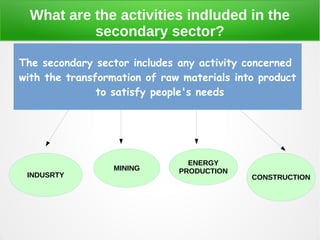
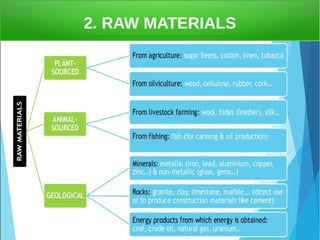
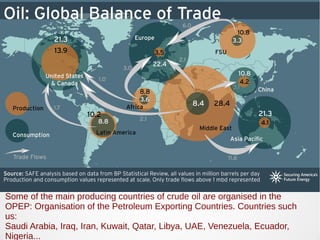
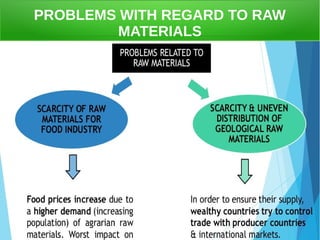
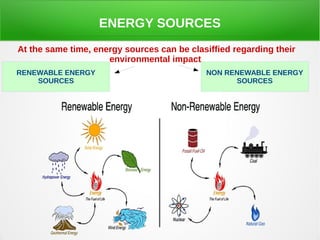
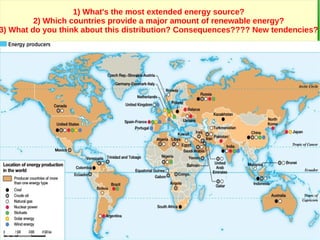
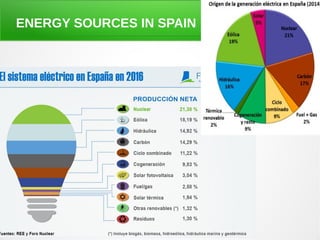
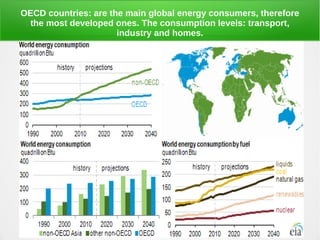
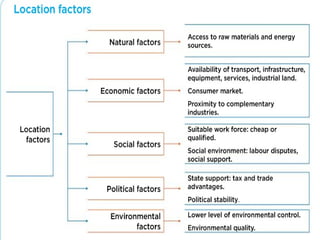
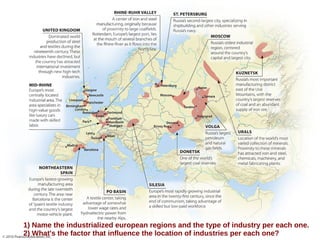
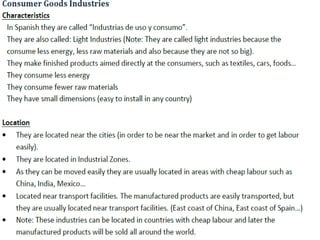
The secondary sector includes activities that transform raw materials into products, including industry, mining, energy production, and construction. Industry transforms raw materials into manufactured goods using energy sources and production factors. Mining locates, extracts, and refines minerals from the earth. Energy production transforms energy sources like natural gas into electricity. Construction creates buildings and infrastructure using plans and building materials. The main producing countries of raw materials are Canada, Australia, Russia, Brazil, South Africa, the US, and China. The largest consumers are Western Europe, the US, Japan, China, and India.