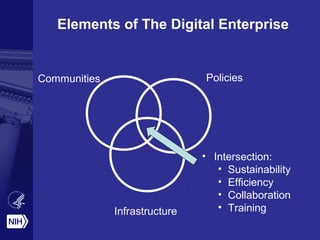
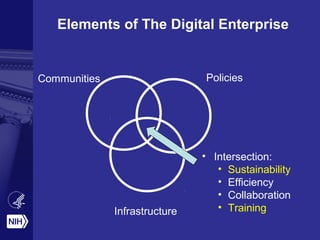
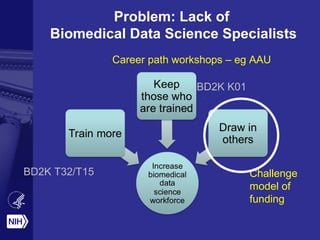
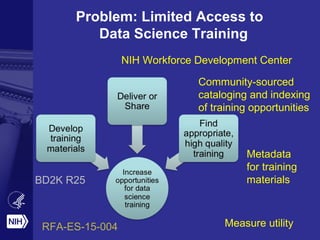
The document discusses the importance of data science at the NIH, highlighting its relationship with social computing and behavioral modeling to improve health outcomes. It outlines the NIH's goals, such as fostering an open ecosystem for biomedical research and developing the Precision Medicine Initiative, which aims to enhance personalized healthcare through extensive research and genomic data sharing. The document also emphasizes the need for collaboration, reproducibility, and training in biomedical data science to address contemporary health challenges.
![Data Science at NIH and its
Relationship to Social Computing,
Behavioral-Cultural Modeling, &
Prediction
Philip E. Bourne, PhD, FACMI
Associate Director for Data Science
National Institutes of Health
SBP15, Washington DC
April 2, 2015
[Thanks to Patty Mabry]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sbp040215-150404071450-conversion-gate01/75/Data-Science-at-NIH-and-its-Relationship-to-Social-Computing-Behavioral-Cultural-Modeling-Prediction-1-2048.jpg)




![47/53 “landmark” publications
could not be replicated
[Begley, Ellis Nature,
483, 2012] [Carole Goble]
3. Reproducability](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sbp040215-150404071450-conversion-gate01/85/Data-Science-at-NIH-and-its-Relationship-to-Social-Computing-Behavioral-Cultural-Modeling-Prediction-7-320.jpg)




















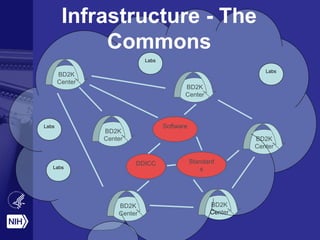
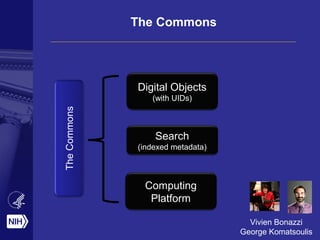
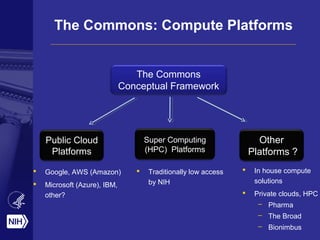
![The Commons:
Business Model
[George Komatsoulis]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sbp040215-150404071450-conversion-gate01/85/Data-Science-at-NIH-and-its-Relationship-to-Social-Computing-Behavioral-Cultural-Modeling-Prediction-33-320.jpg)