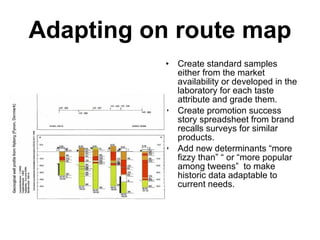
The document discusses business risk management, particularly the balance between opportunities and threats, illustrated through the analysis of market, credit, and operational risks. It emphasizes the importance of identifying boundary conditions, measuring volatility, and utilizing predictive analytics to mitigate risks, using the 2008 credit crisis as a case study. A case study on launching a new soft drink is also presented, highlighting the complexities of operational risk and the strategies for effective risk management and protection.

















![Our references The Project Management Time Cycle – Vol. I TIME CYCLE MODULE: From concept to feasibility ISBN 1440493332 available at Amazon Economy to Ecology Our goal is to help promote clean, safe and better practices in economy and ecology worldwide. Balanced, efficient and a little more sustainable. Kindle Blog Ecothrust ASIN: B0029ZAUAY For any queries mail to [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/businessriskcasestudyba32-090721225024-phpapp01/85/Business-Risk-Case-Study-Ba-32-27-320.jpg)
