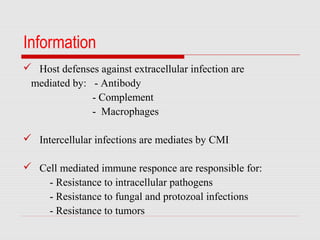
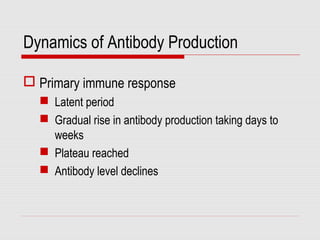
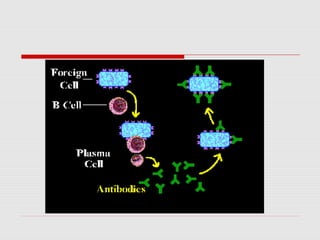
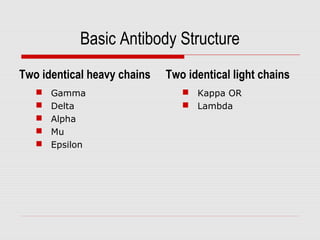
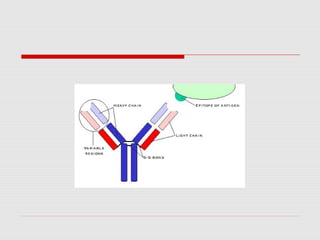
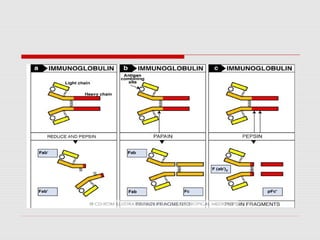
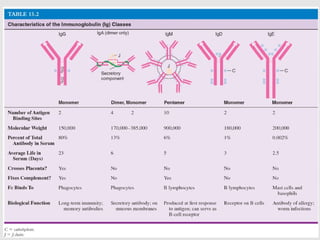
The document discusses the two types of immune responses: cell-mediated (CMI) and humoral, detailing their mechanisms and phases. CMI involves T-cells and macrophages responding to intracellular pathogens, while the humoral response produces antibodies against foreign antigens. Key components include antigen processing, cytokine signaling, and the roles of various T-cell subsets and antibody classes in immunity.