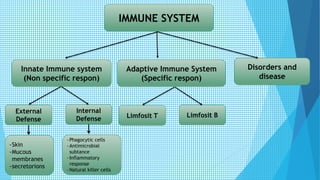
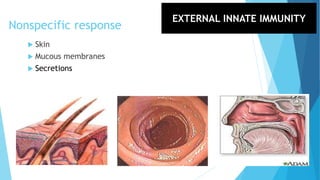
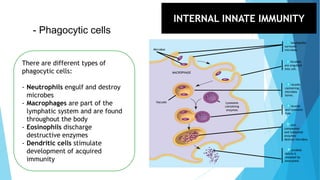
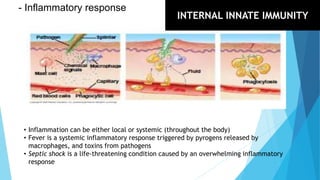
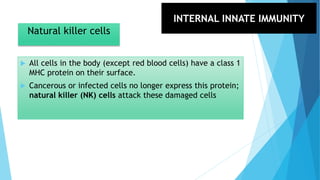
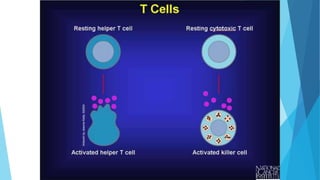
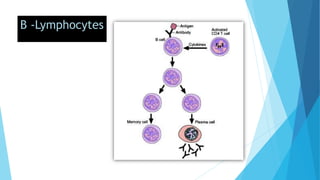
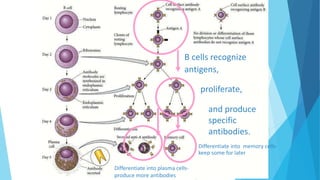
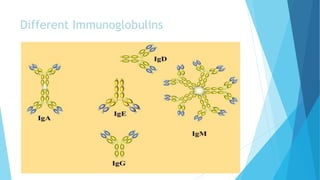
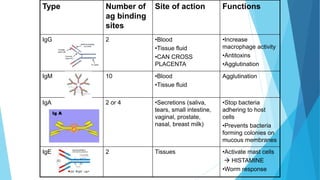
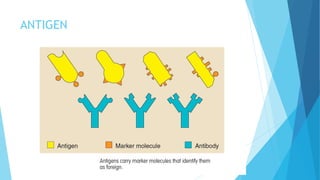
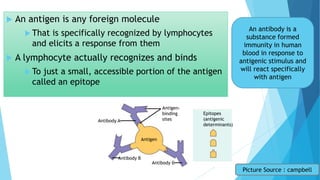
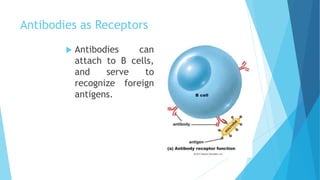
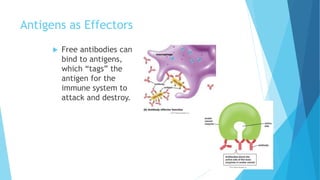
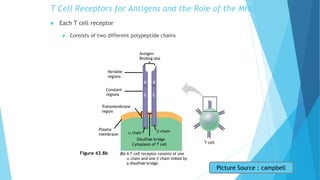
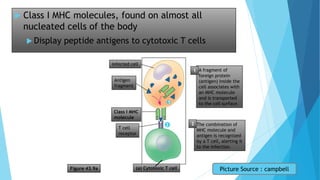
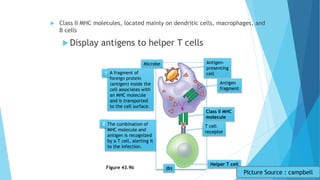
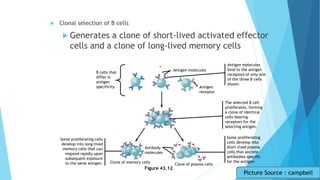
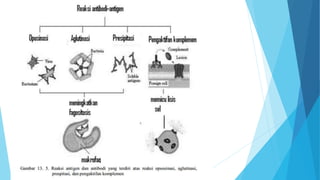
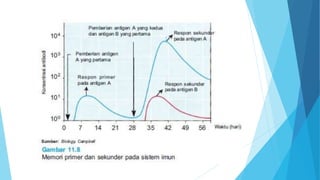
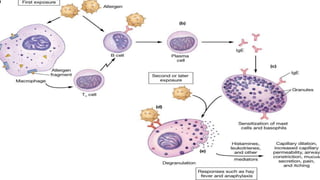
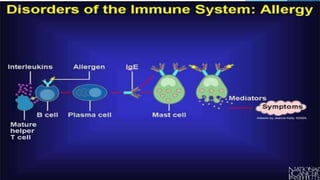
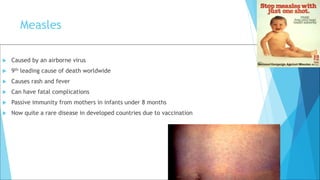
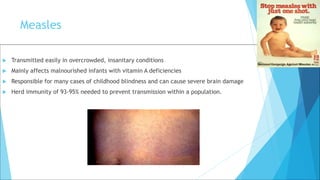
The immune system has two main branches - the innate immune system which provides immediate non-specific defense mechanisms, and the adaptive immune system which has antigen-specific acquired immunity. The innate system uses physical and chemical barriers along with phagocytic cells and the complement system. The adaptive system uses lymphocytes and antibody production. Antigens are recognized by B and T cells, leading to clonal selection and a memory-based secondary response. Immune disorders occur when tolerance is lost, such as allergies, while deficiencies allow diseases like smallpox and measles to spread. Vaccination has controlled many infectious diseases.