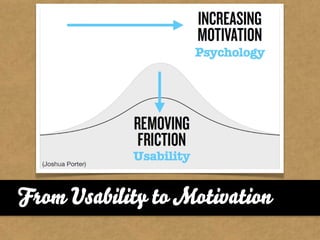
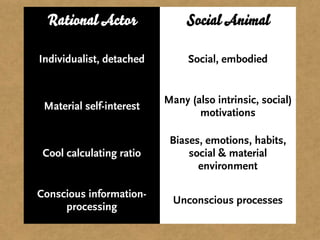
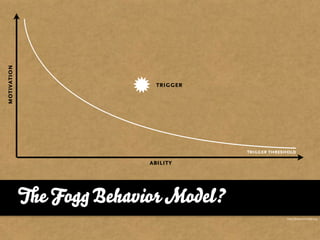
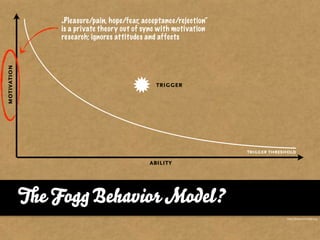
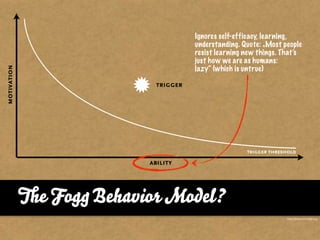
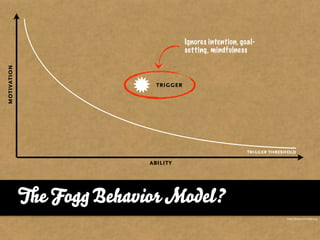
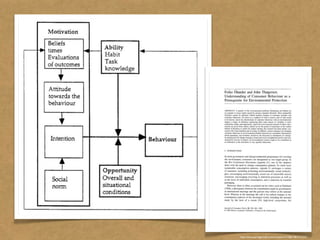
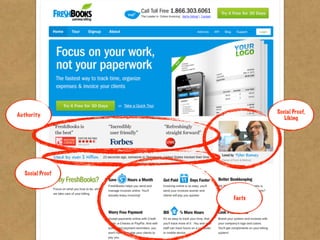
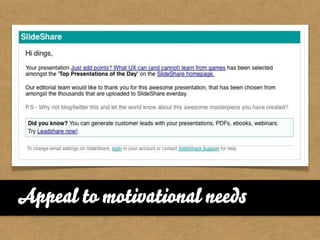
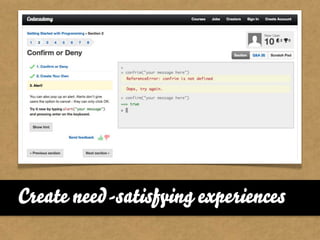
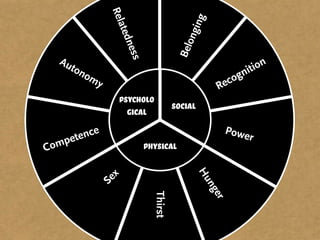
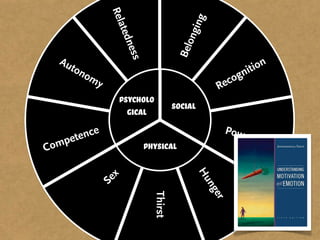
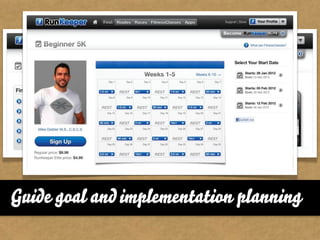
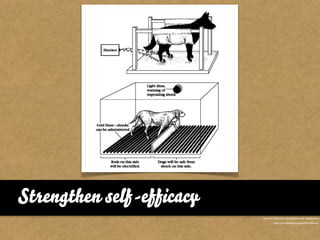
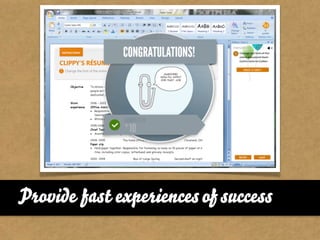
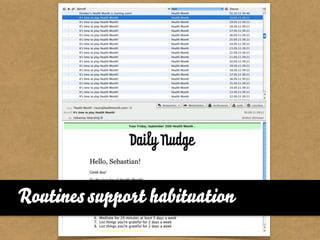
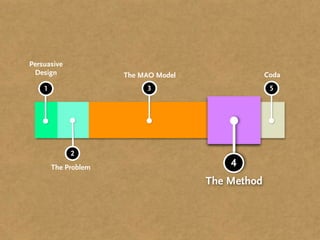
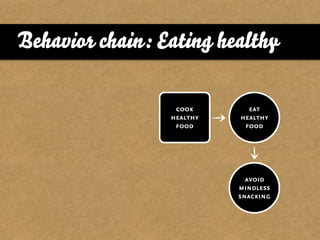
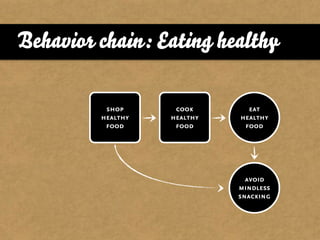
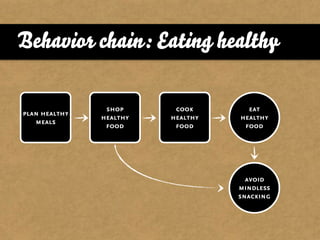
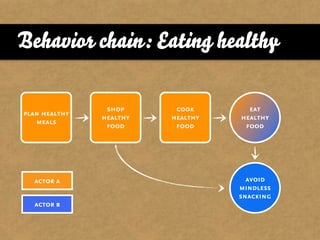
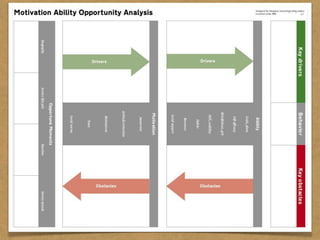
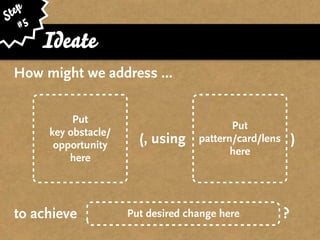
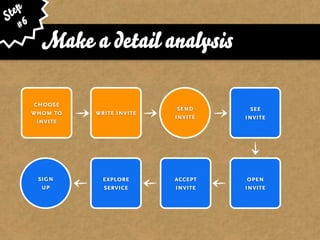
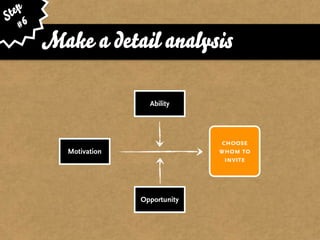
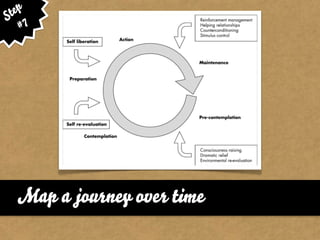
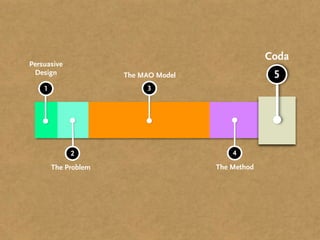
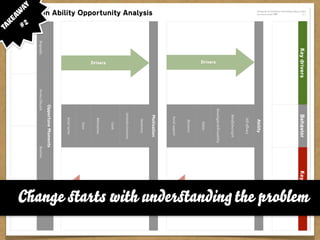
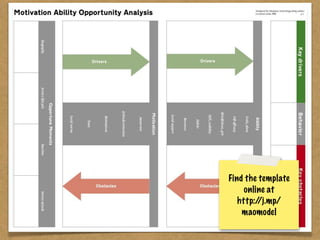
The document presents the Mao model of persuasive design, emphasizing the need to understand human behavior and motivators to effectively influence change. It critiques existing behavior models for lacking considerations of emotions, context, and social factors while offering a structured approach to analyze and facilitate behavior change. Key methods include defining goals, involving participants, and analyzing obstacles to design interventions that can catalyze desired actions.