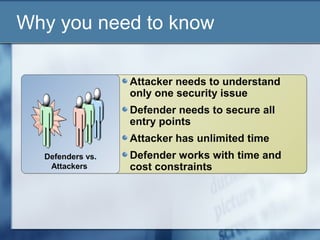
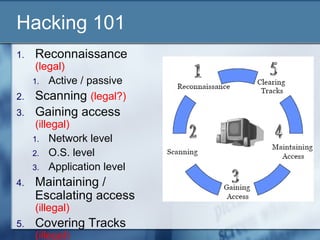
The document discusses a presentation about Certified Ethical Hacking. It begins by asking if computer hacking can be ethical and if one can be certified in it. It then explains that ethical hacking involves using hacking skills to test an organization's security defenses for vulnerabilities, with the organization's authorization. The rest of the document outlines the Certified Ethical Hacking certification program, including what is covered in the training course and exam. It provides examples of hacking tools and techniques taught as well as sample exam questions. The presentation emphasizes that ethical hacking is just one part of managing security risks and that there is no single solution to security issues.


























![The CEH Exam – Sample Questions
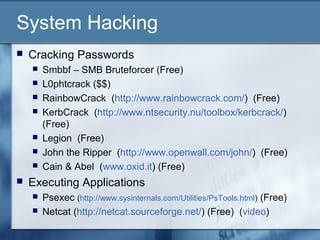
Netcat is a simple network utility which reads and
writes data across network connections, using TCP
or UDP protocol. Which of the following command
scans for open ports between [1 - 140]?
(Select the Best Answer)
A. nc -xx -q -w2 my-attacker-IP-address [1-140]
B. nc -vv -z -w2 my-attacker-IP-address 1-140
C. nc my-attacker-IP-address (1,140)
D. nc 140 my-attacker-IP-address -vv
Answer: B](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/super1-130127133203-phpapp01/85/Super1-30-320.jpg)




