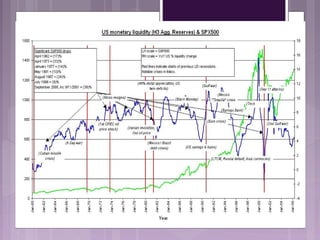
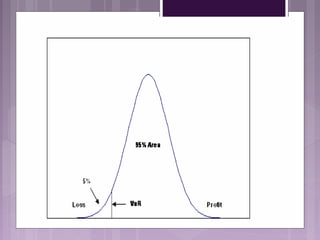
This document discusses the need for risk management. It outlines several events in the 1970s and 2000s that caused financial losses and volatility, raising the need for effective risk management. Globalization and deregulation also increased the importance of risk management by exposing organizations to more currency and interest rate risks. The document then defines various risk management tools like Value at Risk (VAR) and stop-loss limits and discusses how to measure different types of risk like market, liquidity, credit, and operational risk.