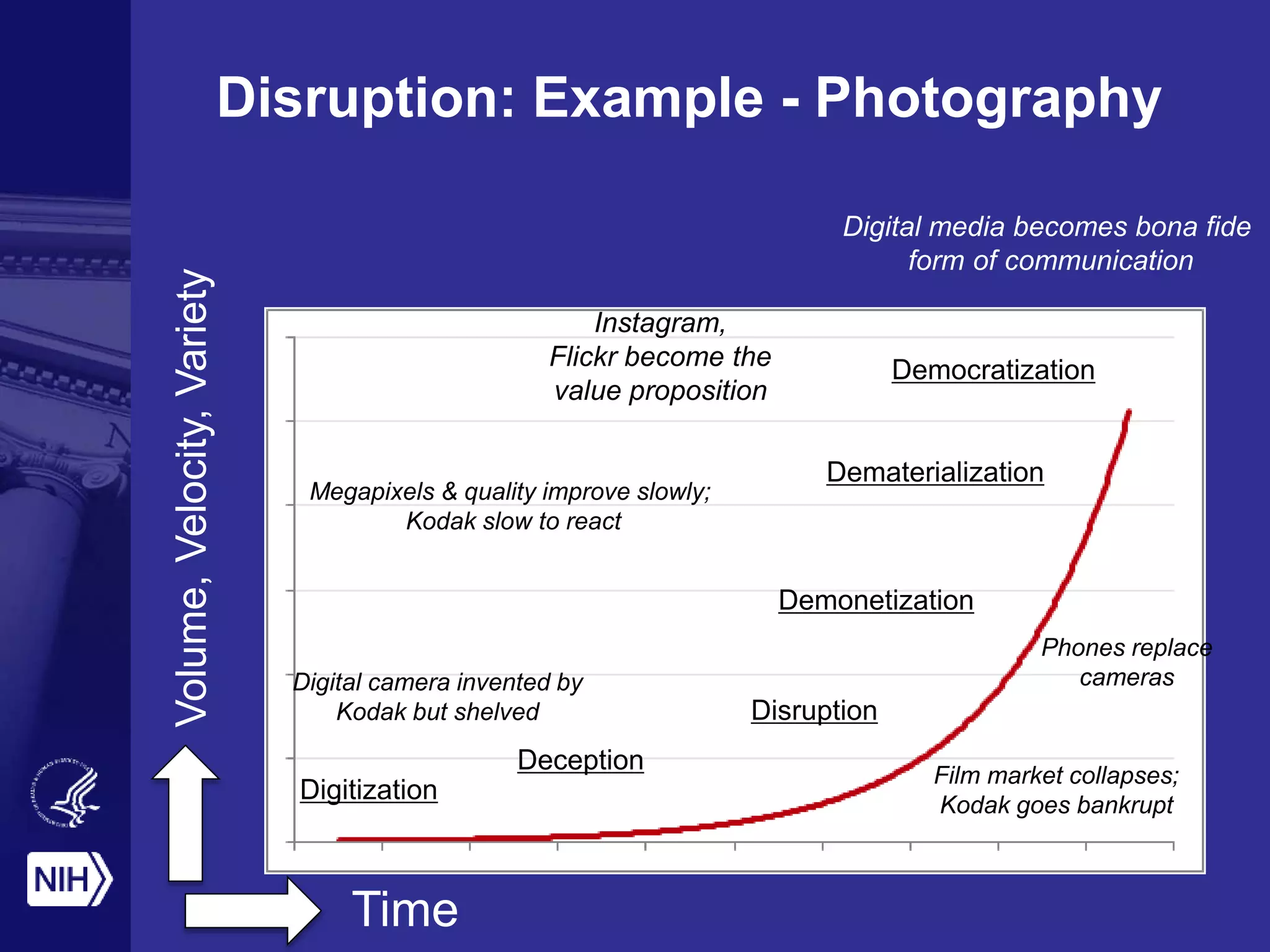
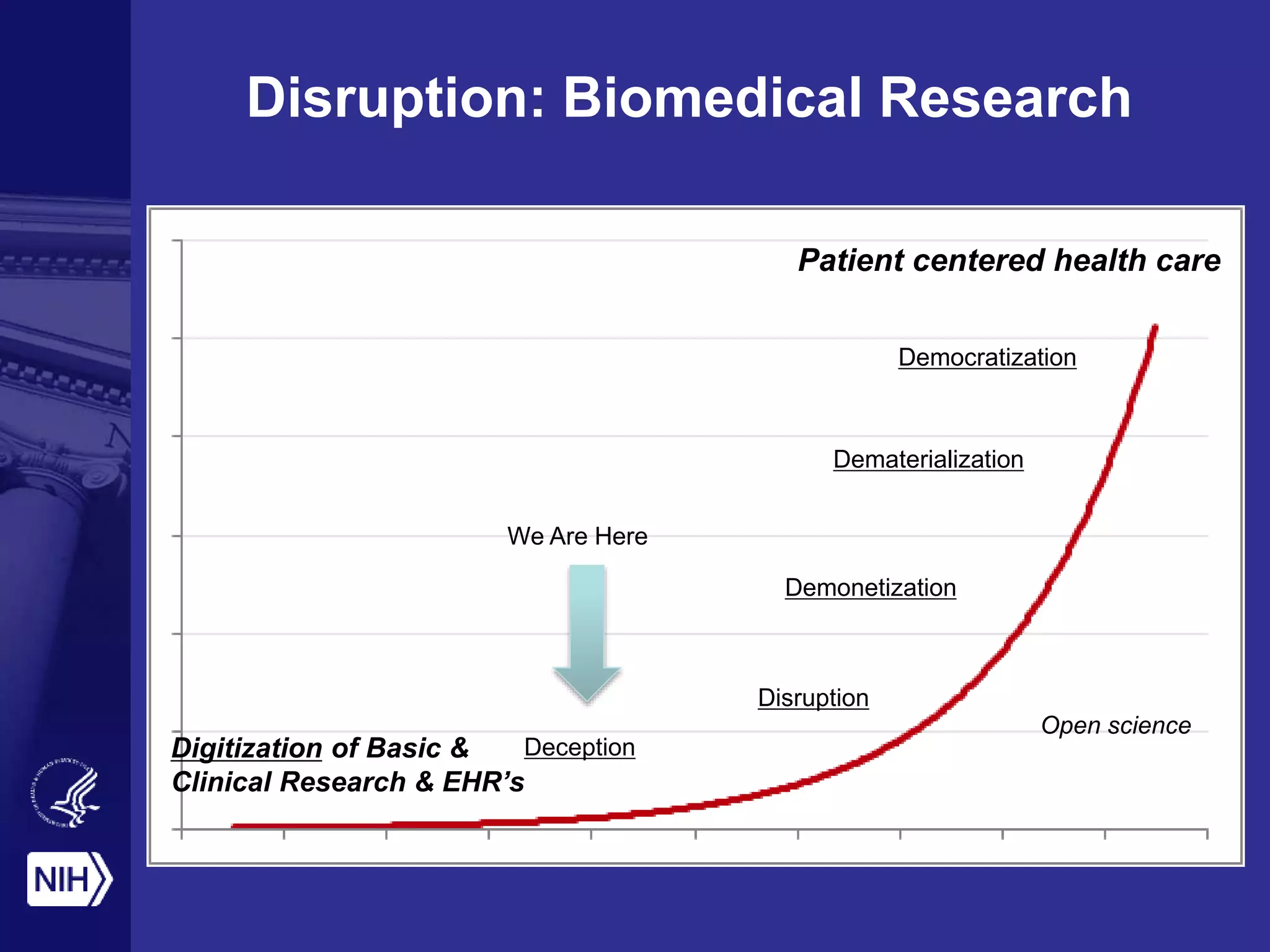
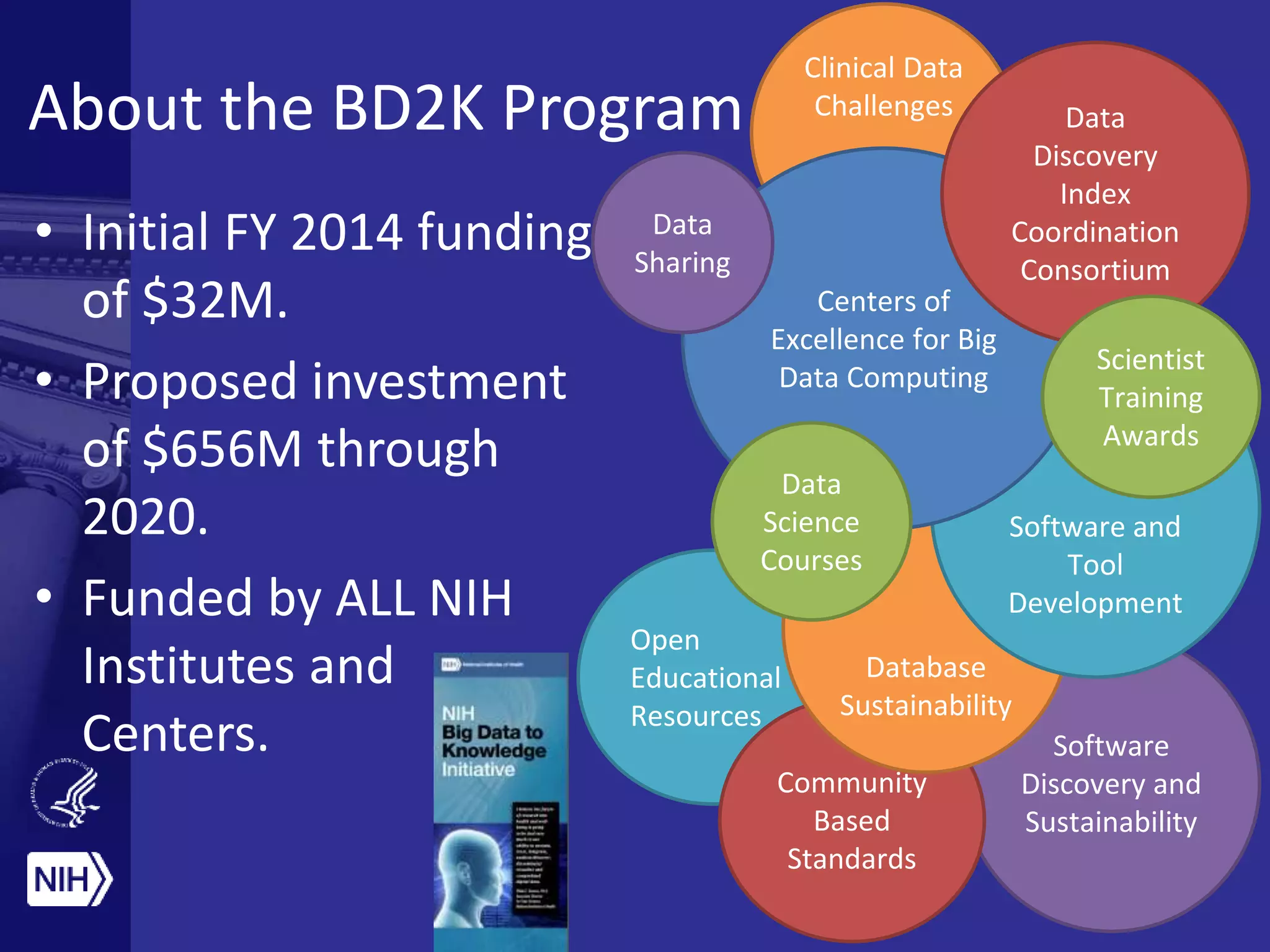
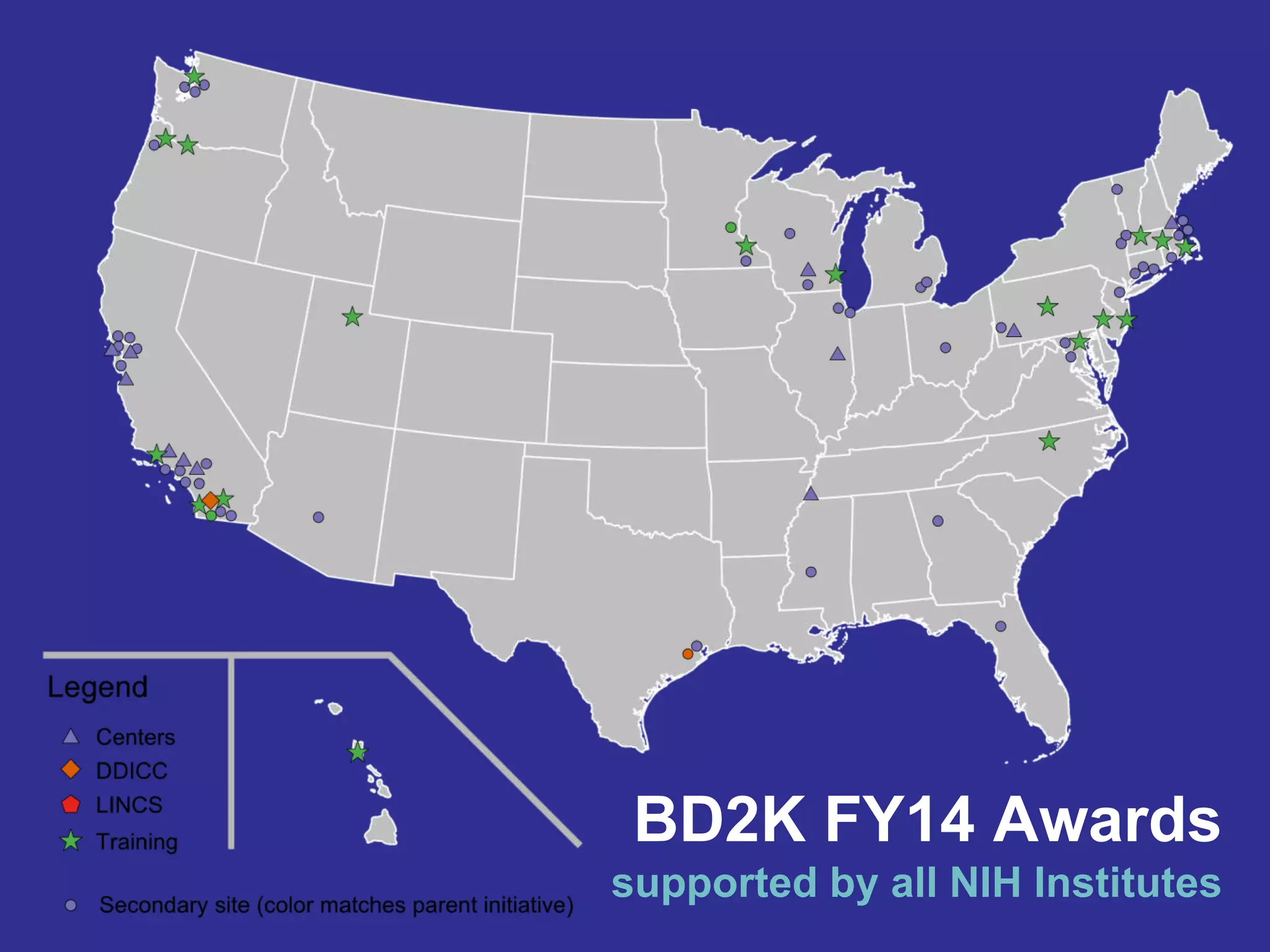
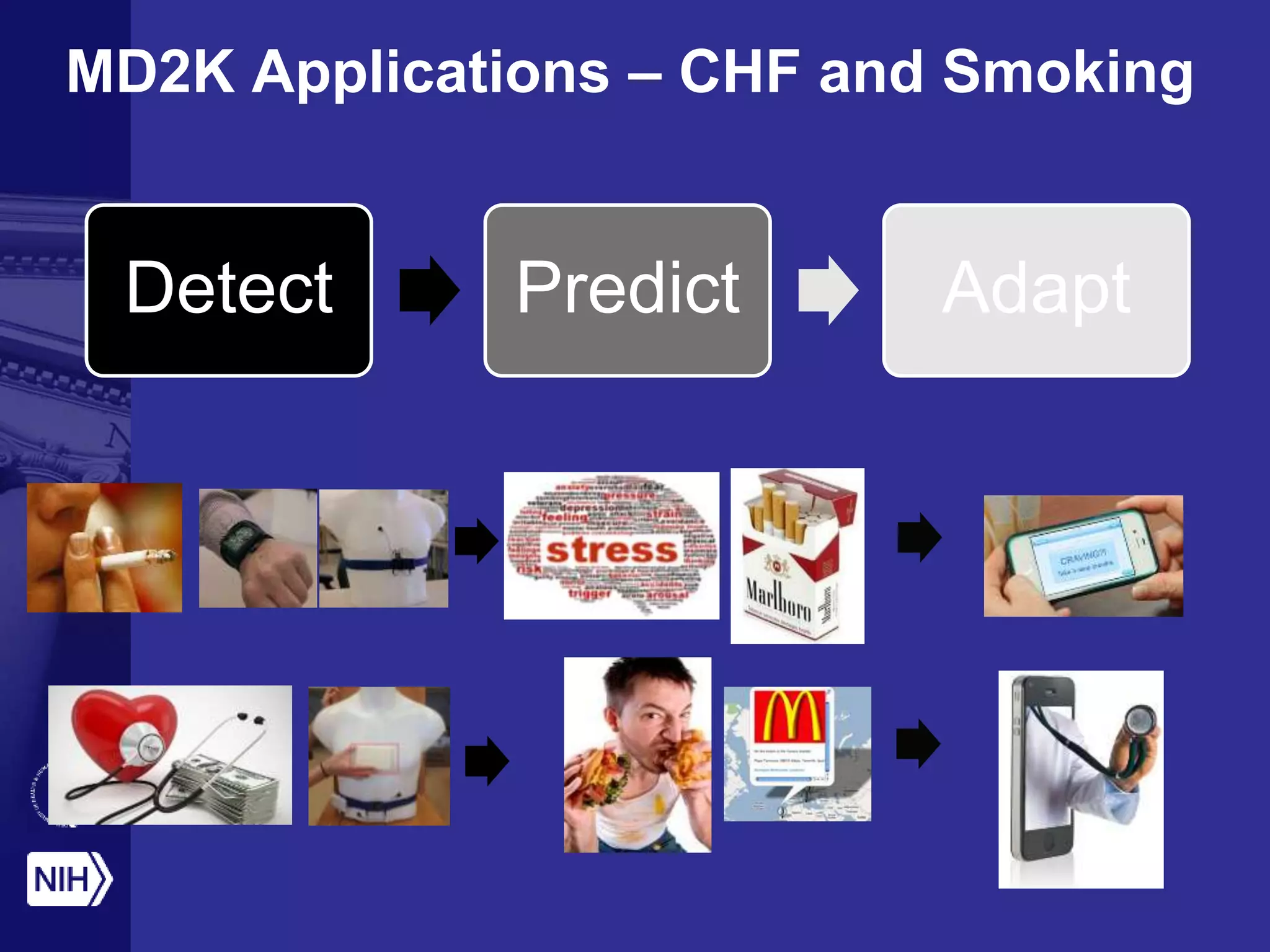
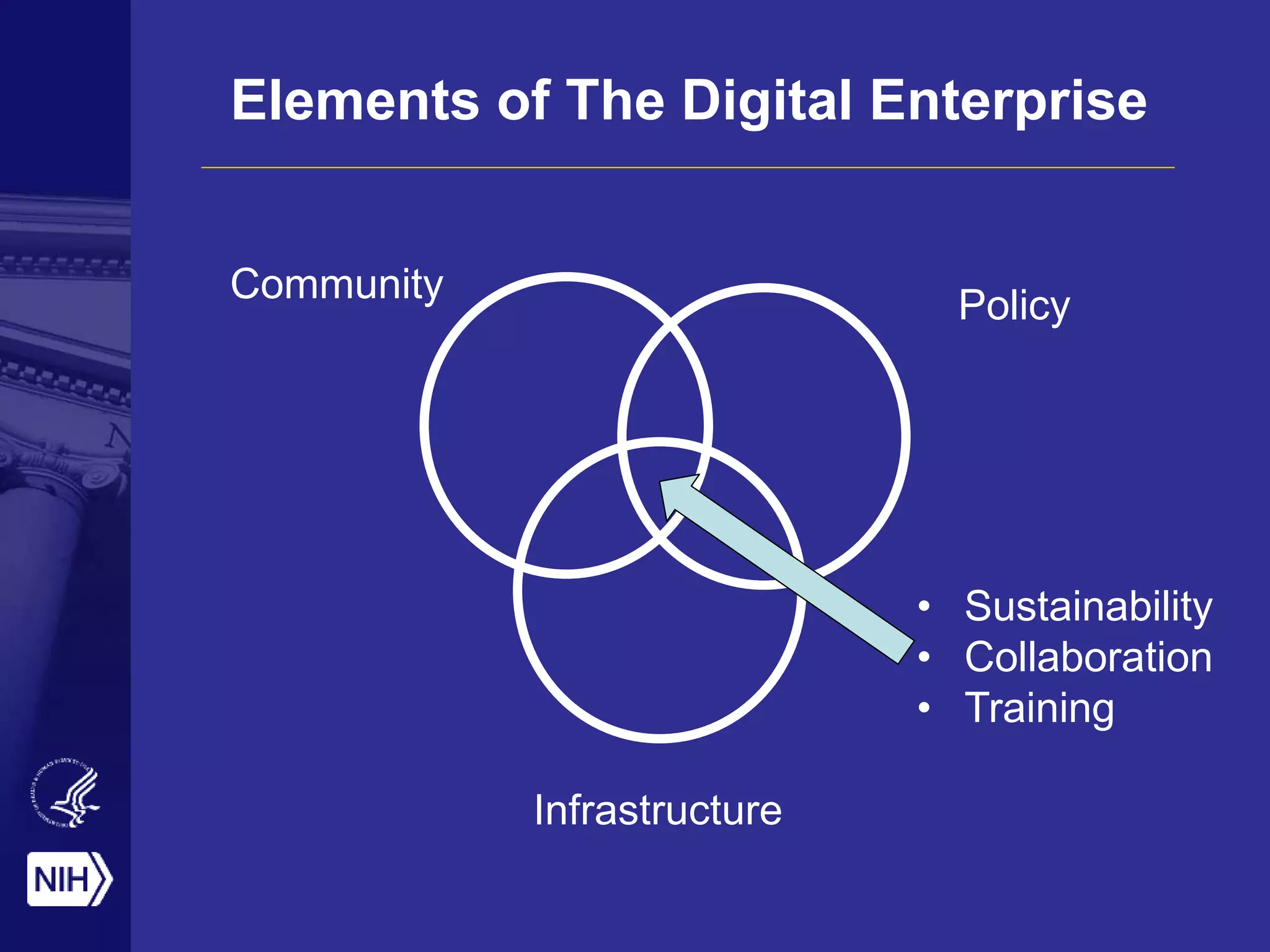
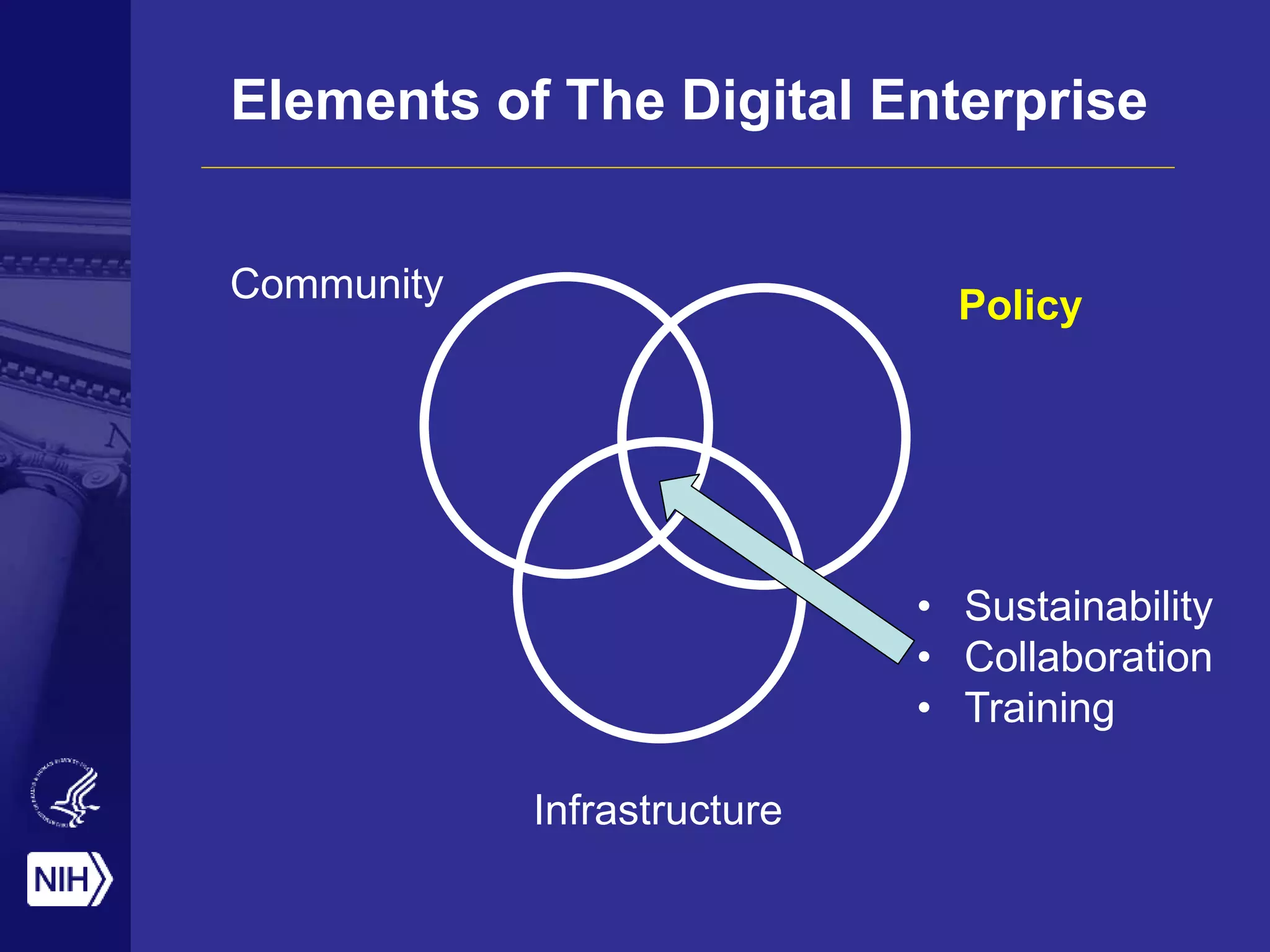
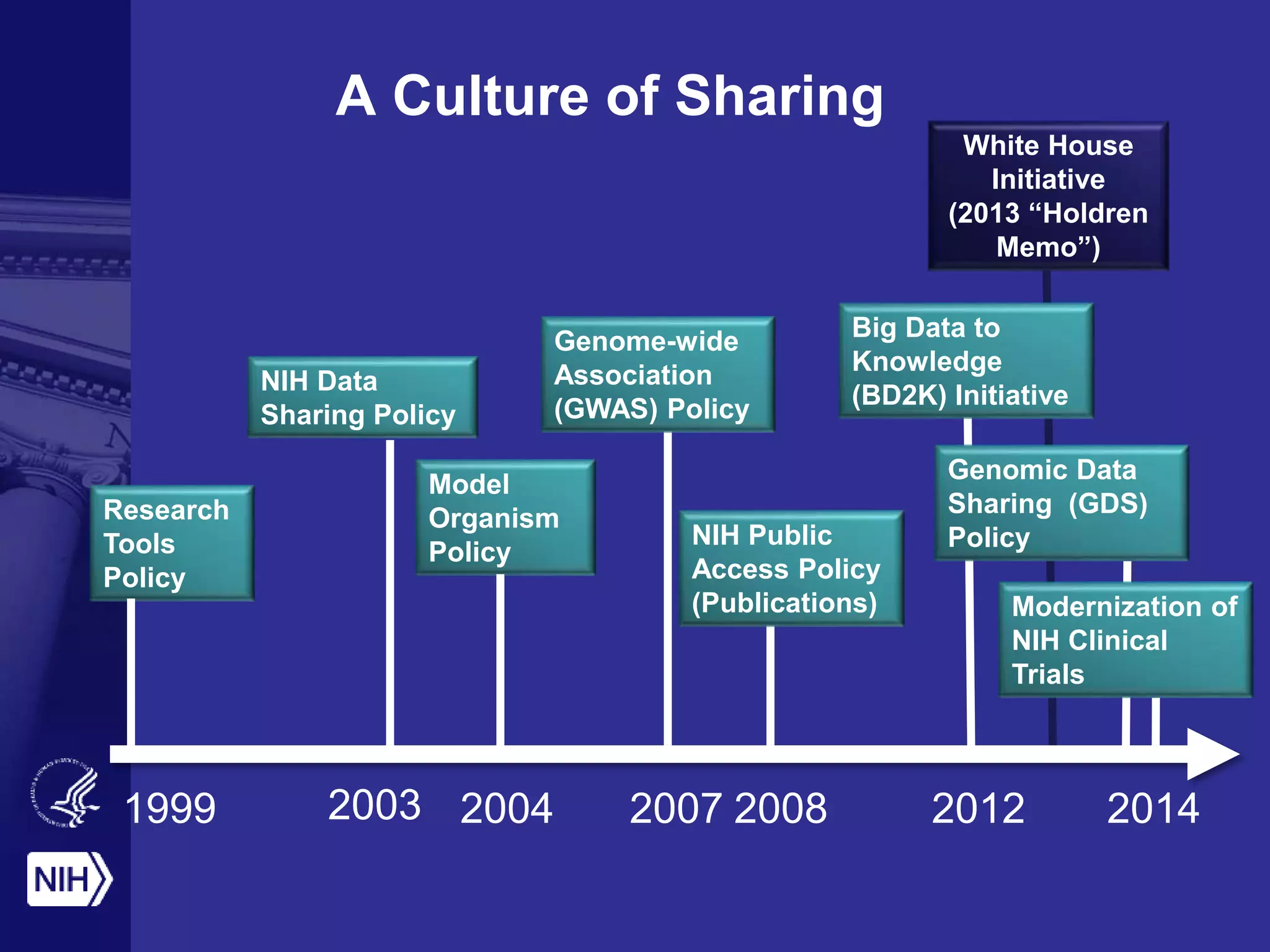
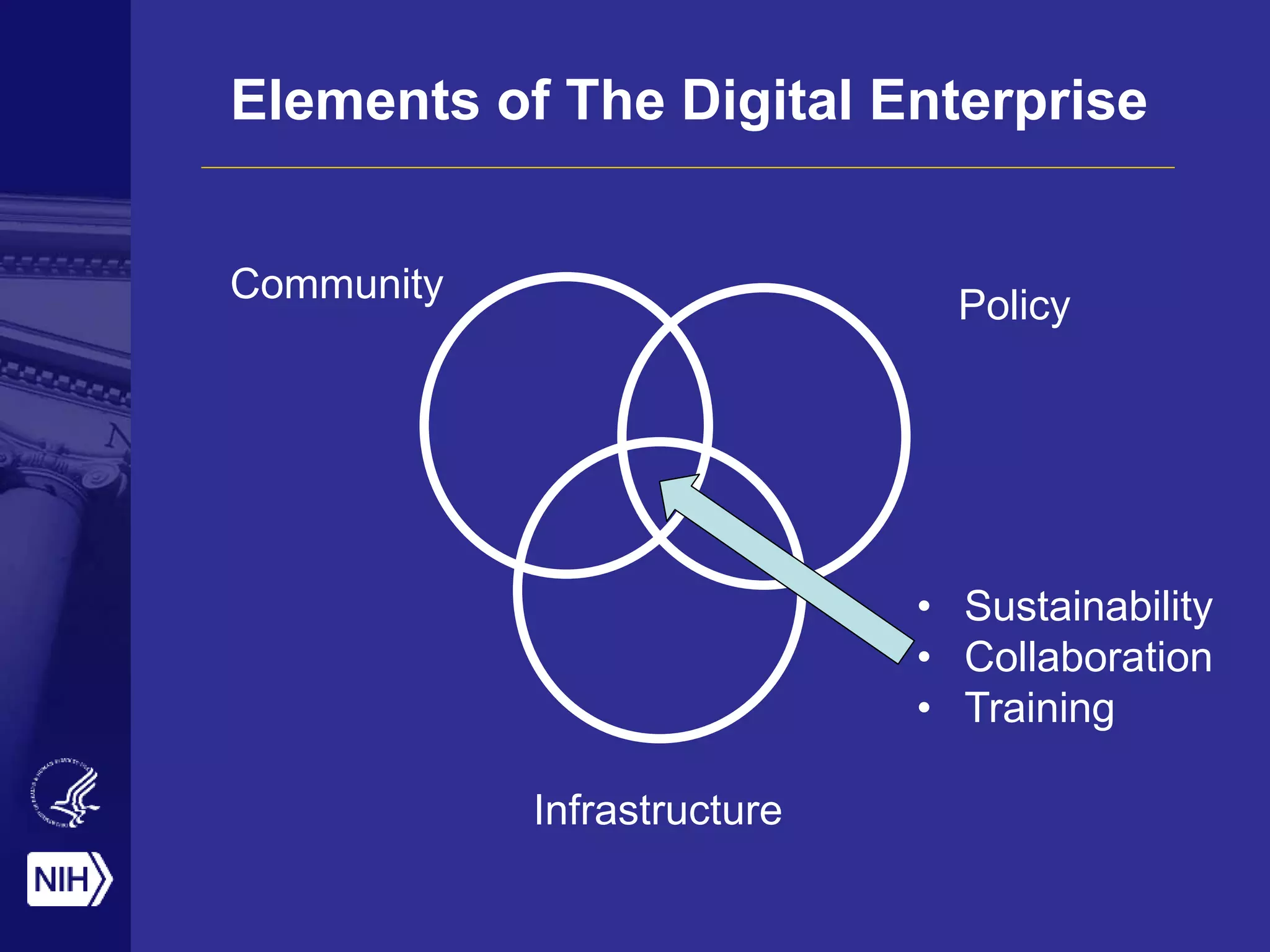
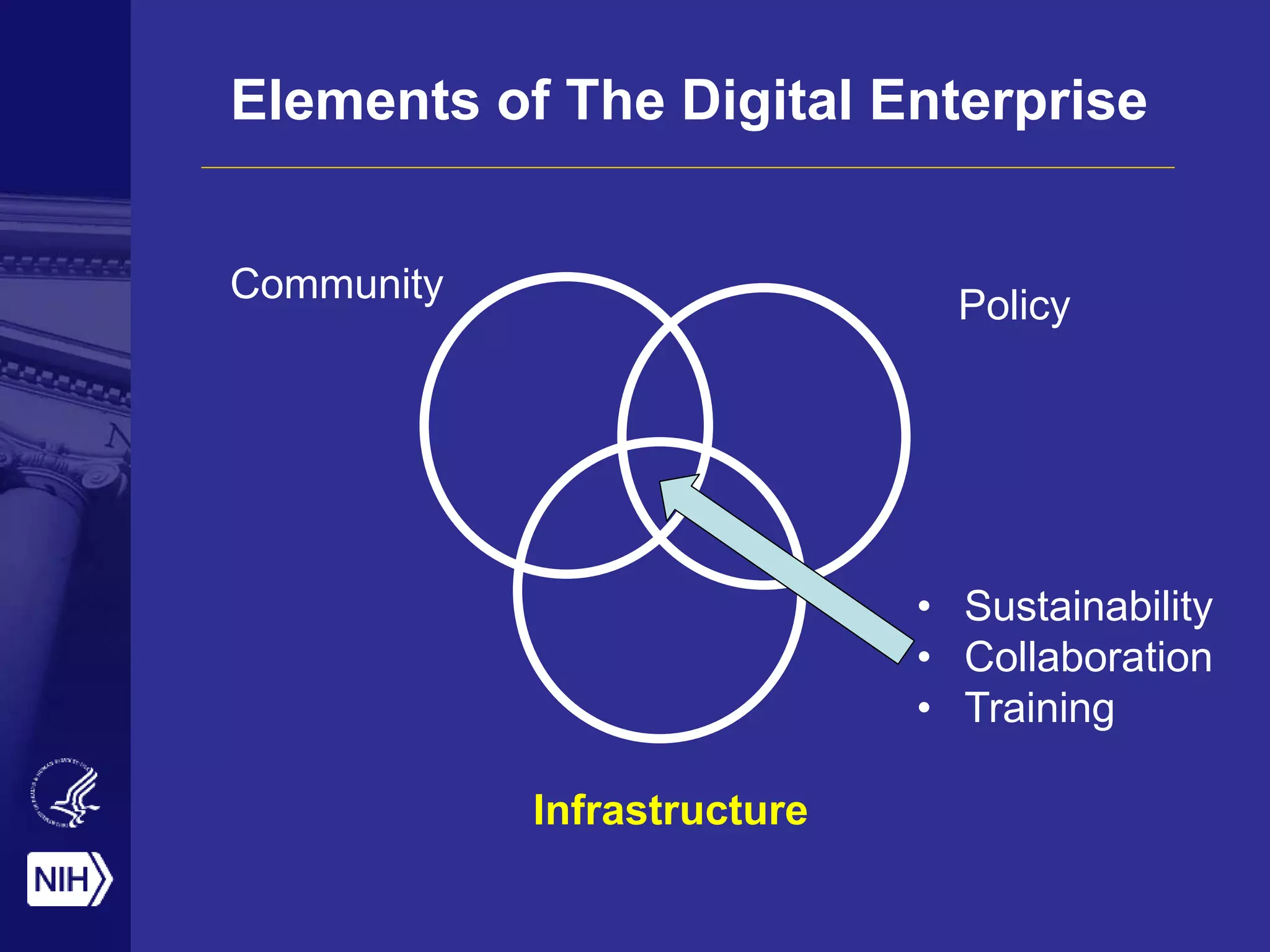
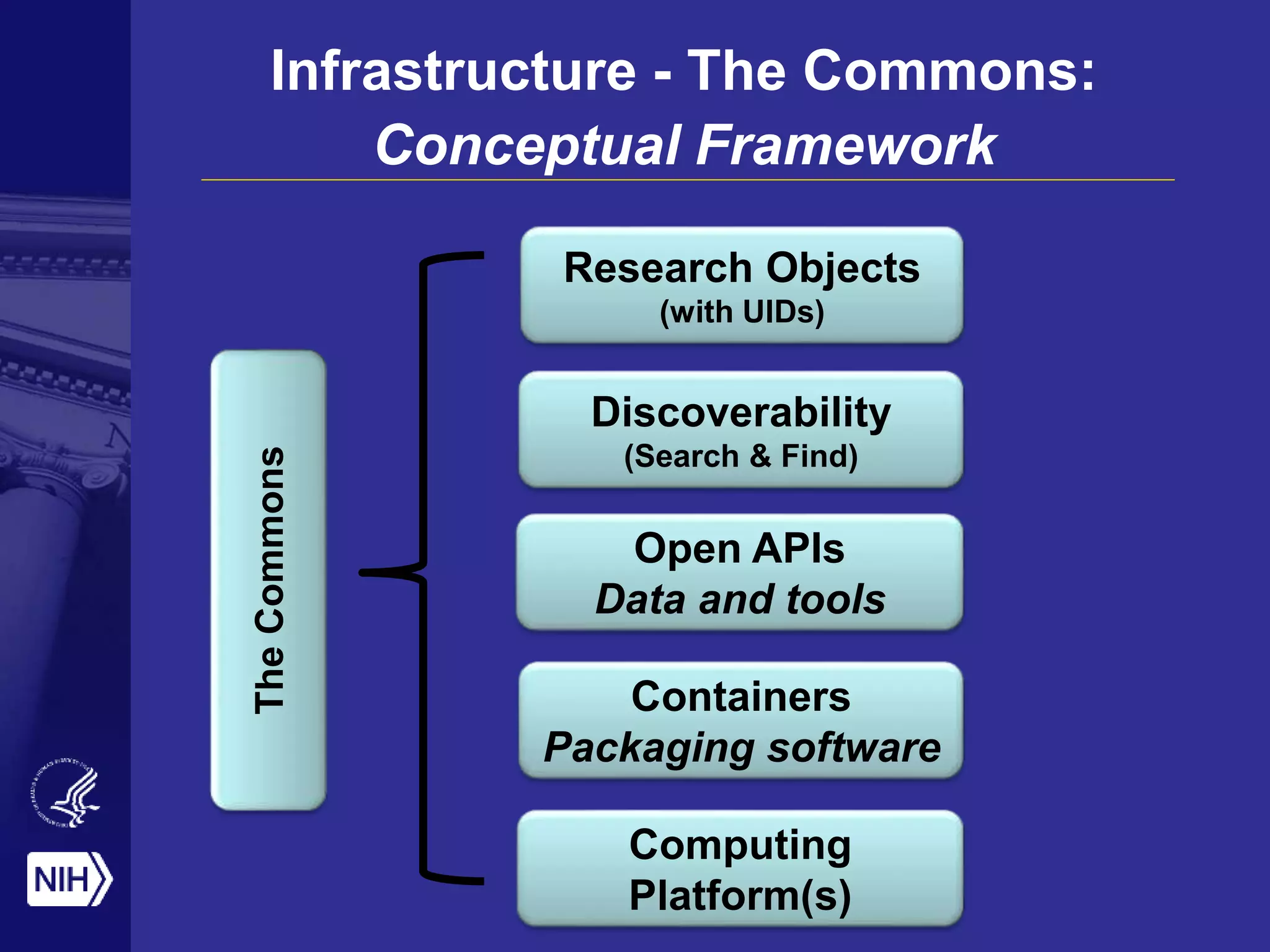
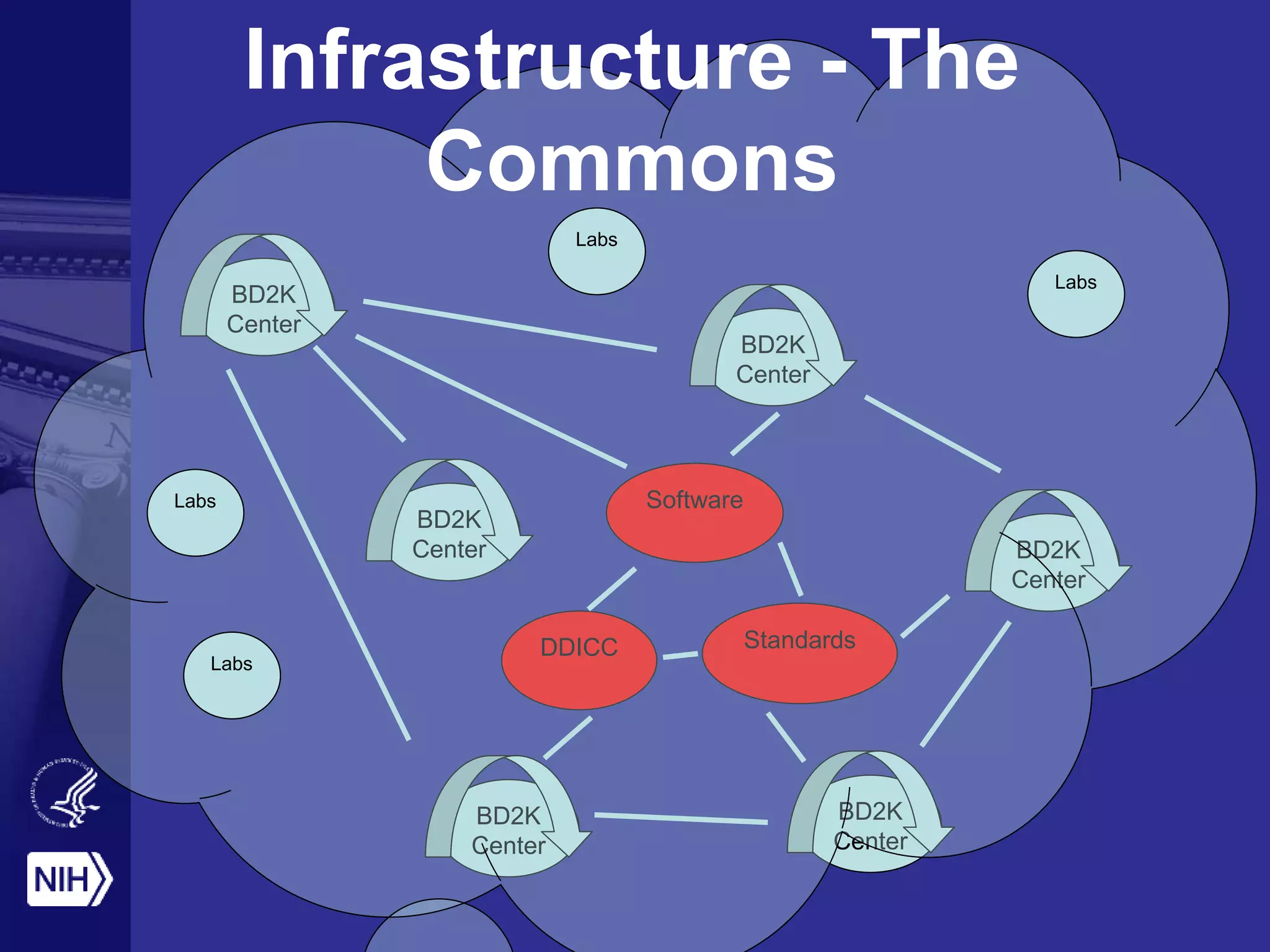
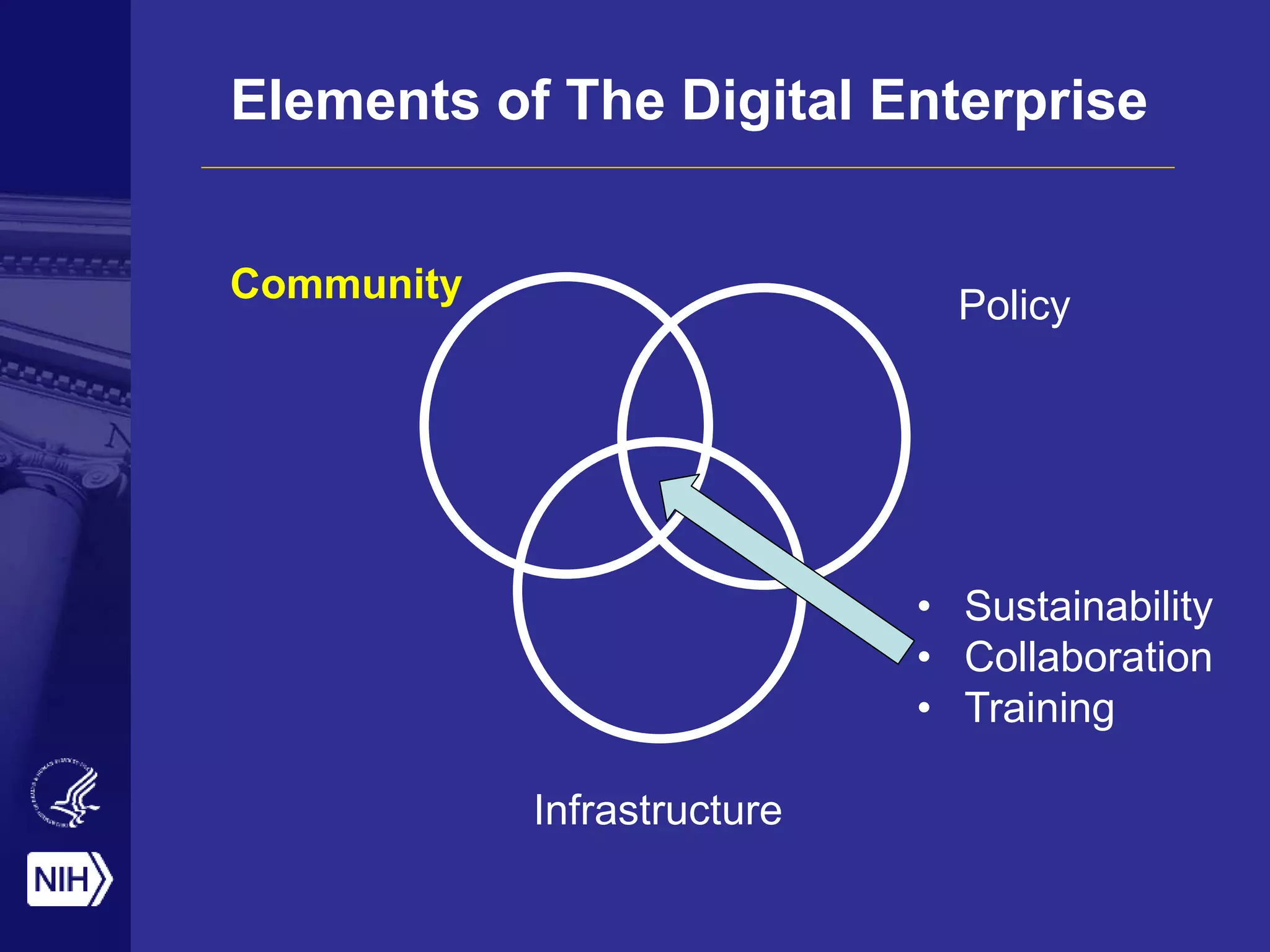
Big data is disrupting biomedical research through digitization of data sources. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) launched the Big Data to Knowledge (BD2K) initiative to support this disruption. BD2K funds various programs including data sharing policies, data science training, and the development of shared infrastructure and standards. This infrastructure includes the "Commons" which would provide discoverable, accessible, interoperable and reusable research objects to catalyze collaboration using open APIs and computing platforms. SRP could interact with BD2K through initiatives like open science competitions, data standards development, and leadership in trans-NIH big data efforts.