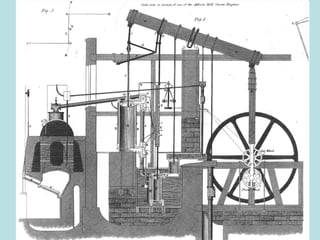
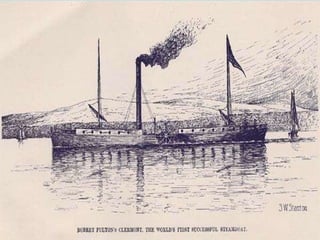
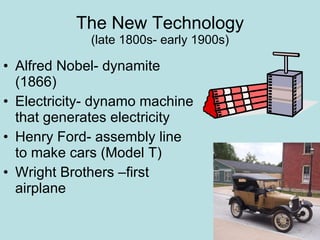
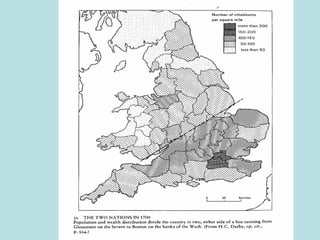
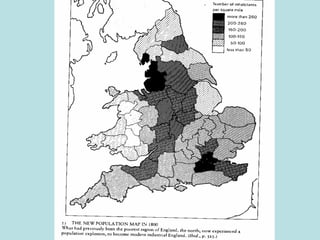
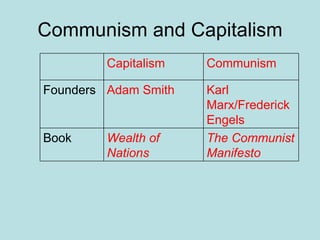
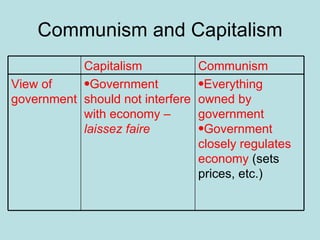
The Industrial Revolution transformed Britain from a largely agrarian society to an industrialized one between 1750-1850. New farming techniques increased food production, allowing the population to grow. Many moved to cities for factory work, living in poor conditions. Britain was well-suited for industrialization due to its natural resources like coal and iron, as well as economic and political stability. New technologies like the steam engine drove industrial growth. While some prospered, many workers faced long hours, low pay, and unsafe conditions, leading to social unrest and calls for reform.