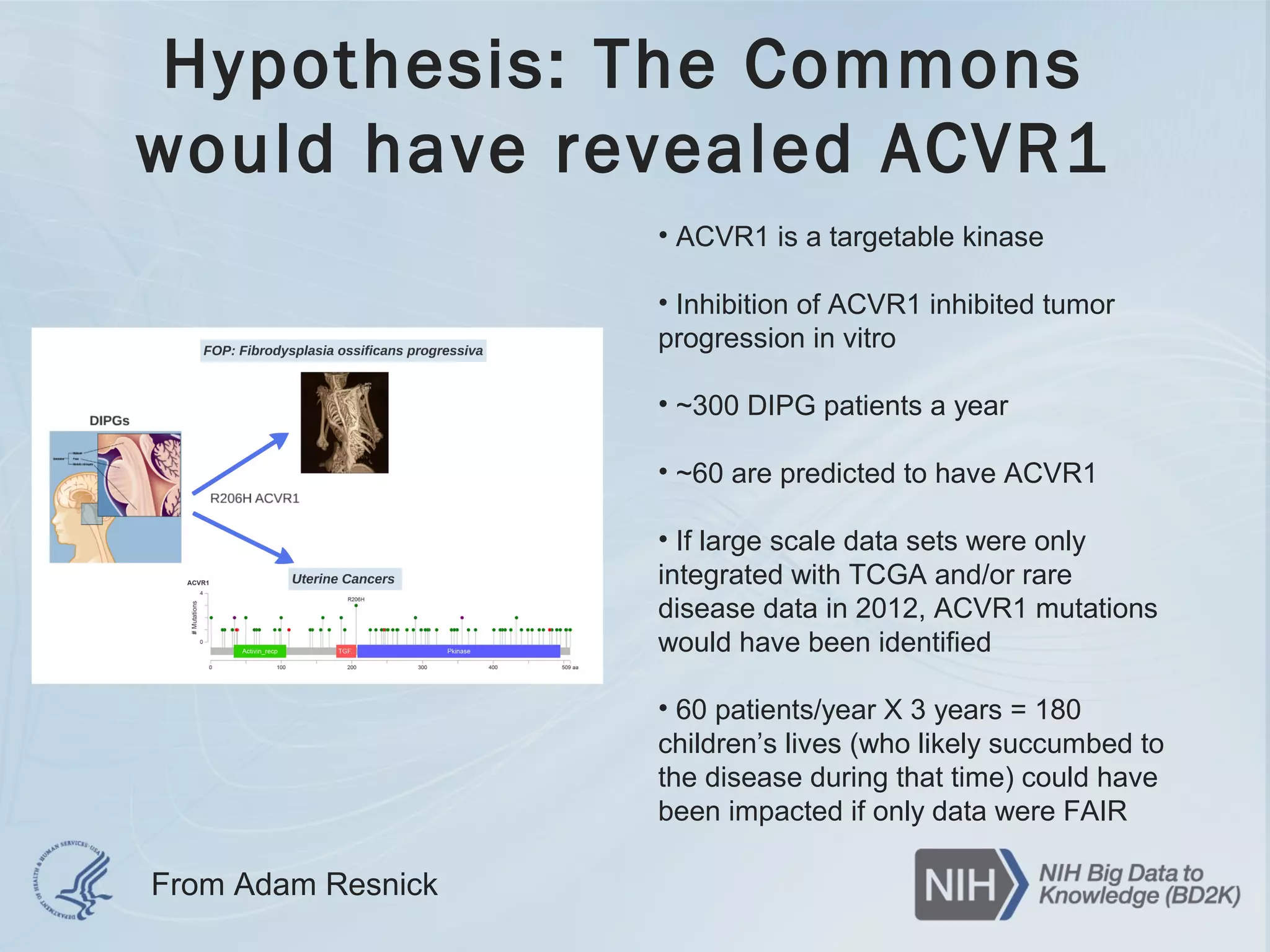
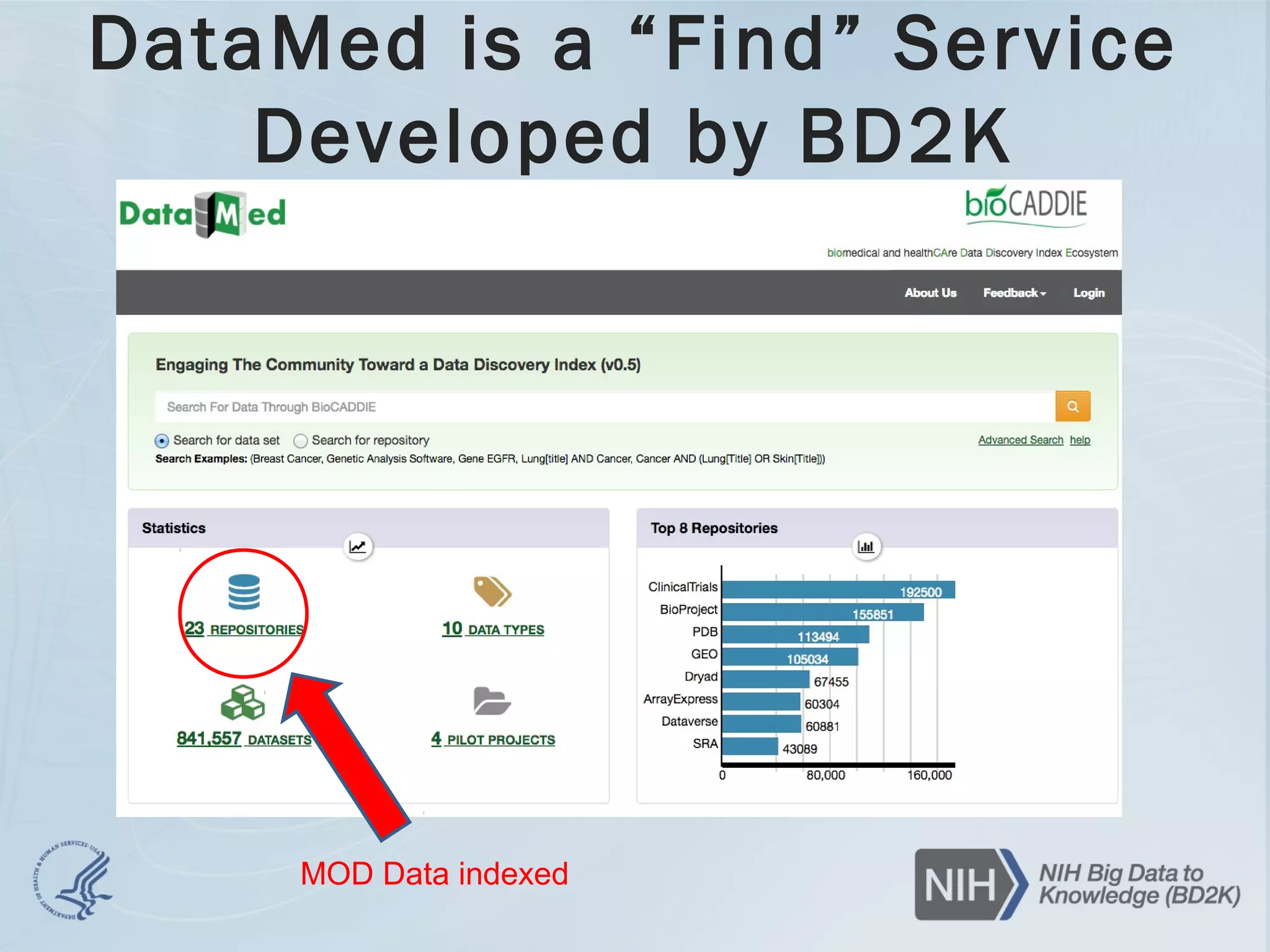
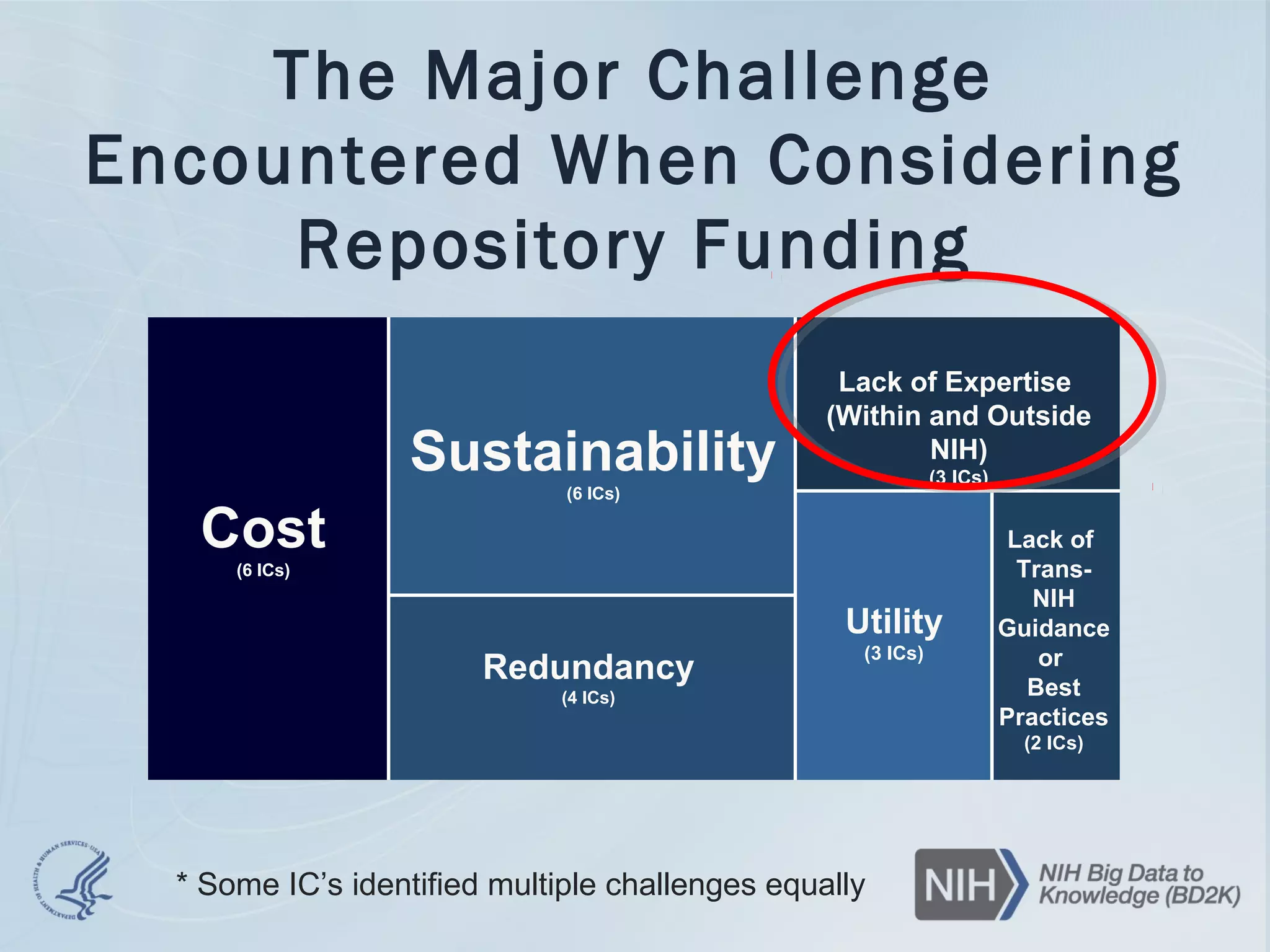
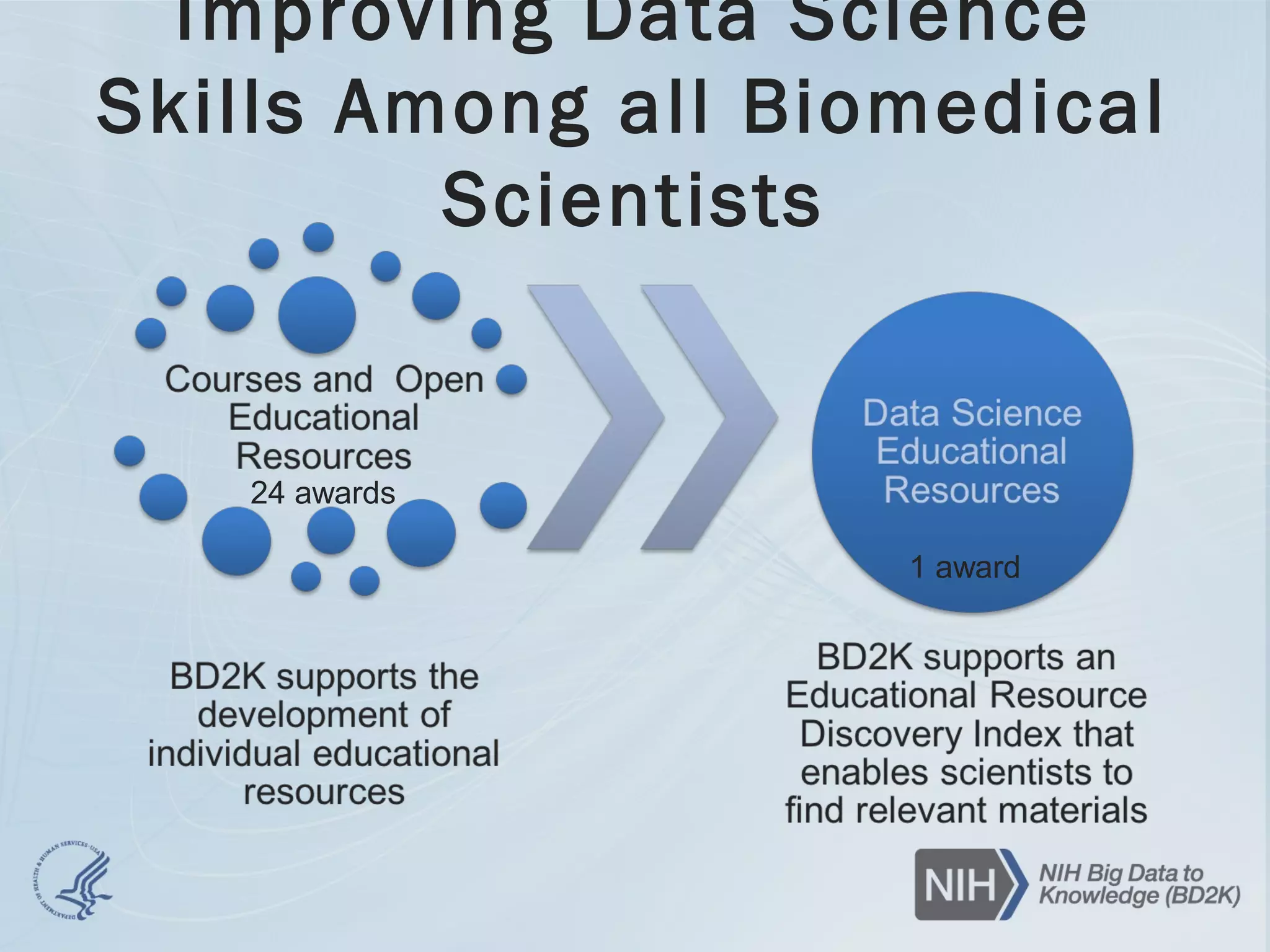
- The document discusses challenges related to biomedical data including that data is growing rapidly, stored across silos, and expensive to maintain while demands for sharing are increasing. It also notes a lack of data science skills.
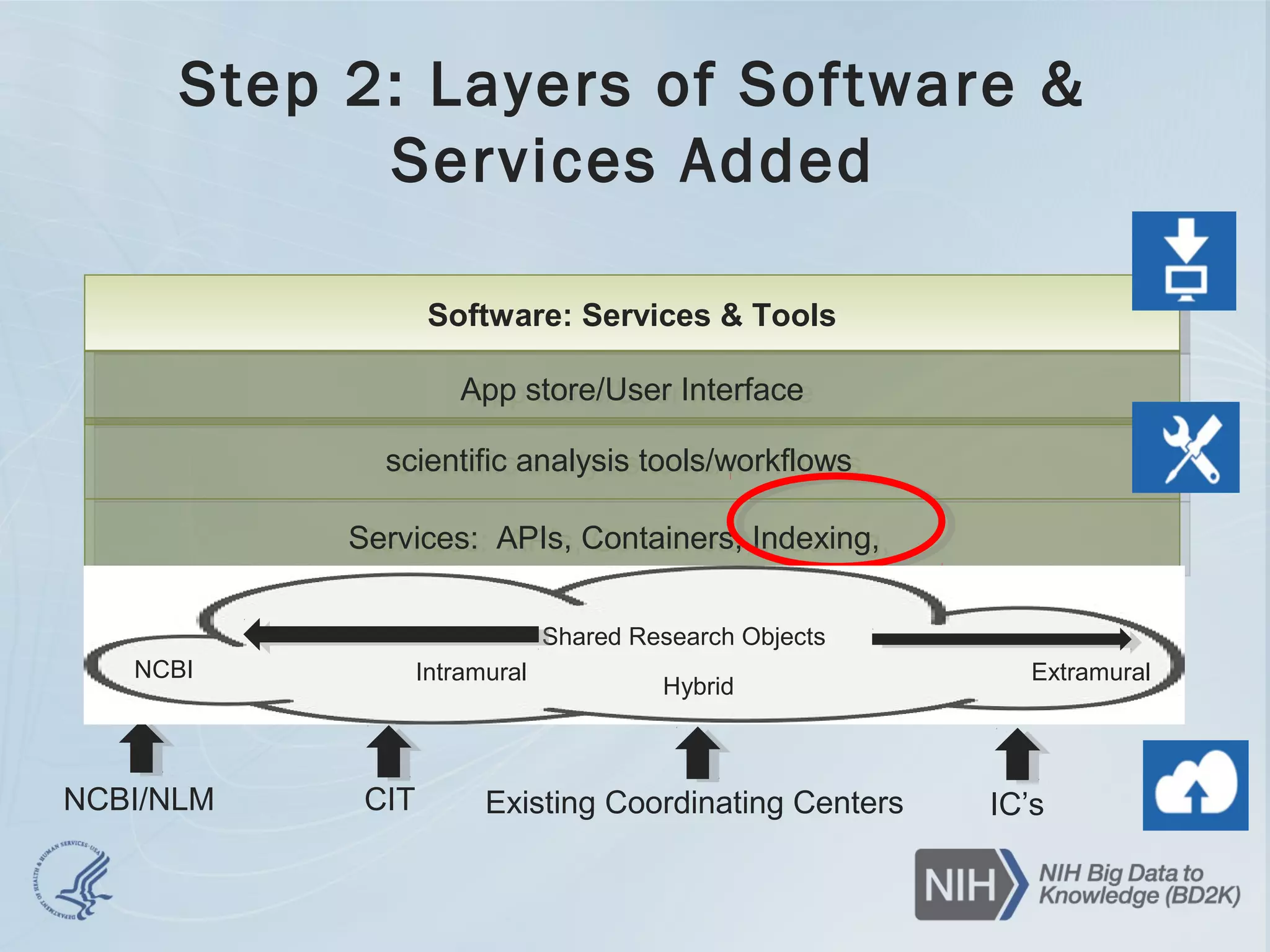
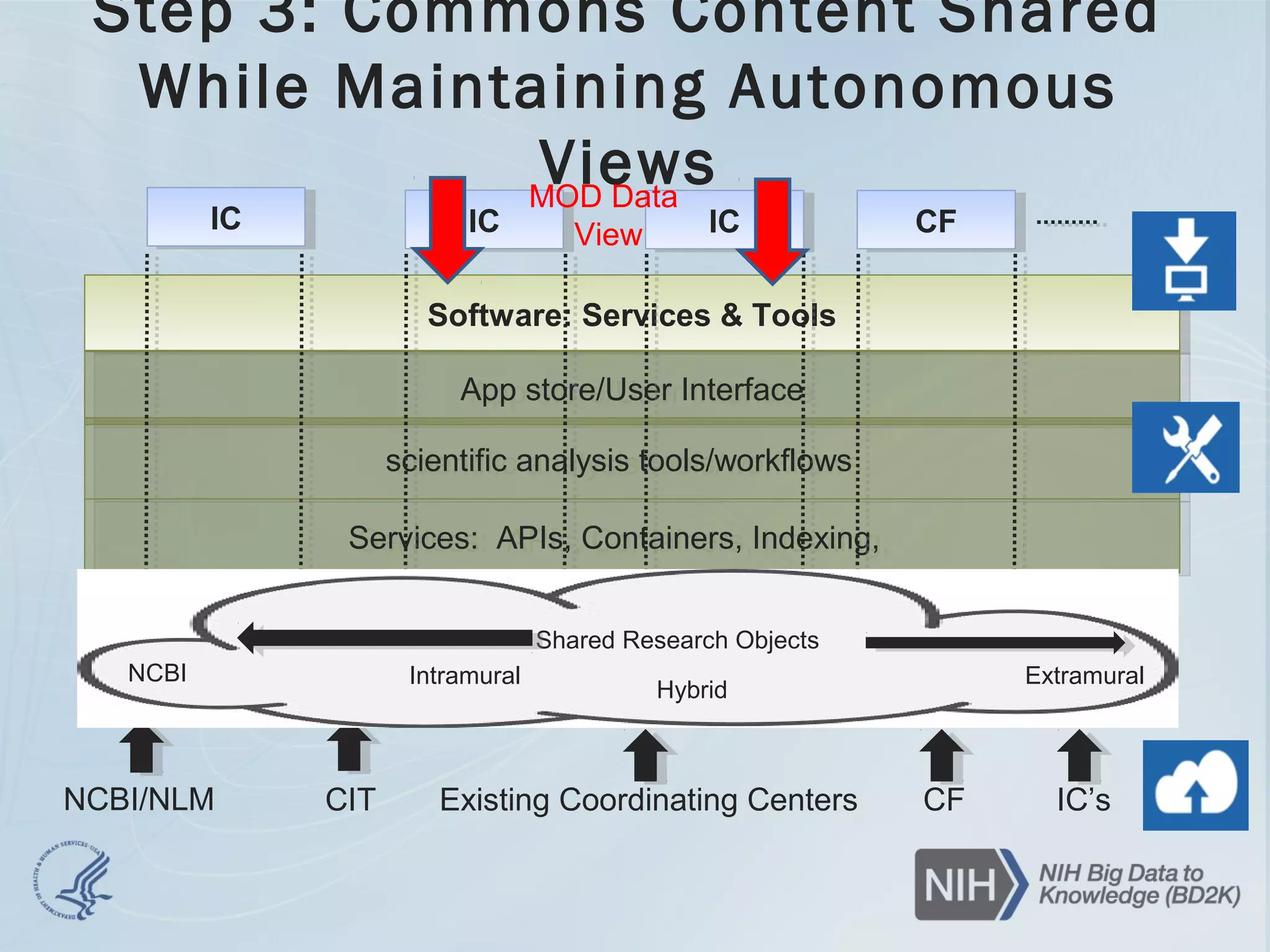
- Solutions explored include developing the NIH Commons, which would integrate disparate cloud initiatives using BD2K standards to make data findable, accessible, interoperable and reusable. This could enable new insights from aggregate analysis across datasets.
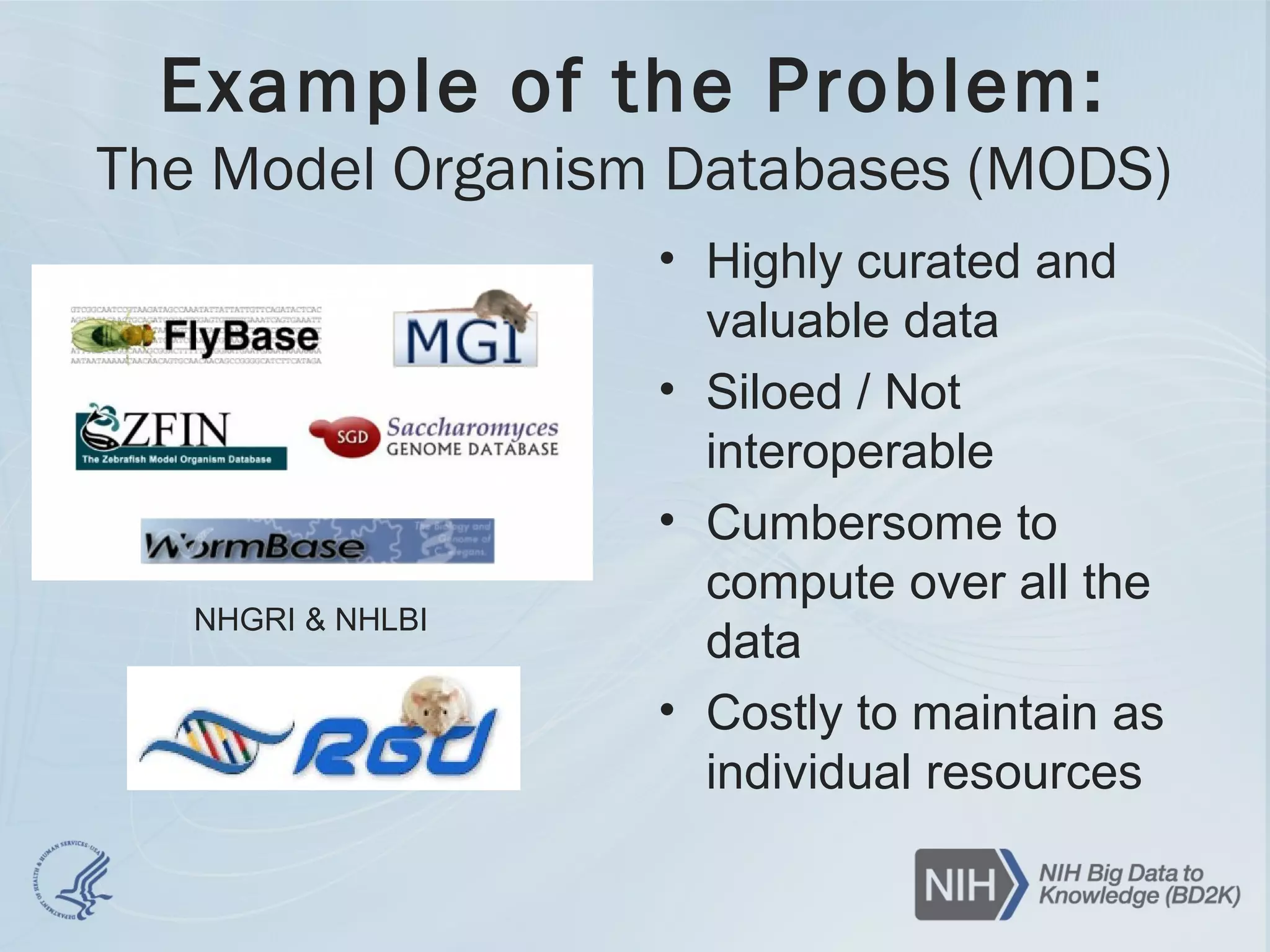
- A 3-year BD2K-sponsored pilot of the Commons is underway to address questions around discoveries, productivity, reproducibility and cost-effectiveness compared to current approaches. The pilot involves moving model organism databases to the Commons as a test case.