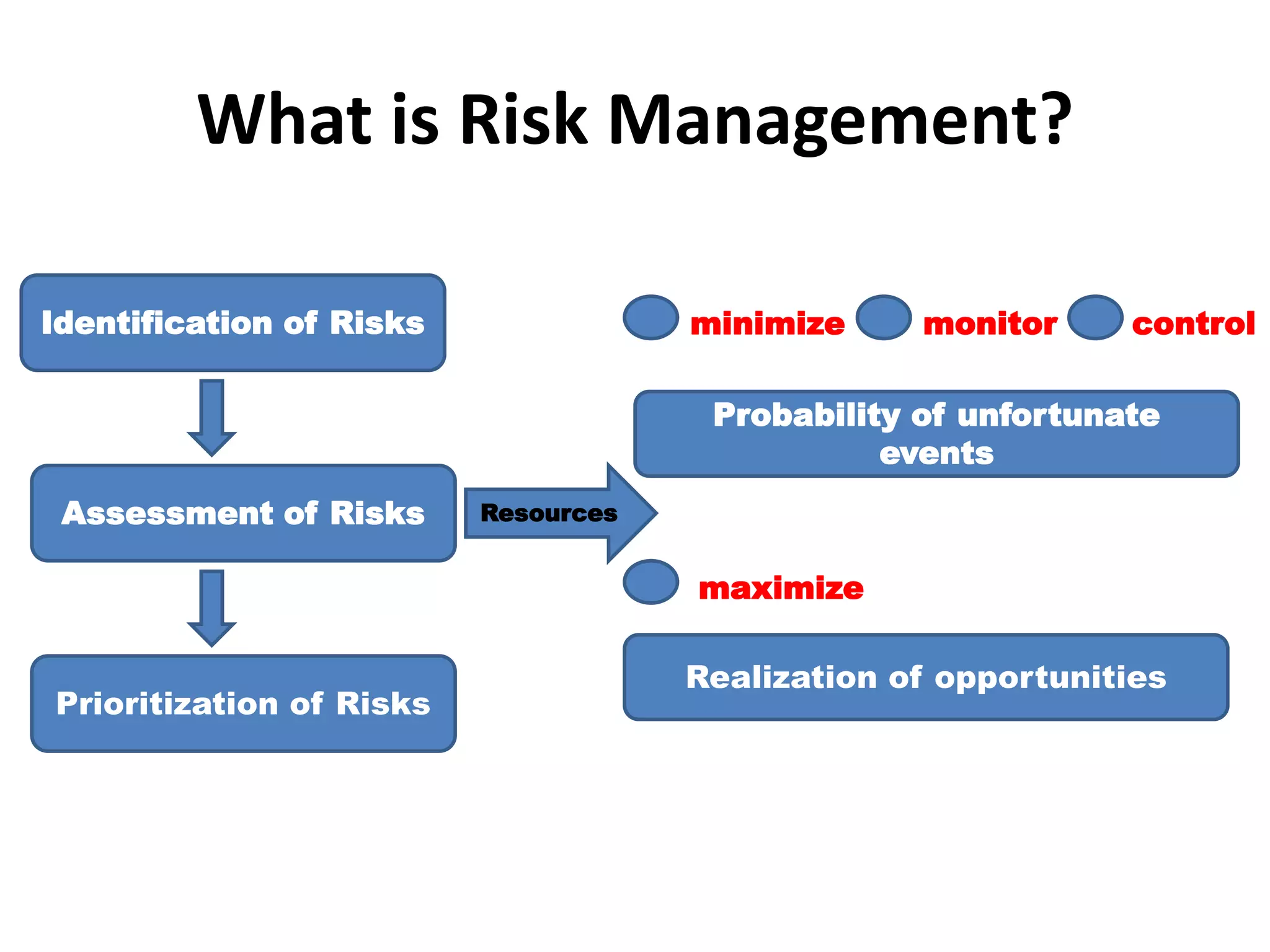
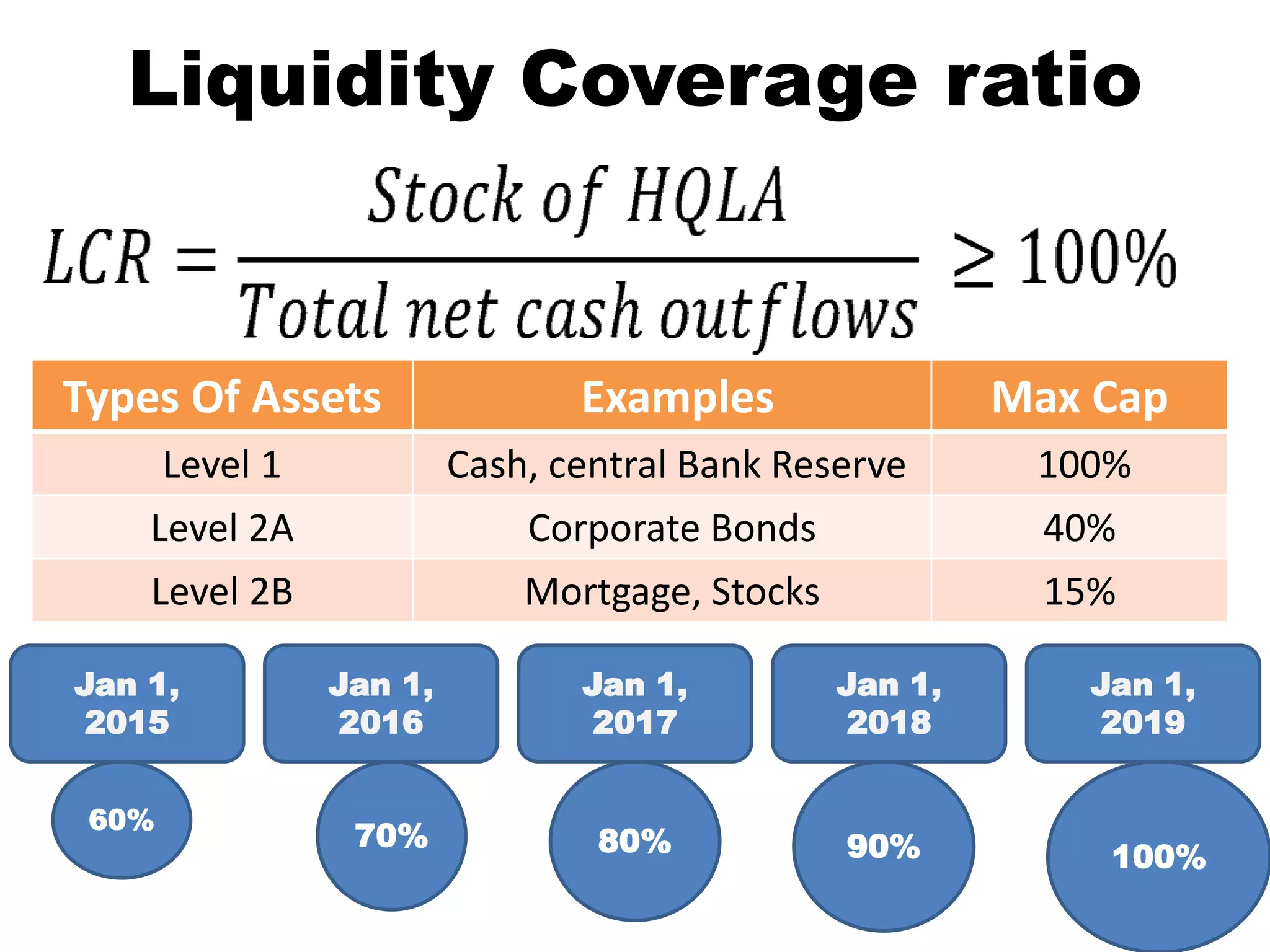
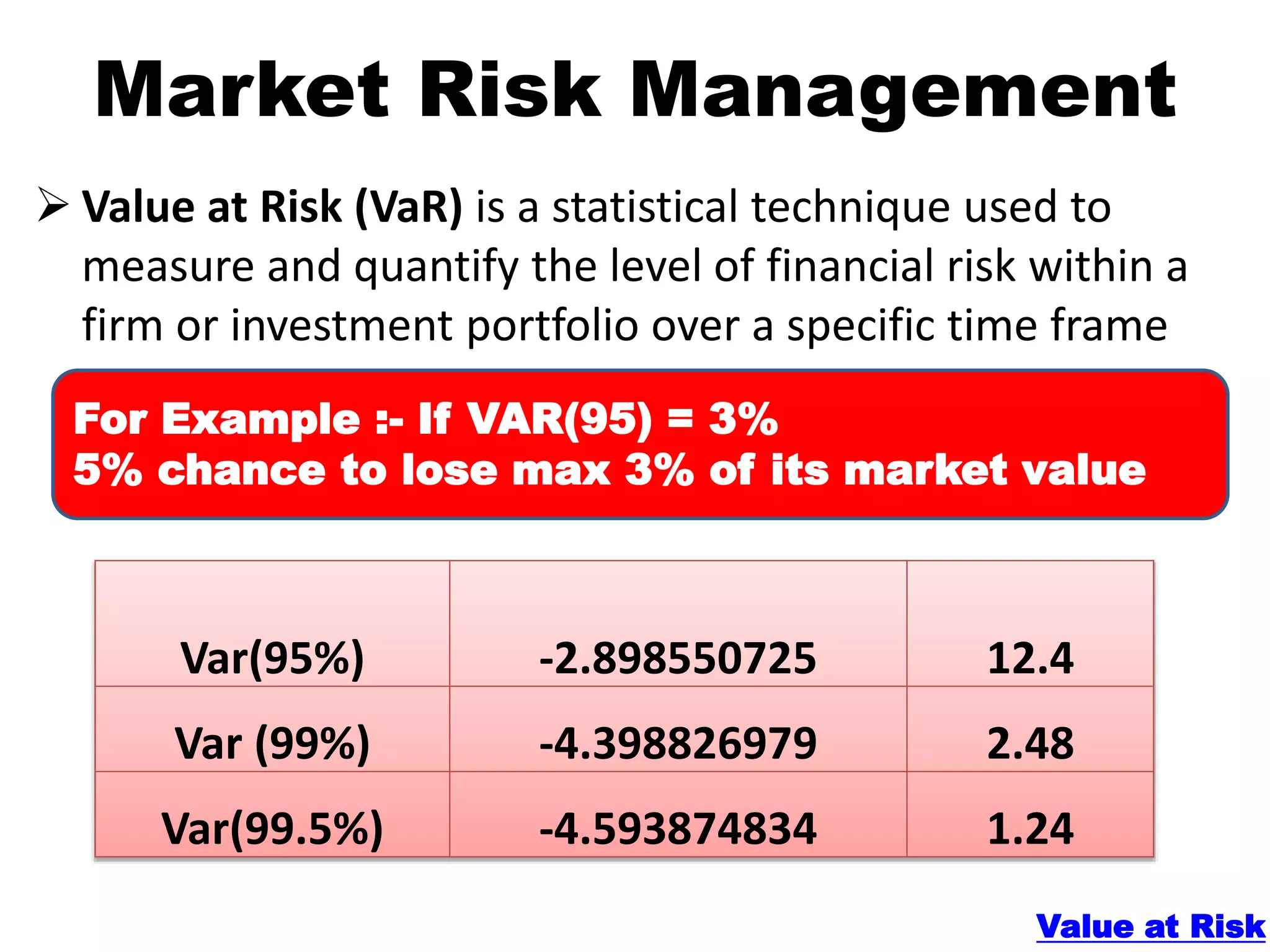
The document discusses various types of risks in banking and rural finance, including credit, liquidity, interest rate, and market risks, as well as methods for their assessment and management. Credit risk involves the likelihood of borrower default and is measured using metrics like the expected loss method and Altman Z-score. Liquidity risk is the inability to meet short-term obligations, while market risk refers to potential losses from market factors, with tools like Value at Risk (VaR) used for measurement.