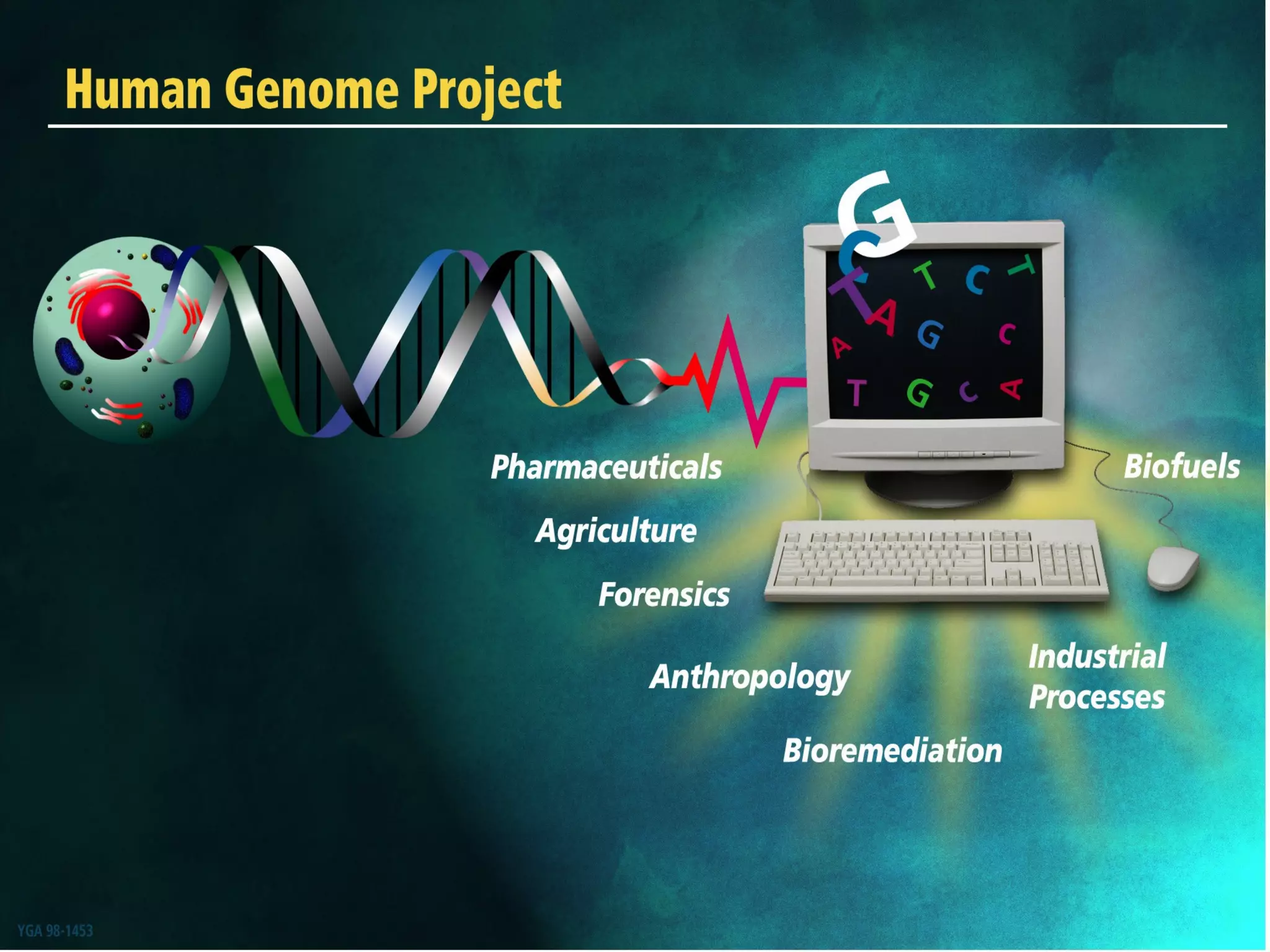
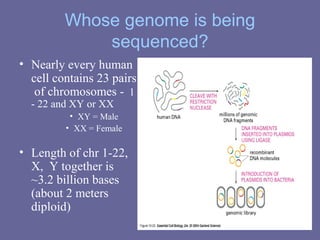
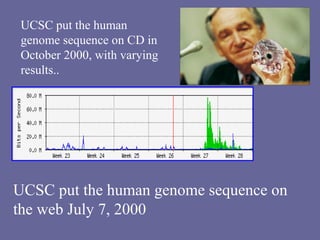
The Human Genome Project began in 1990 with the goal of mapping all the genes in human DNA to better understand human health and disease. Over 13 years and $3 billion, an international team sequenced the entire human genome, identifying all 3 billion DNA base pairs and approximately 30,000 genes located on human chromosomes. The project was completed in 2003 and its results are stored in public databases, allowing scientists to better diagnose, treat and prevent genetic disorders.