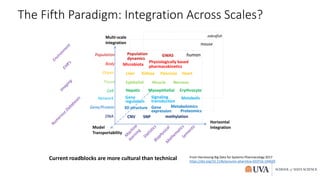
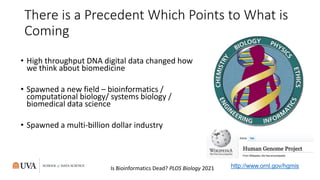
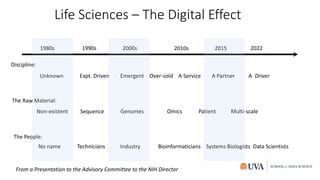
The document discusses the rise of data science and its disruptive impact on higher education. It analyzes precedents like bioinformatics that were enabled by new digital data sources and technologies. The author advocates that universities should embrace data science by establishing interdisciplinary collaborations, investing in data infrastructure, and ensuring research has societal value and responsibility.


![1991-1995
1993-1998
1998-2003
2003-2010
2011-Present
More on the Data Driven Genomic
Revolution
[Adapted from Eric Green, Director NHGRI]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mtu040522-220405120638/85/One-View-of-Data-Science-5-320.jpg)








![One Representation of Data Science –
The 4+1 Model
• Value – assuring societal
benefit
• Design - Communication
of the value of data
• Systems – the means to
communicate and
convey benefit
• Analytics – models and
methods
• Practice – where
everything happens
[From Raf Alvarado]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mtu040522-220405120638/85/One-View-of-Data-Science-17-320.jpg)
![The Data Science Interplay
• Value + Design = Openness,
responsibility
• Value + Analytics = Human
centered AI, algorithmic bias
• Value + Systems =
sustainability, access,
environmental impact
• Design + Analytics = literate
programming, visualization
• Design + Systems =
dashboards, engineering
design
• Analytics + Systems = ML
engineering
[From Raf Alvarado]
Thinking of data as a science unto itself is novel and controversial](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mtu040522-220405120638/85/One-View-of-Data-Science-18-320.jpg)

![Challenges
Fixed level of funding
Opportunities
data commons
Data commons co-locate data
with cloud computing
infrastructure and commonly
used software services, tools &
apps for managing, analyzing and
sharing data to create an
interoperable resource for the
research community.*
*Robert L. Grossman, Allison Heath, Mark Murphy, Maria Patterson and Walt Wells, A Case for Data Commons Towards Data Science as a Service, IEEE
Computing in Science and Engineer, 2016. Source of image: The CDIS, GDC, & OCC data commons infrastructure at a University of Chicago data center.
Bonazzi VR, Bourne PE (2017) Should biomedical research be like Airbnb? PLoS Biol 15(4): e2001818.
Systems
[Adapted from Bob Grossman]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mtu040522-220405120638/85/One-View-of-Data-Science-21-320.jpg)
![Research ethics
committees (RECs) review
the ethical acceptability
of research involving
human participants.
Historically, the principal
emphases of RECs have
been to protect
participants from physical
harms and to provide
assurance as to
participants’ interests and
welfare.*
[The Framework] is
guided by, Article 27
of the 1948 Universal
Declaration of Human
Rights. Article 27
guarantees the rights
of every individual in
the world "to share in
scientific
advancement and its
benefits" (including to
freely engage in
responsible scientific
inquiry)…*
Protect human
subject data
The right of human
subjects to benefit
from research.
*GA4GH Framework for Responsible Sharing of Genomic and Health-Related Data, see goo.gl/CTavQR
Data sharing with protections provides the evidence
so patients can benefit from advances in research.
Balance protecting human subject data
with open research that benefits
patients
[Adapted from Bob Grossman]
Value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mtu040522-220405120638/85/One-View-of-Data-Science-22-320.jpg)