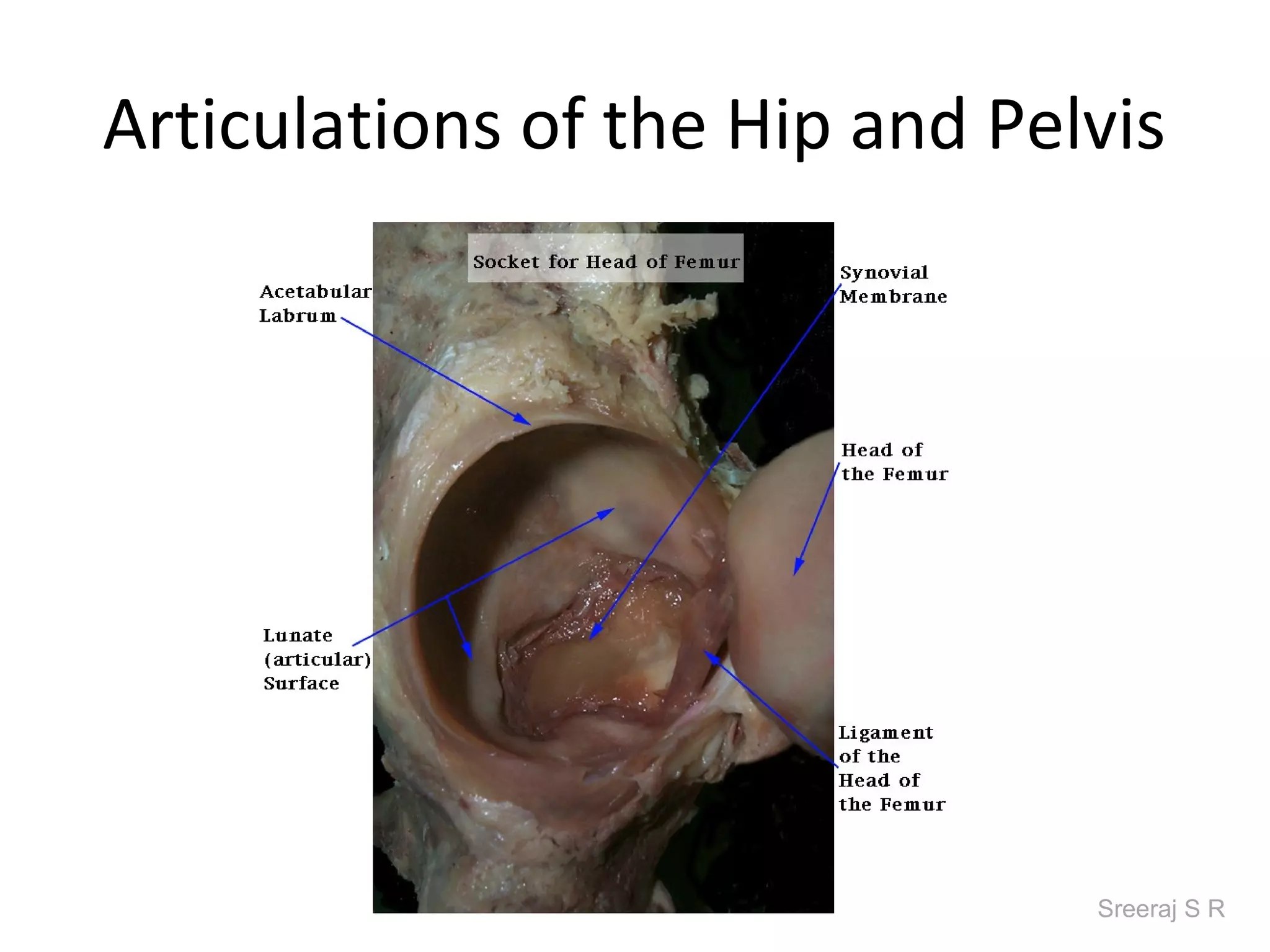
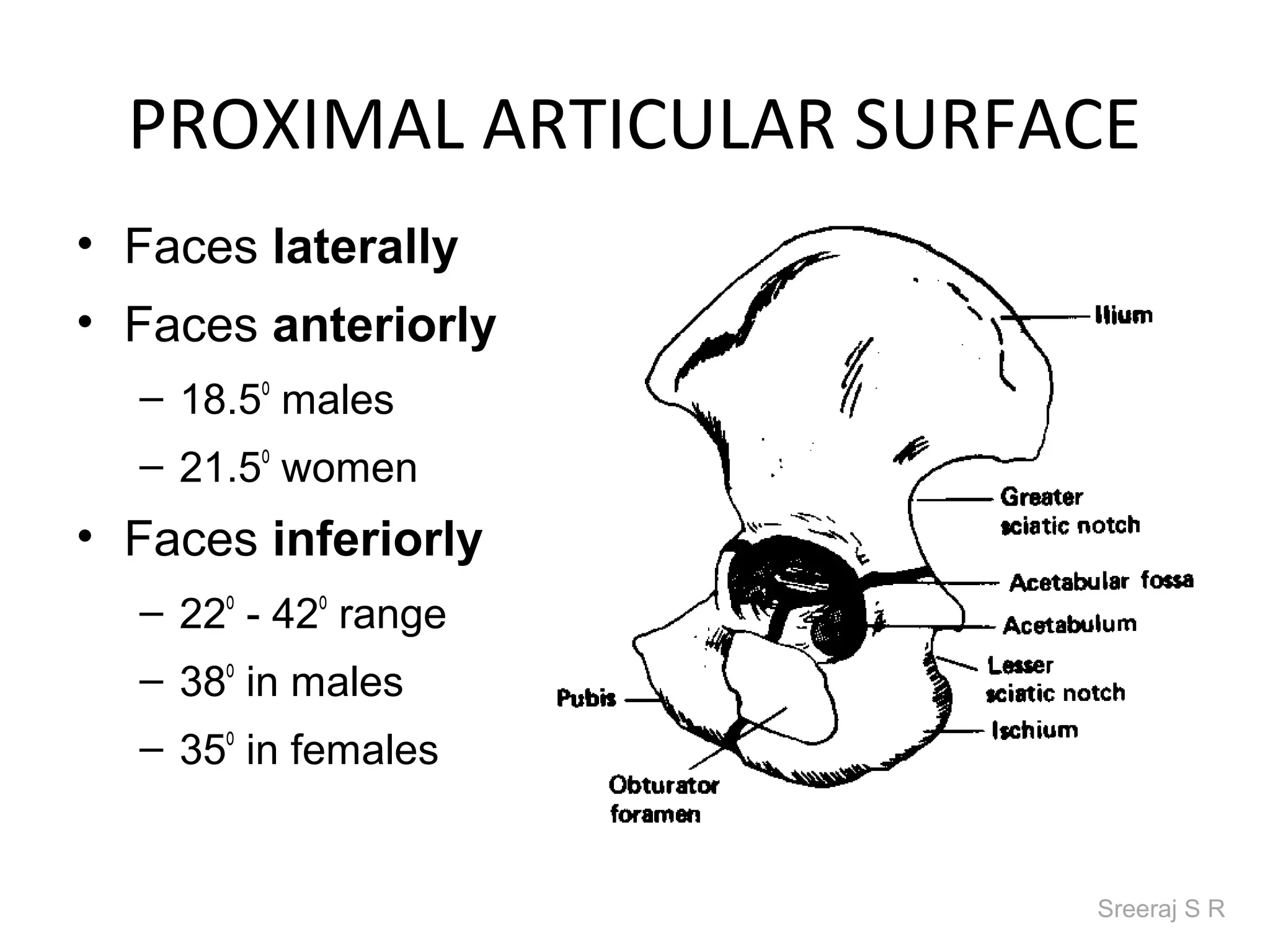
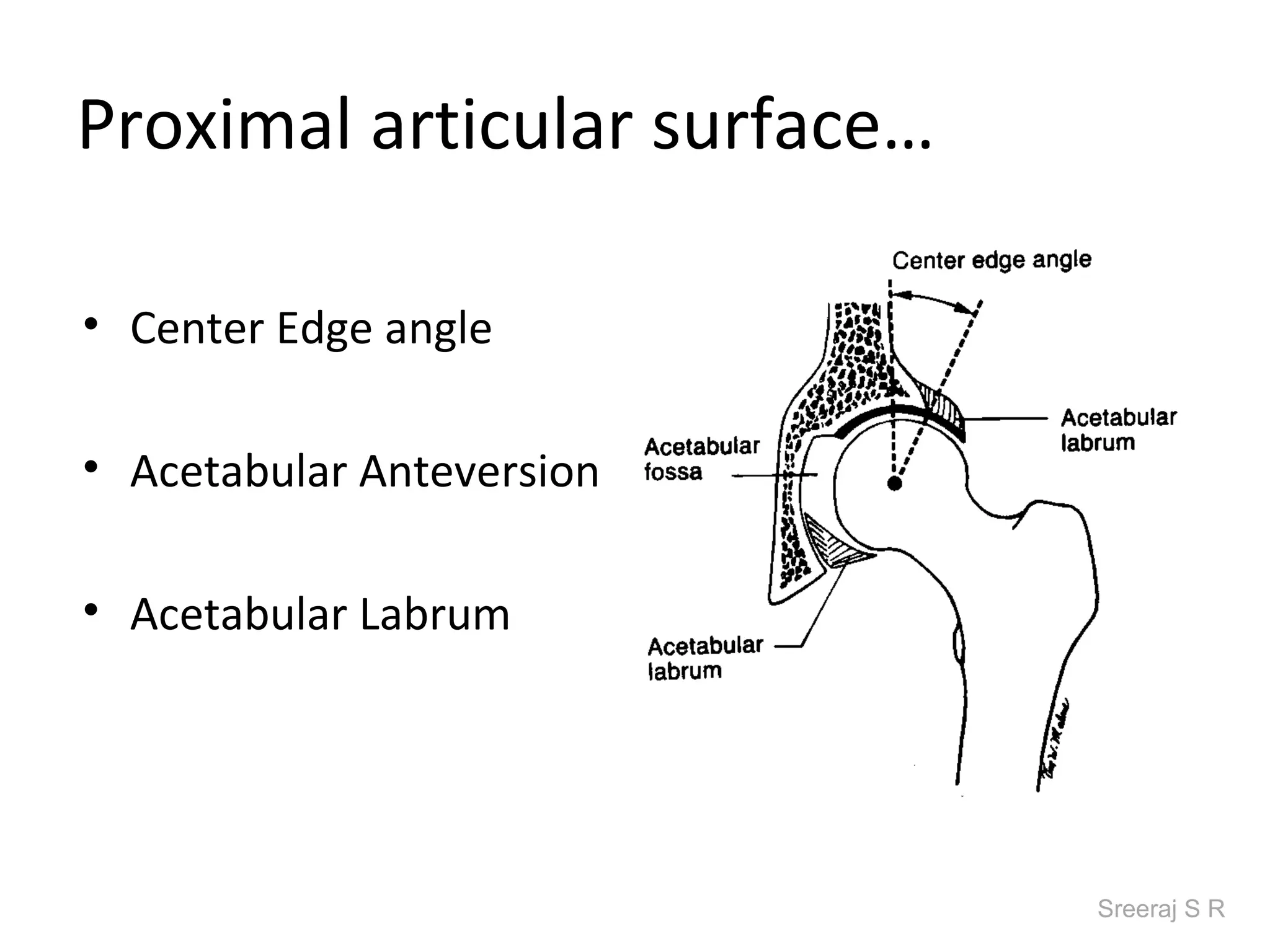
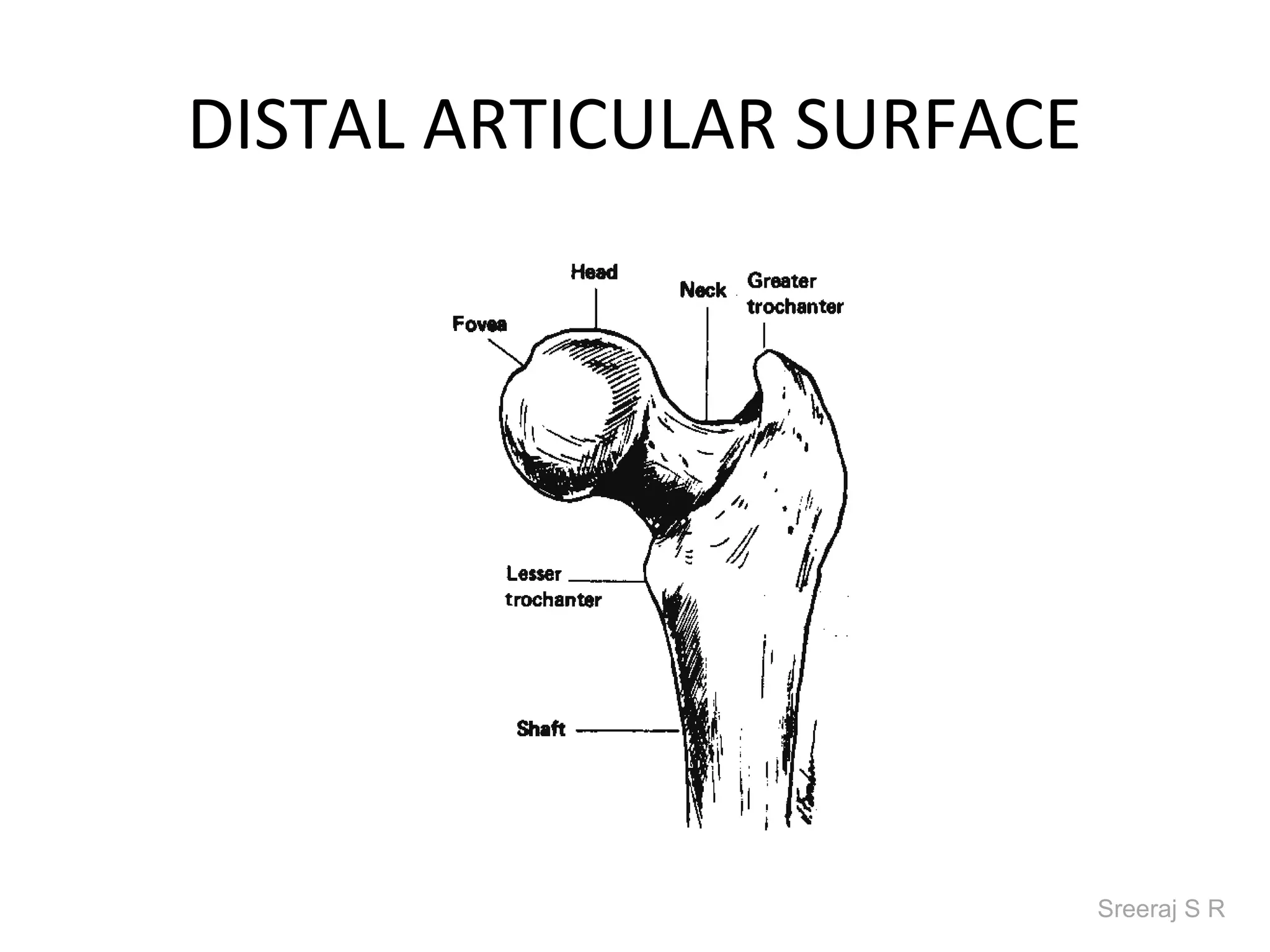
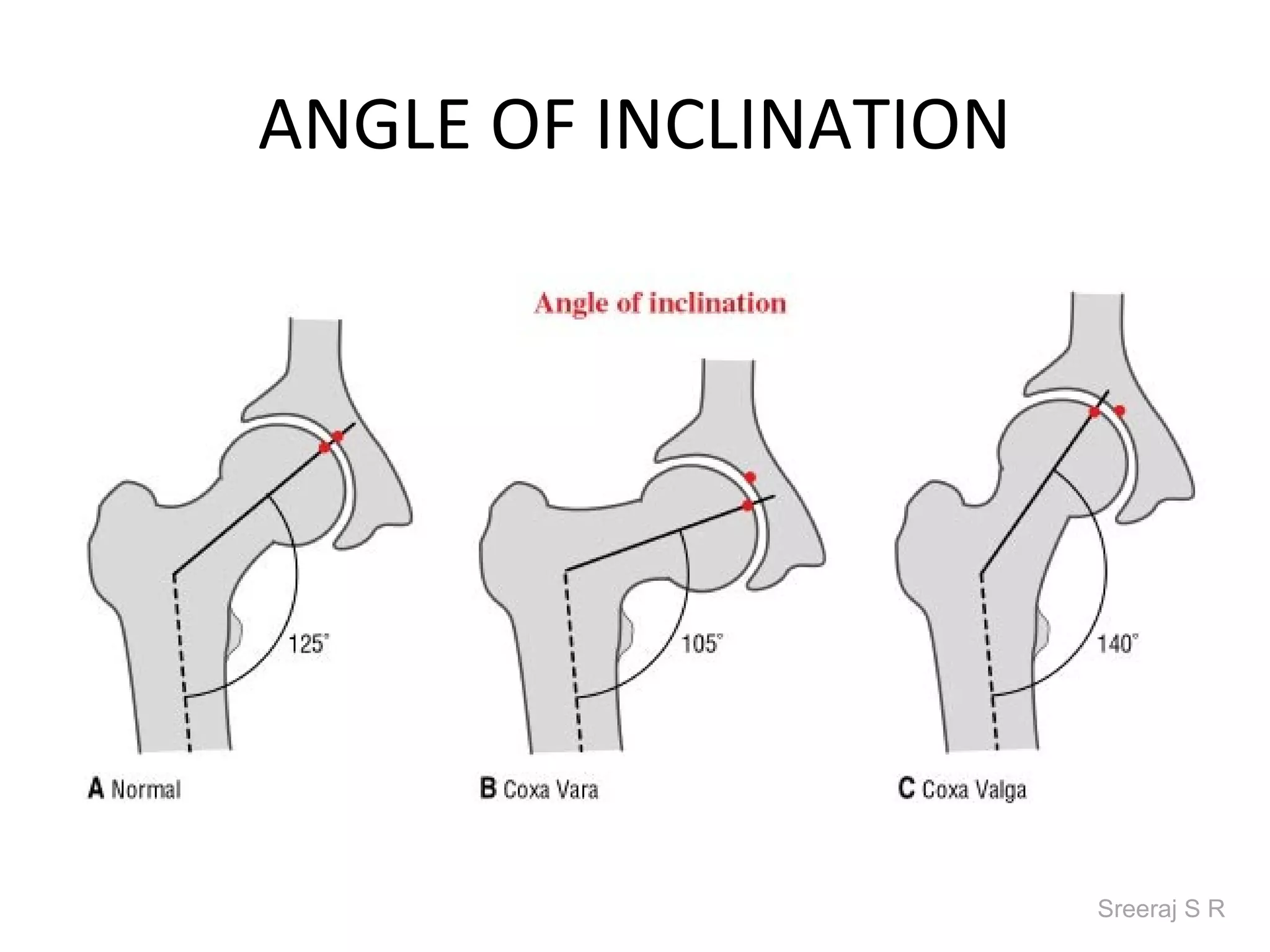
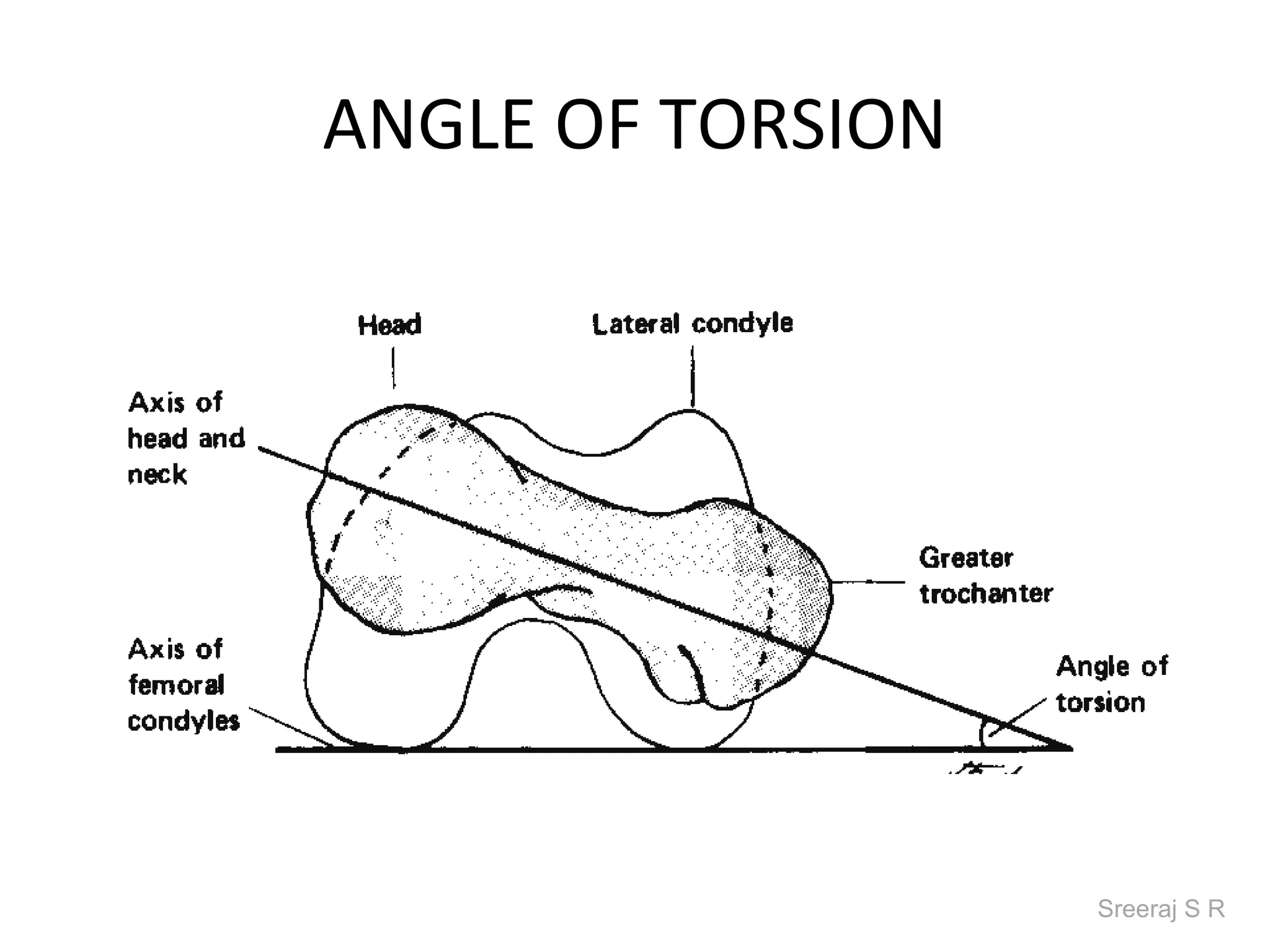
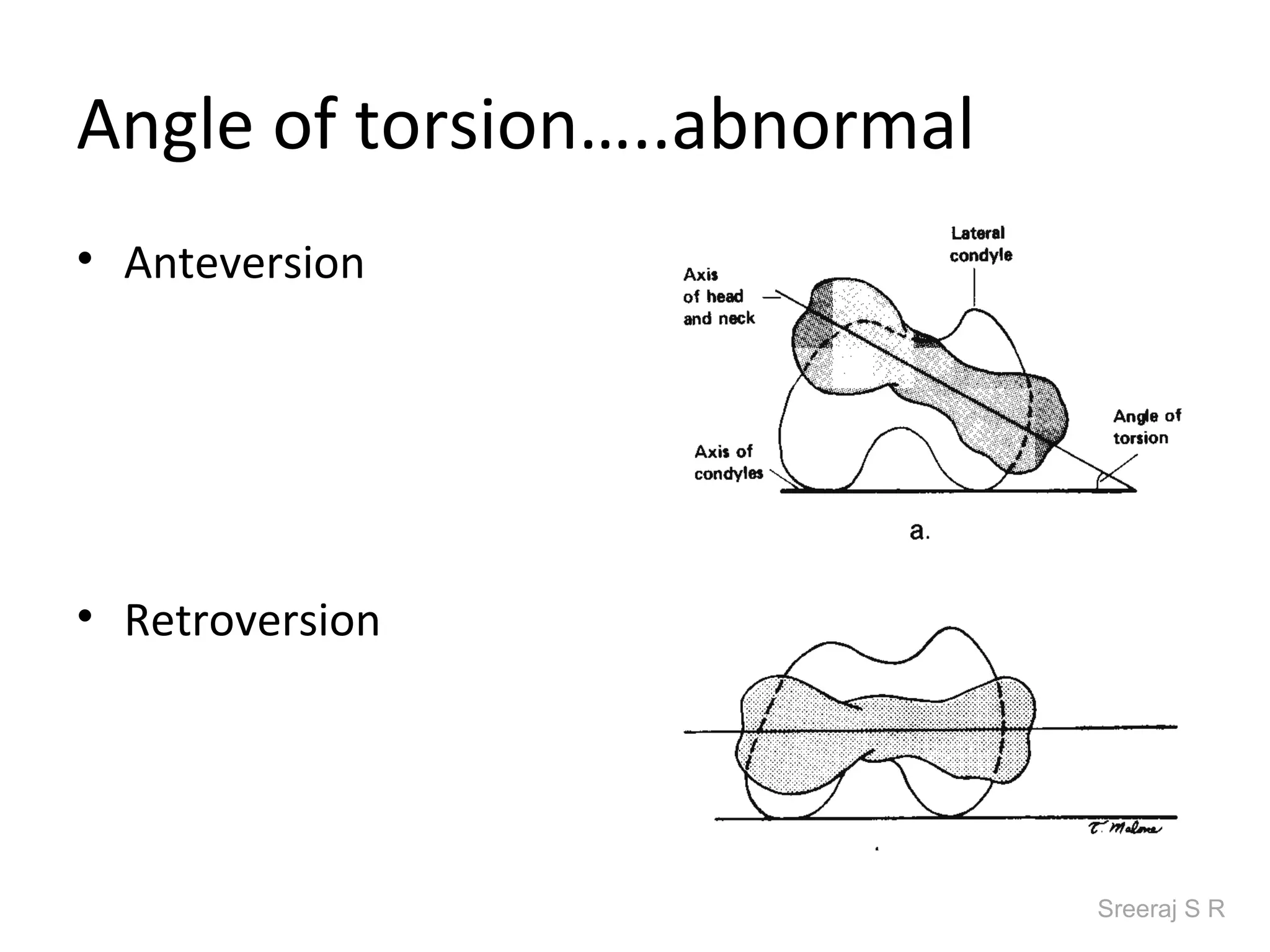
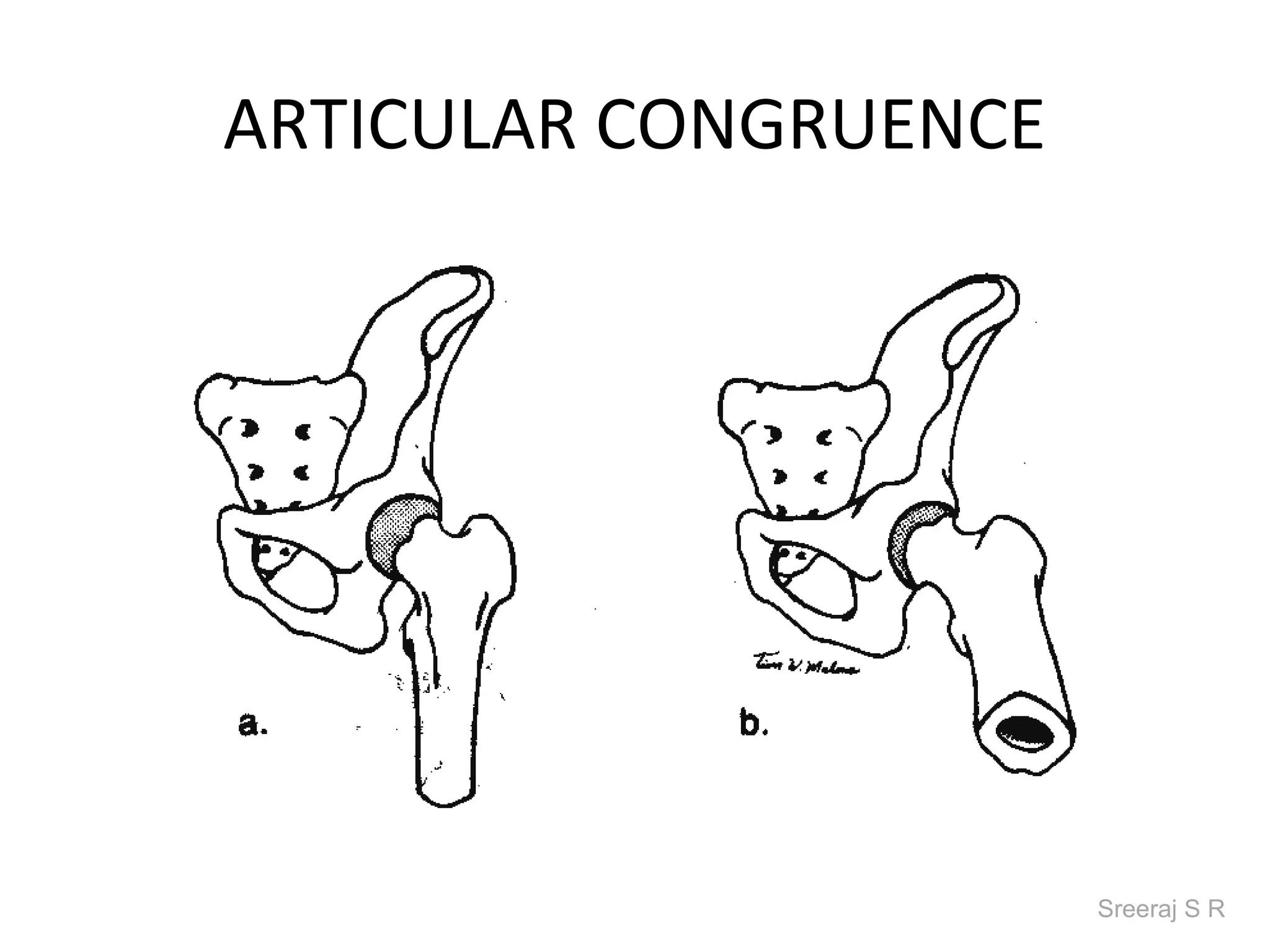
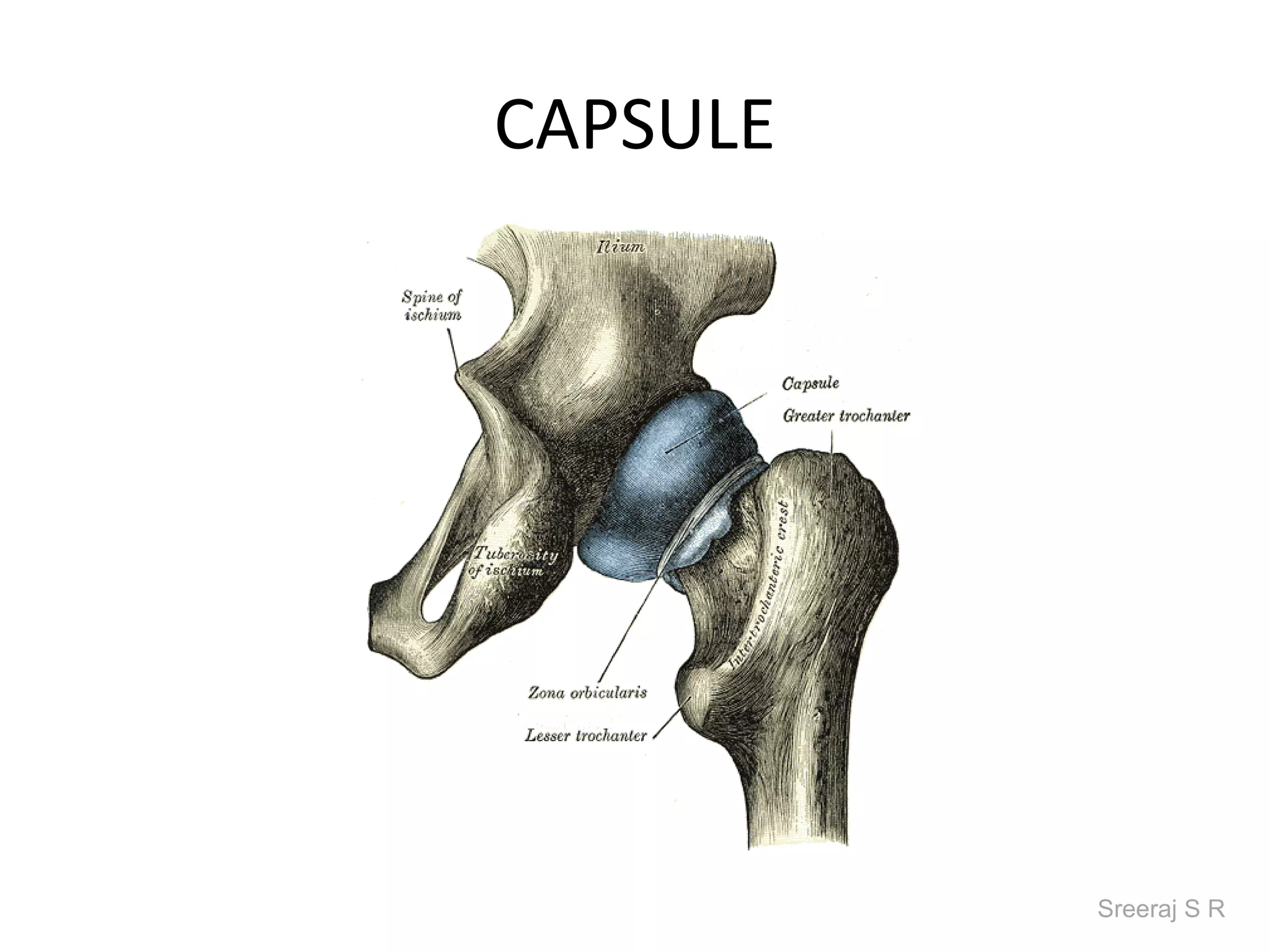
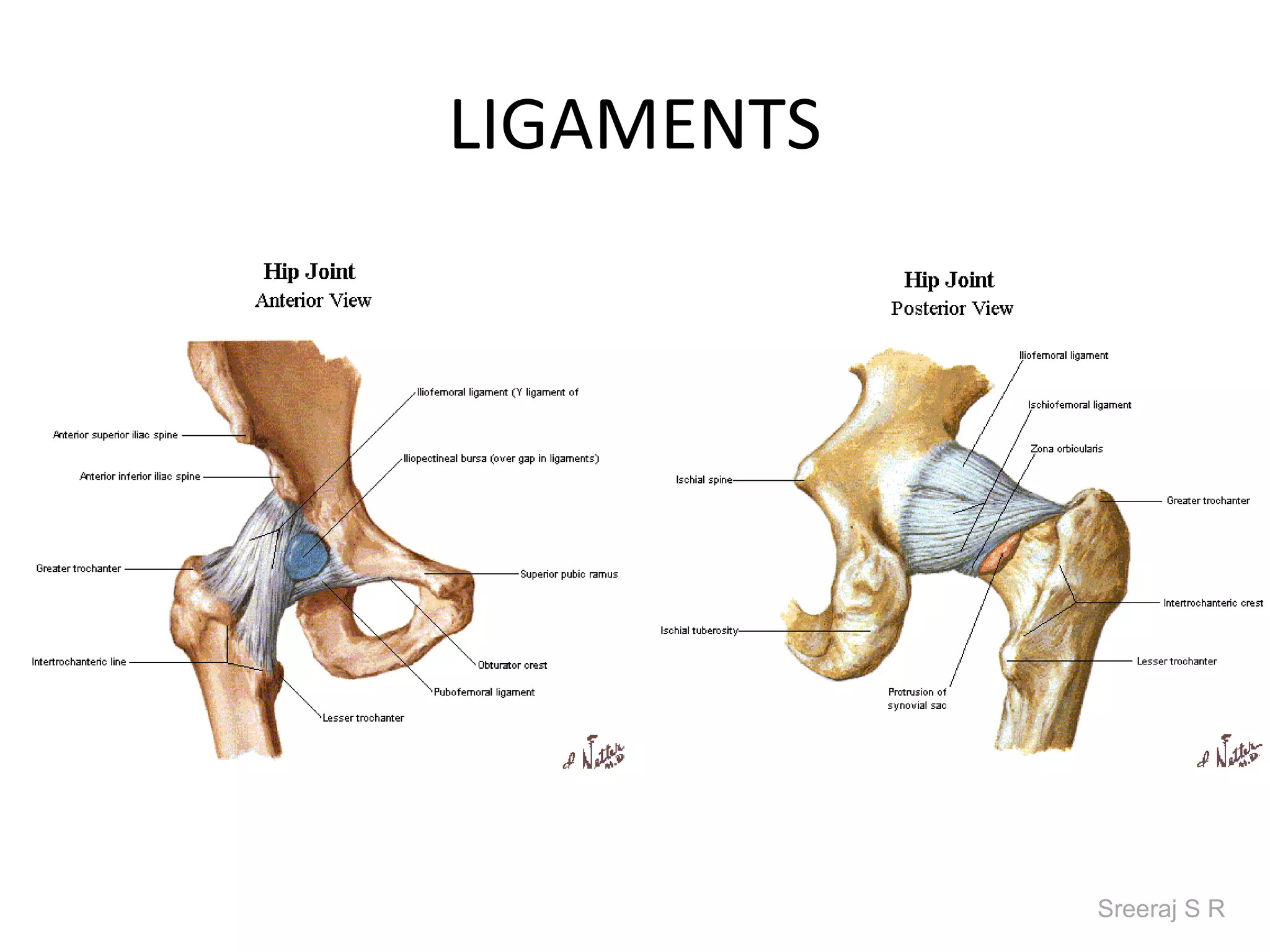
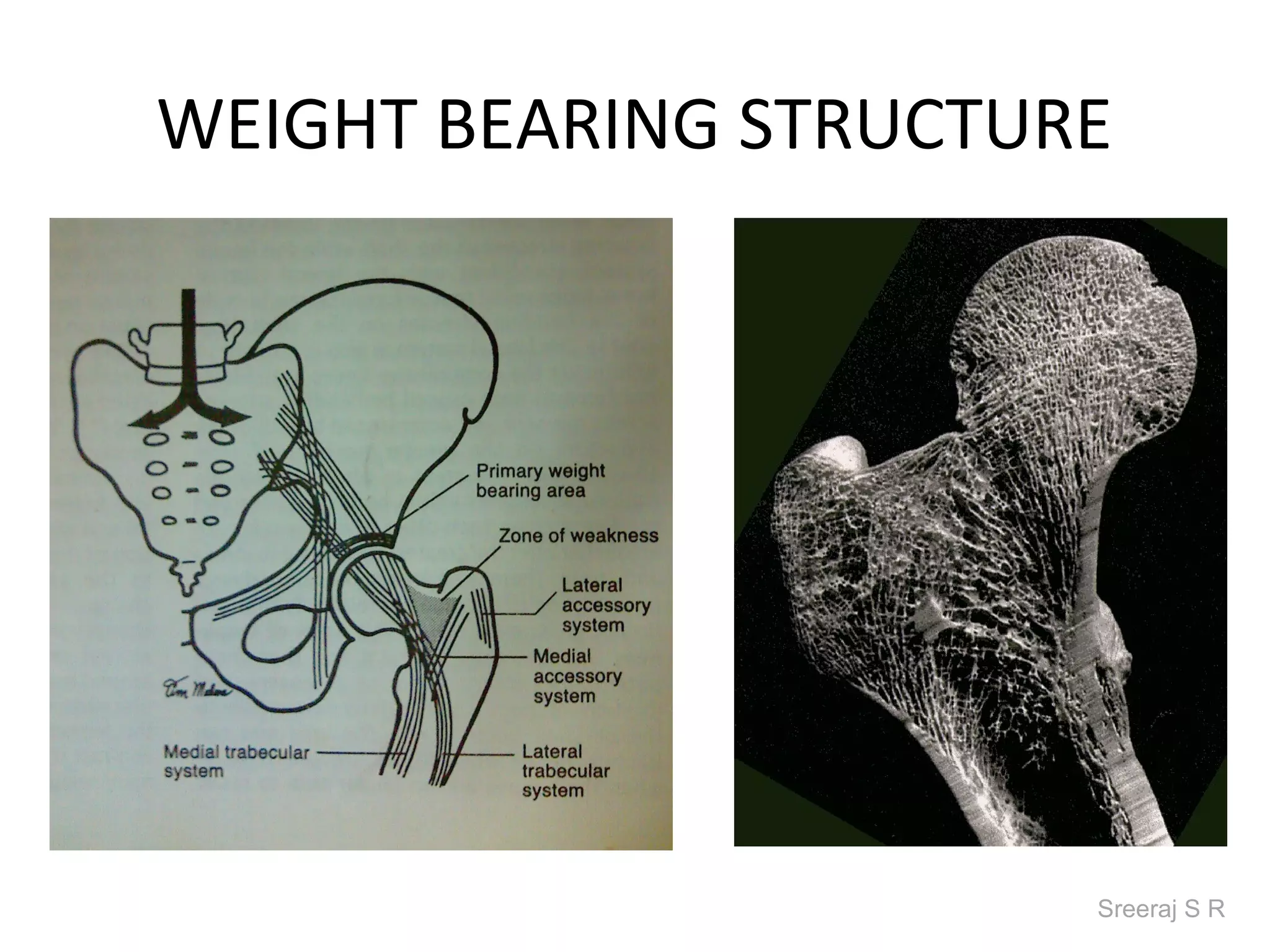
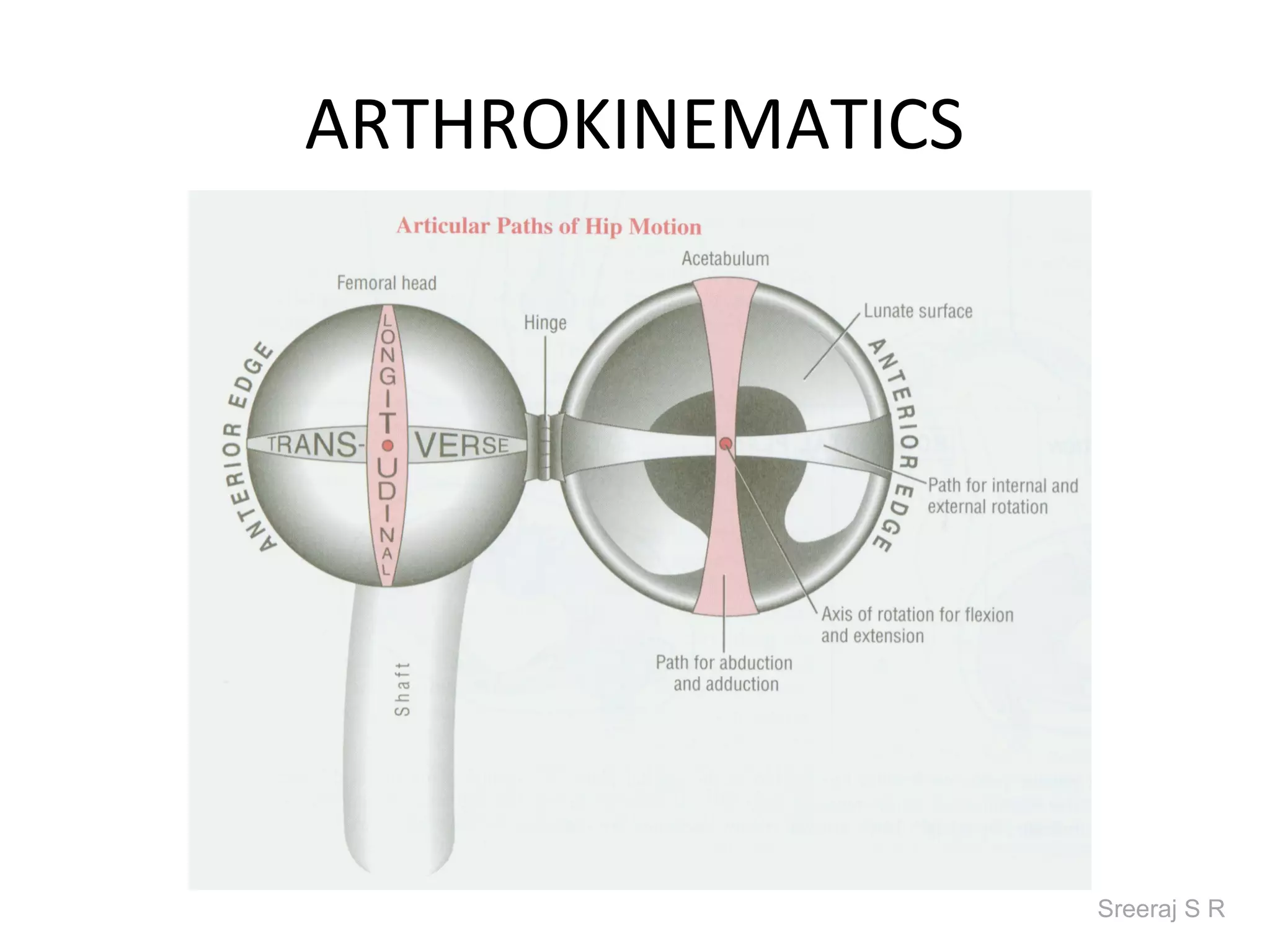
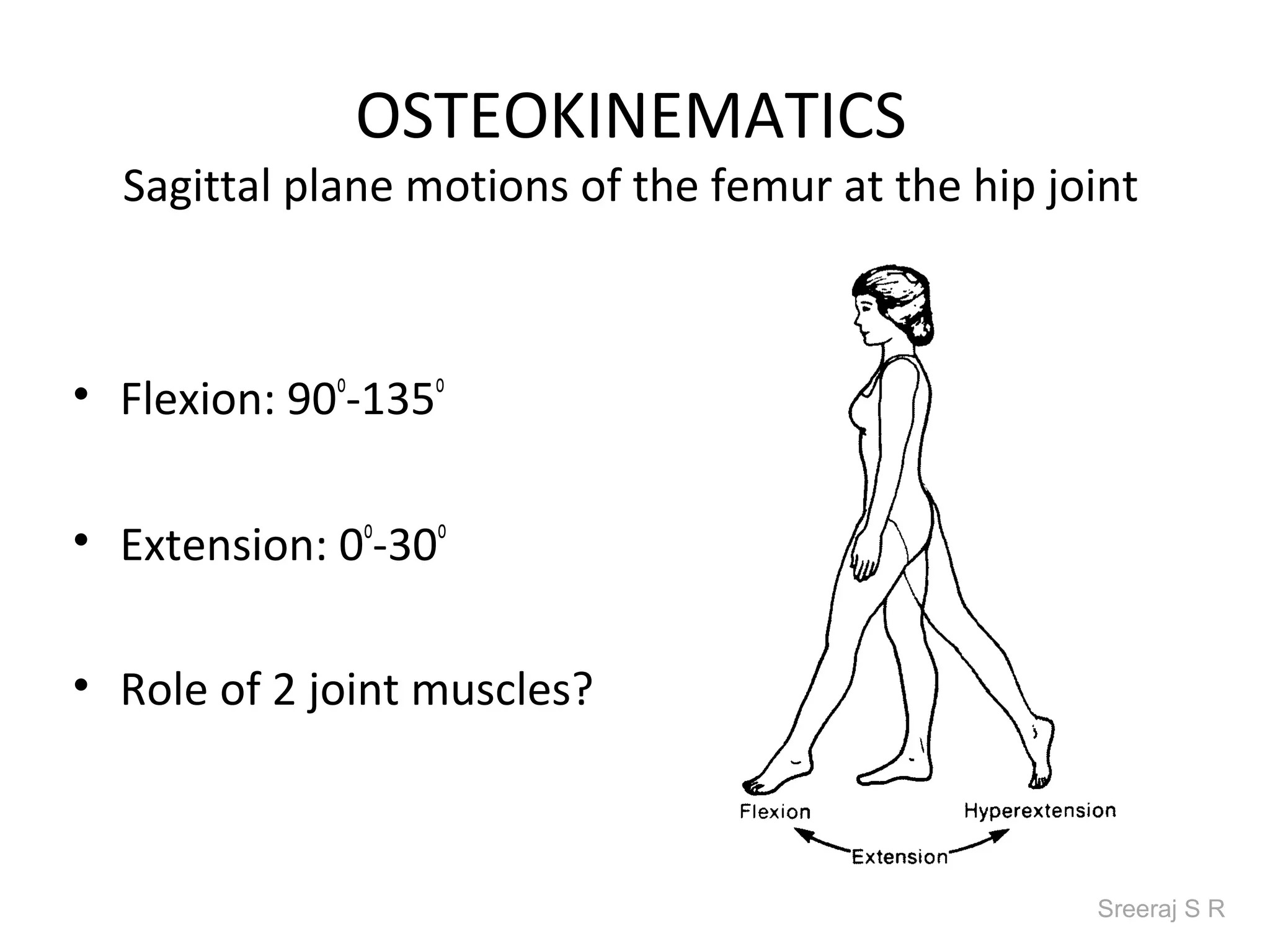
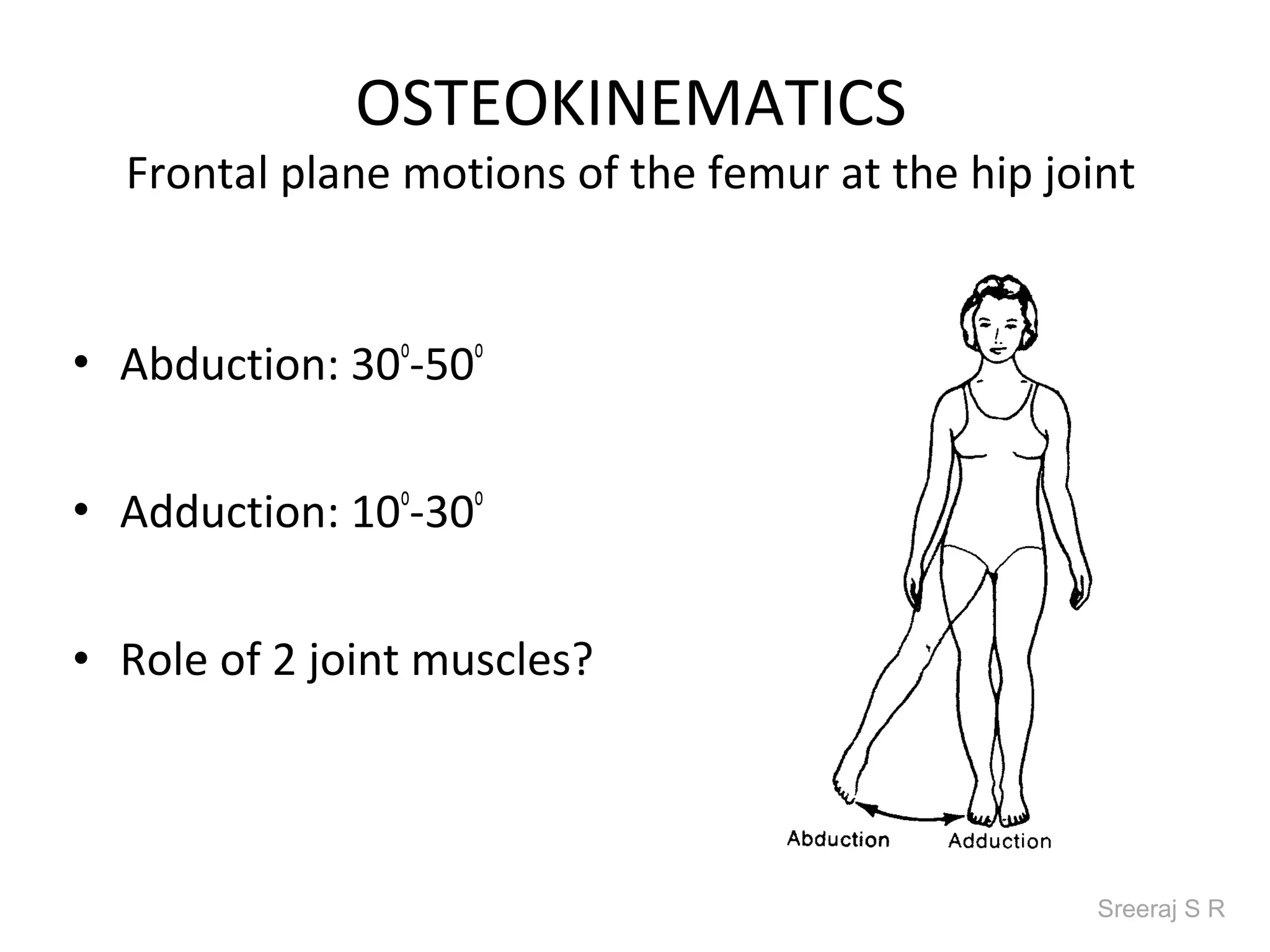
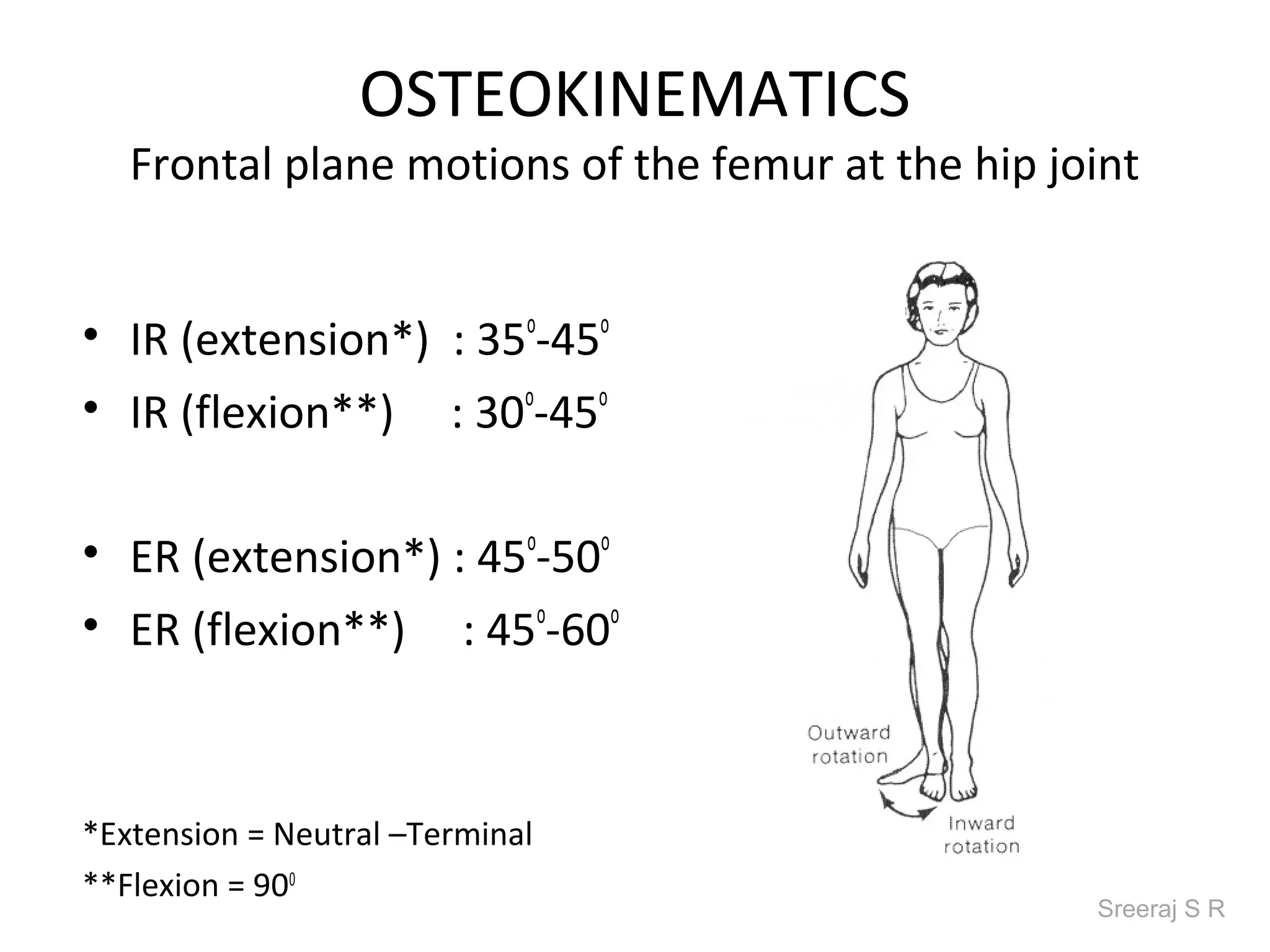
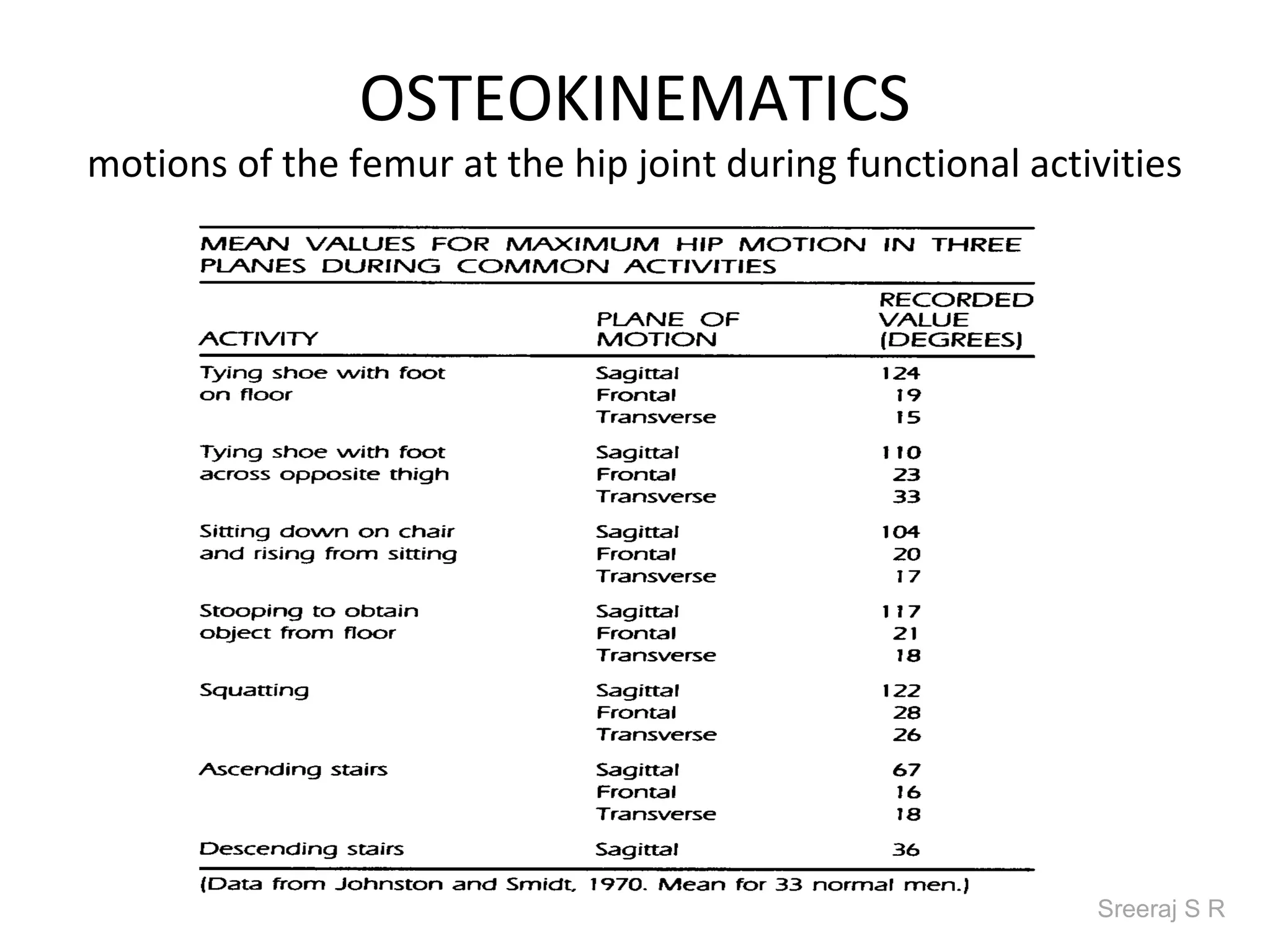
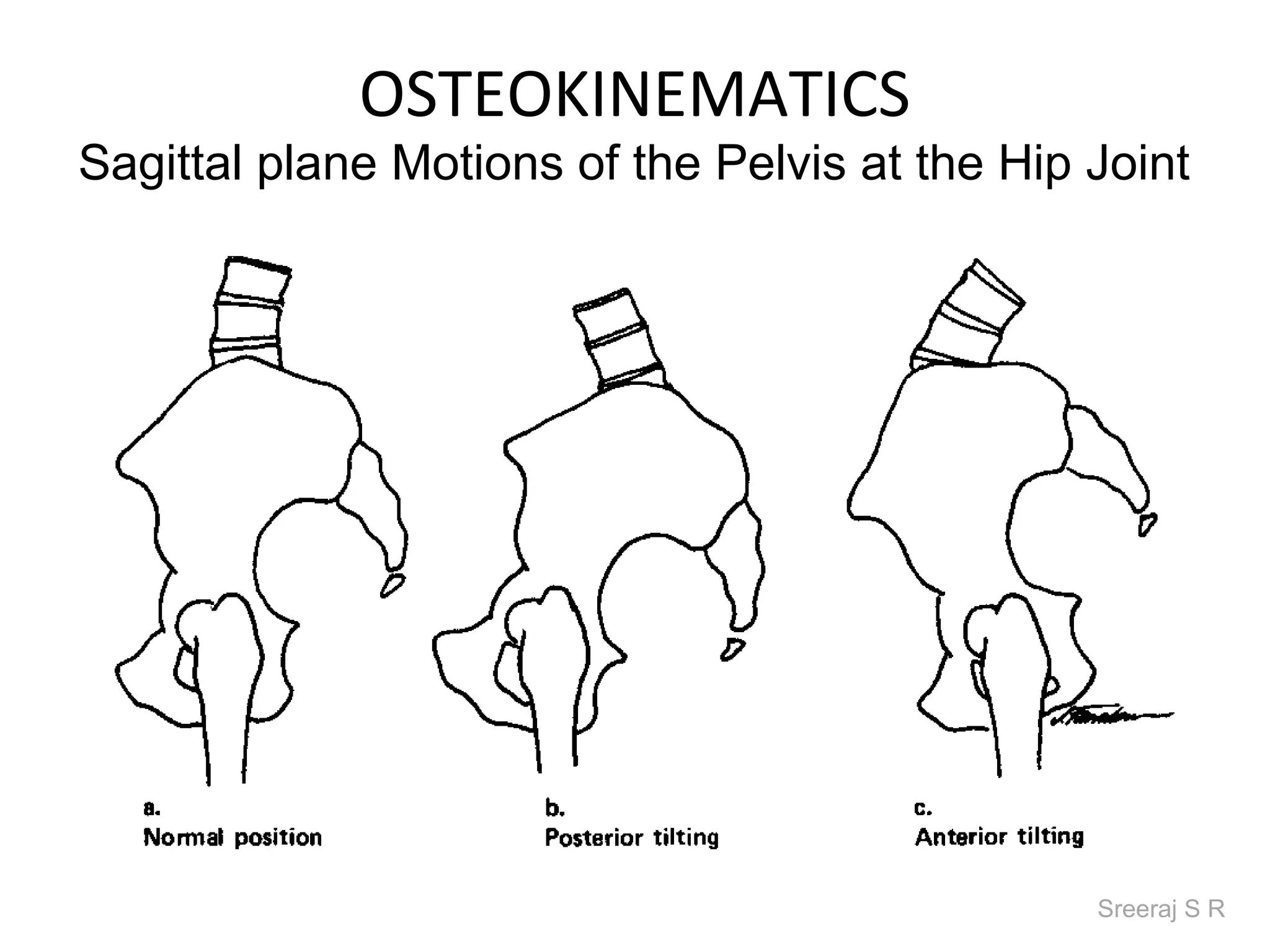
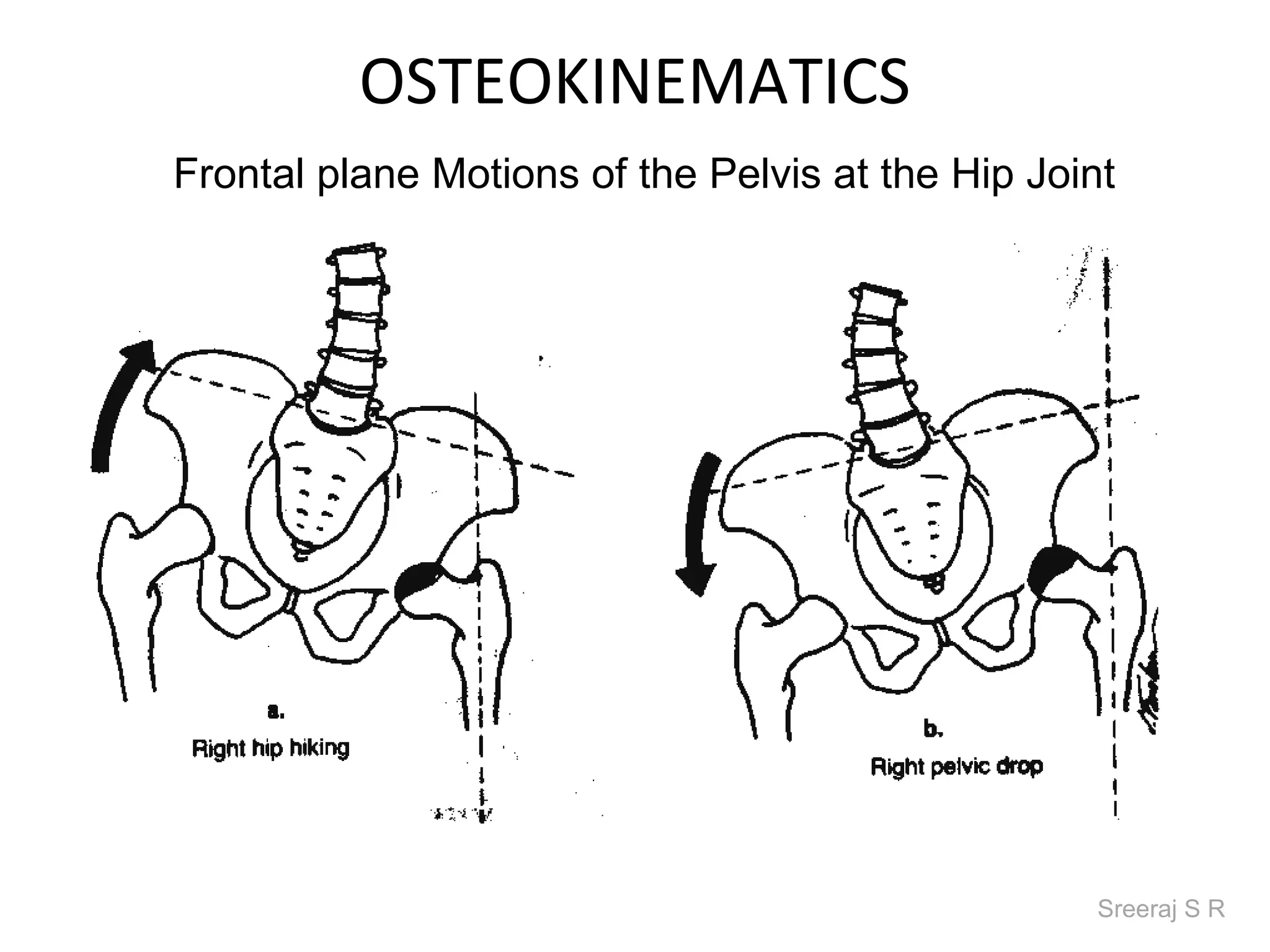
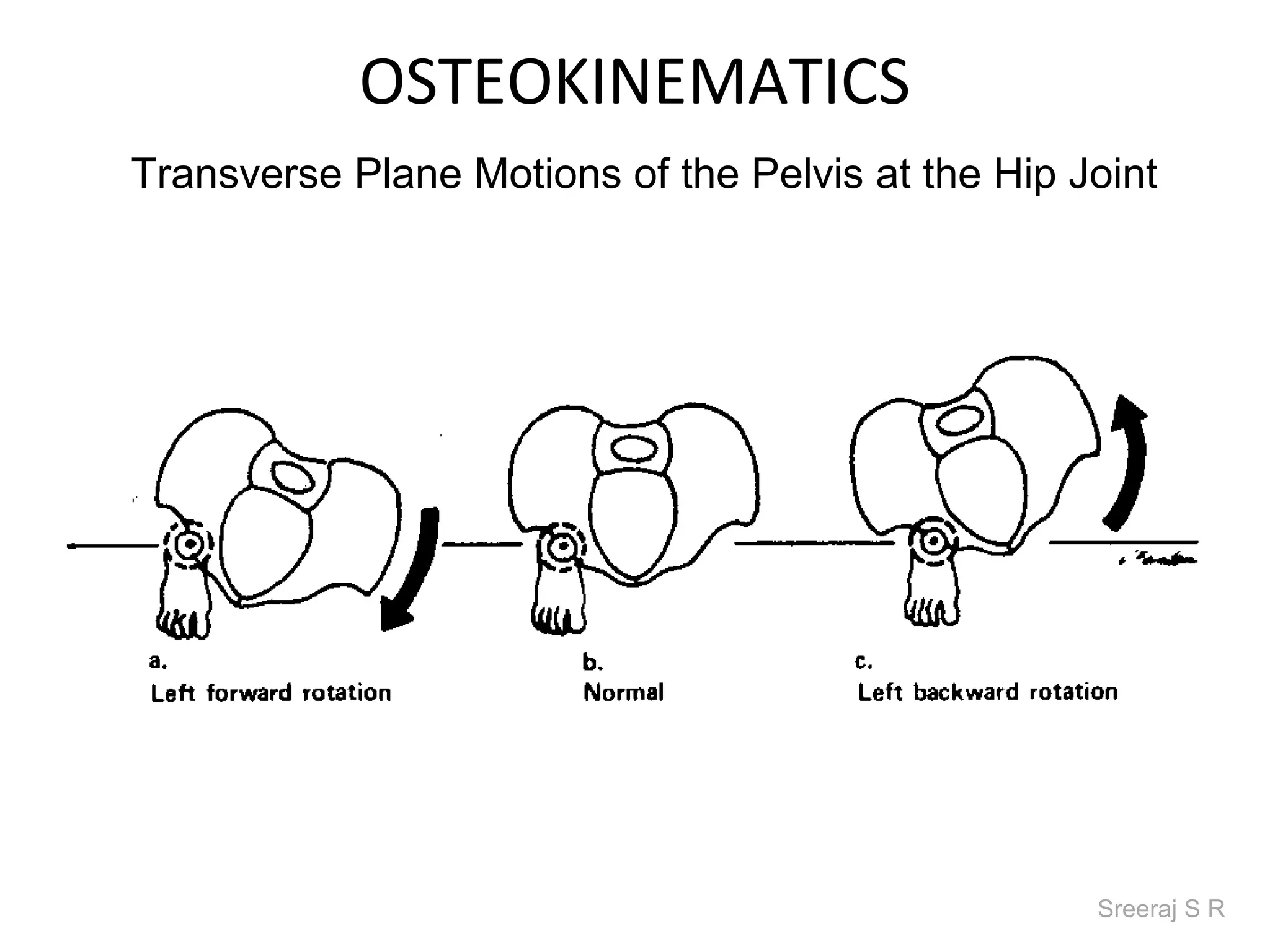
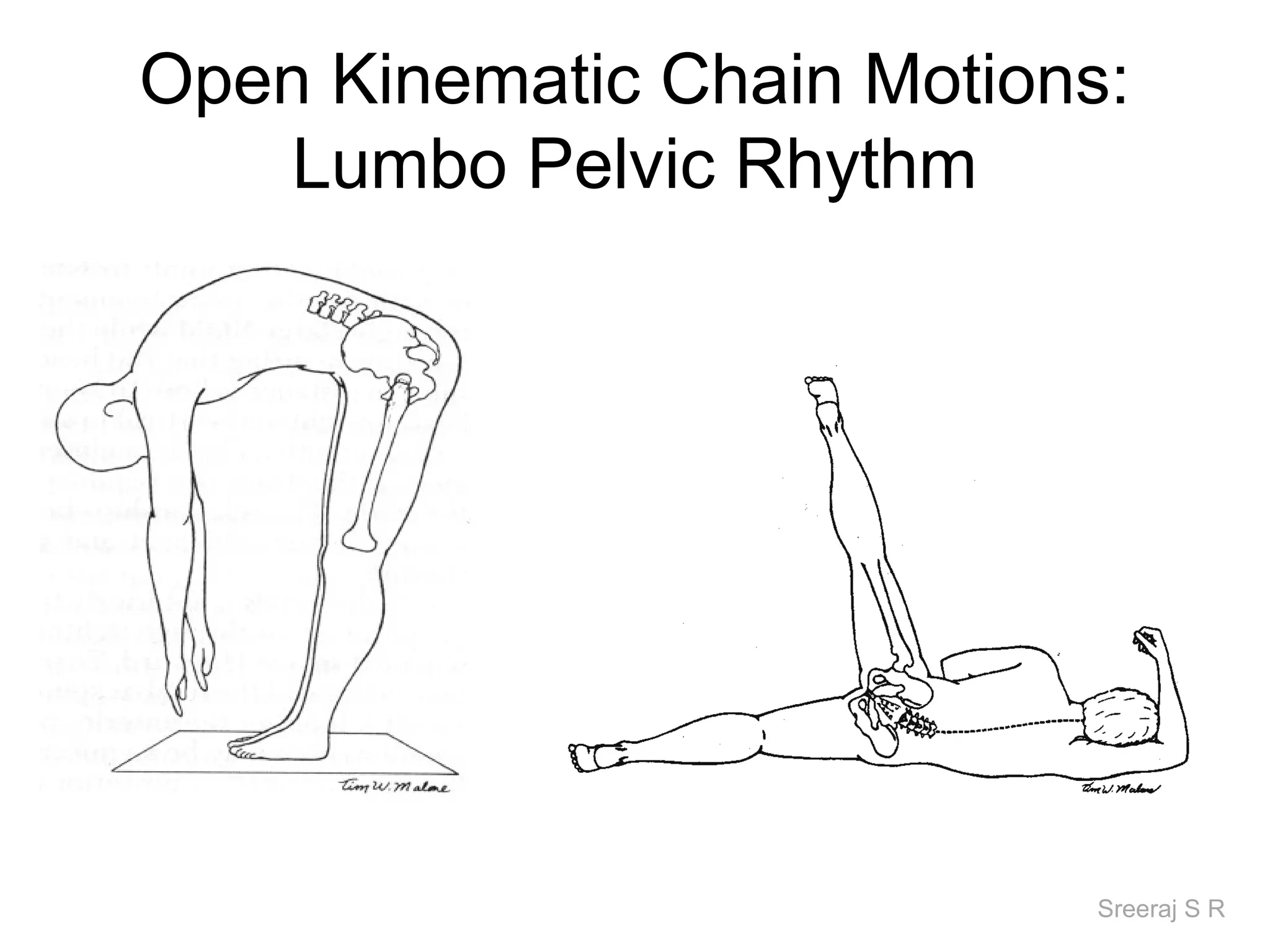
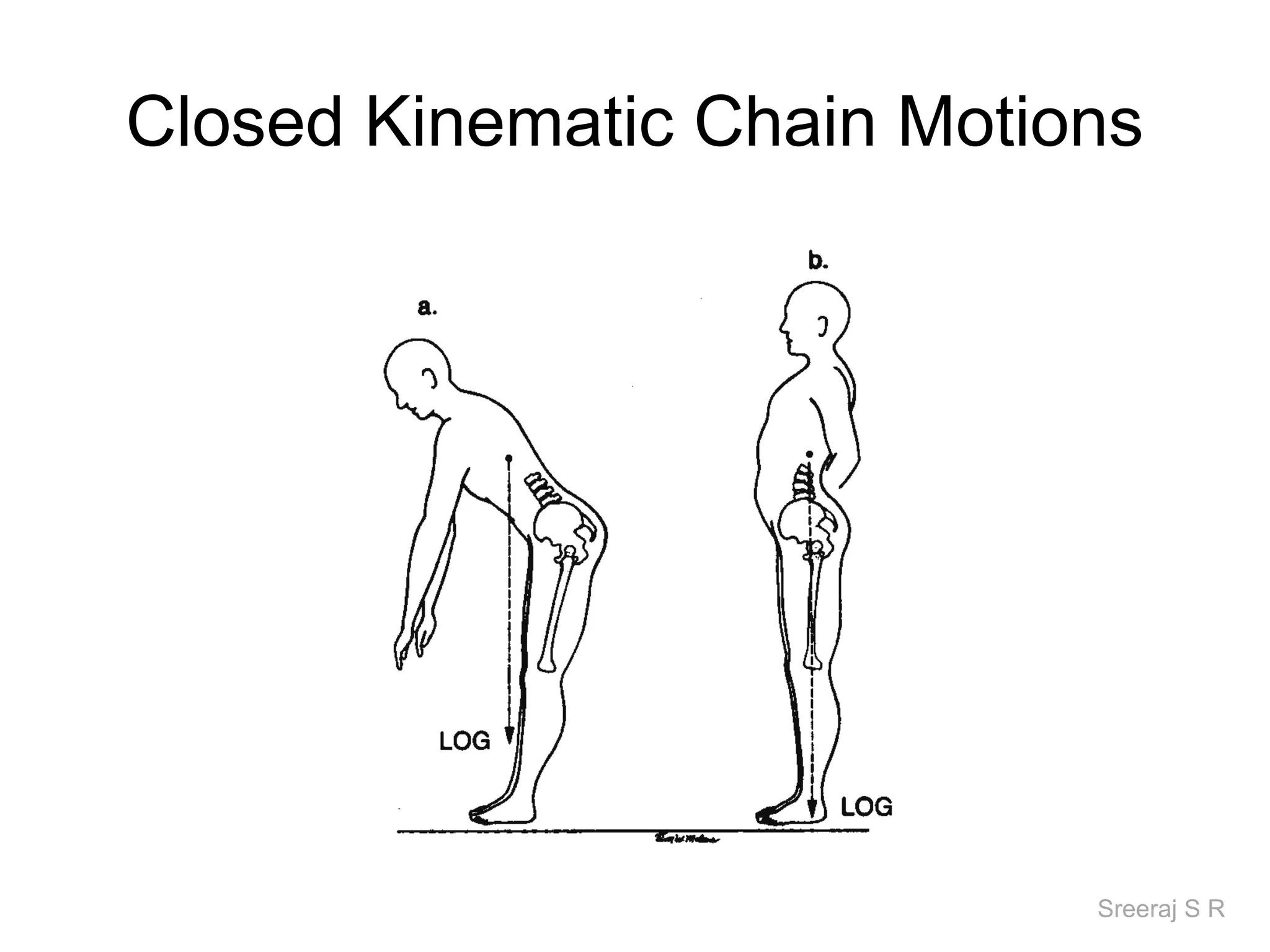
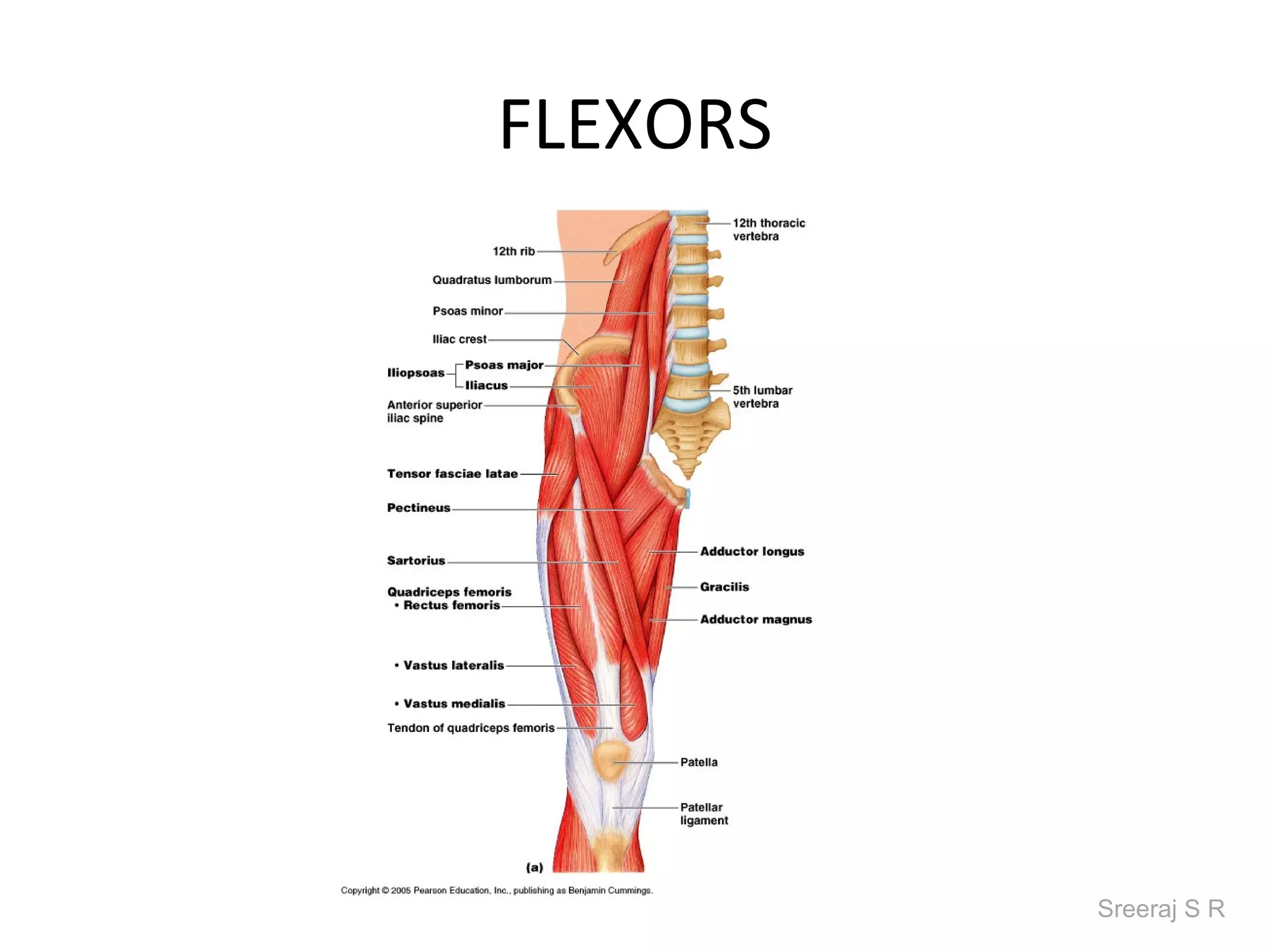
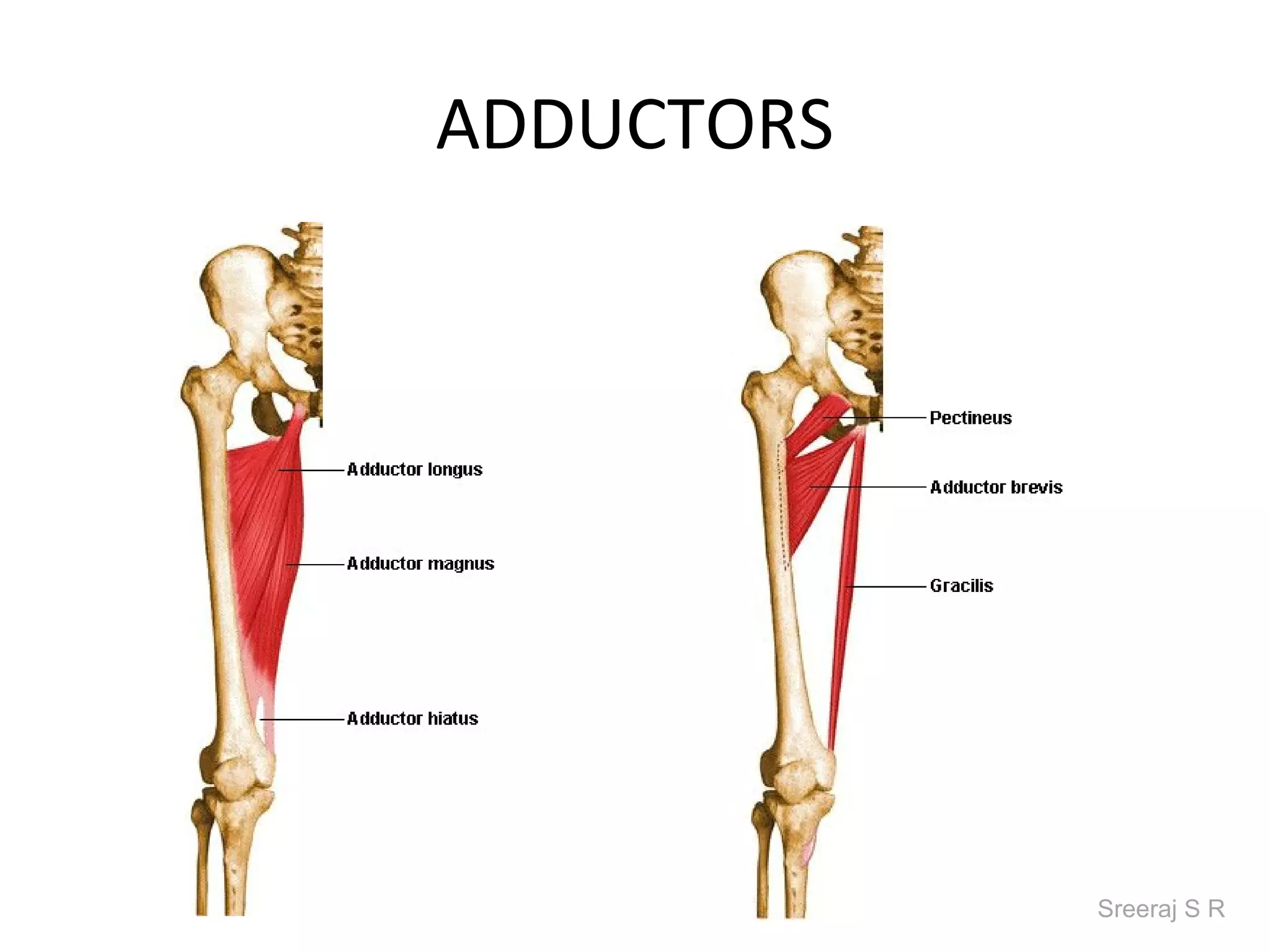
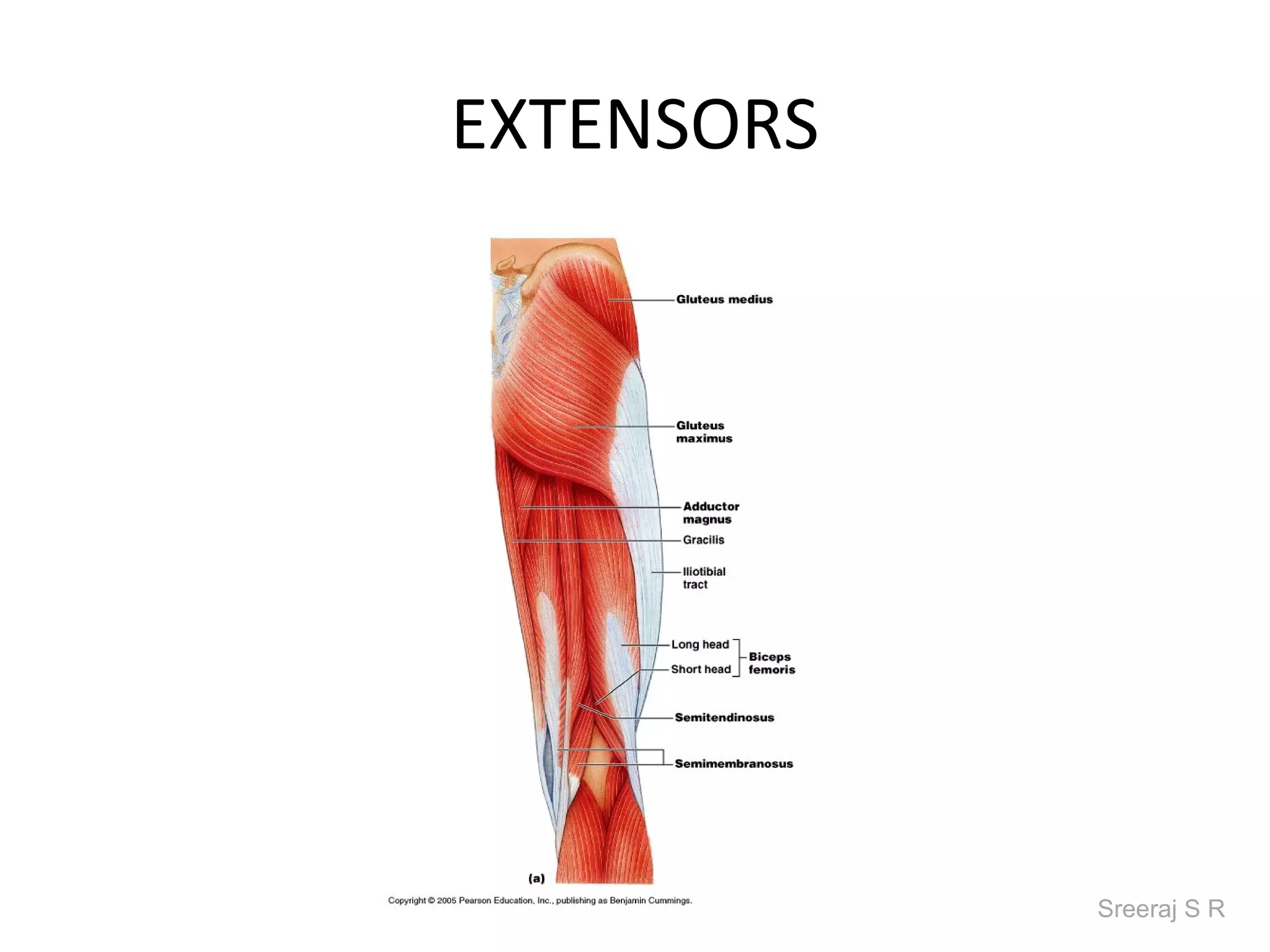
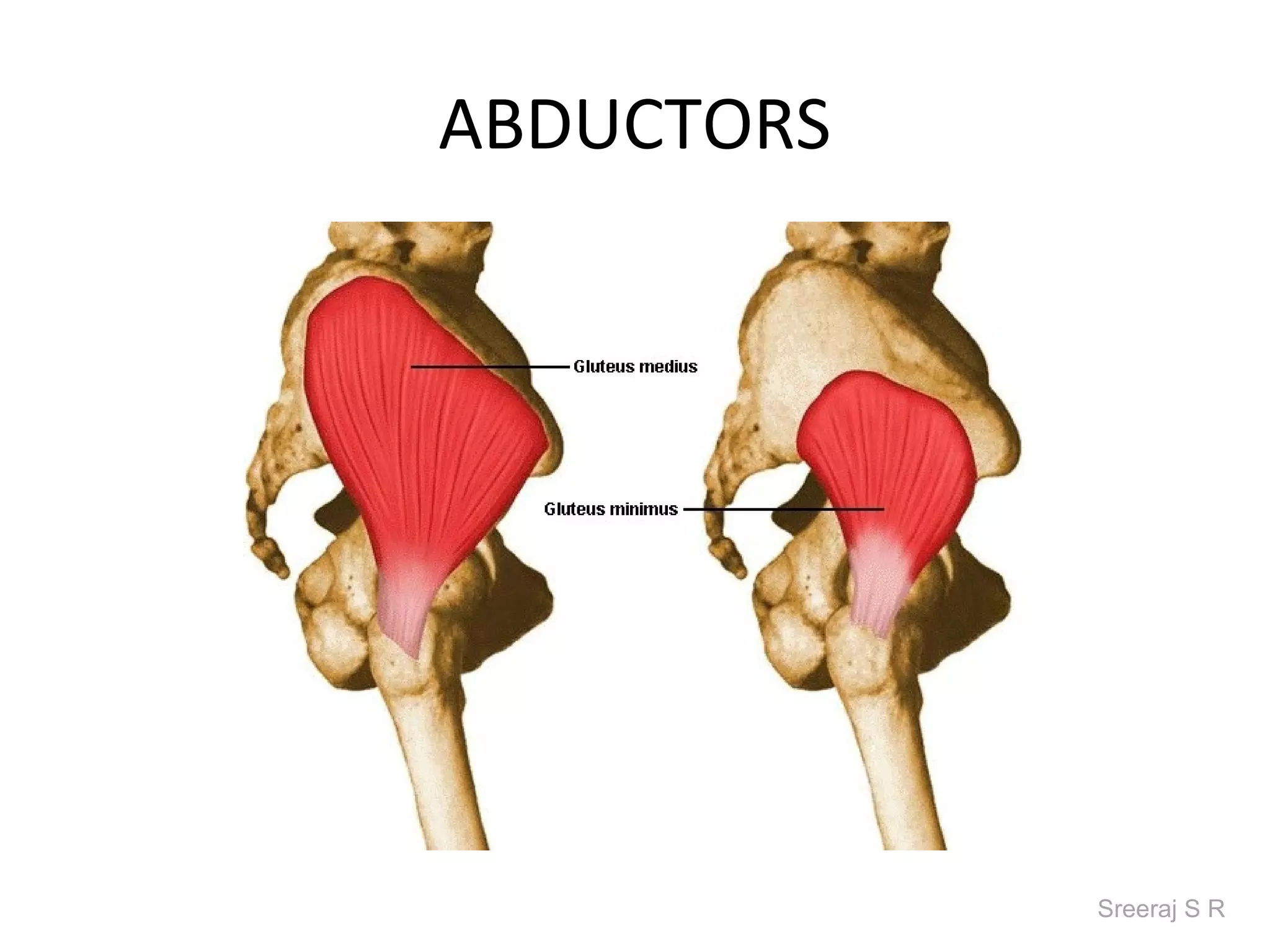
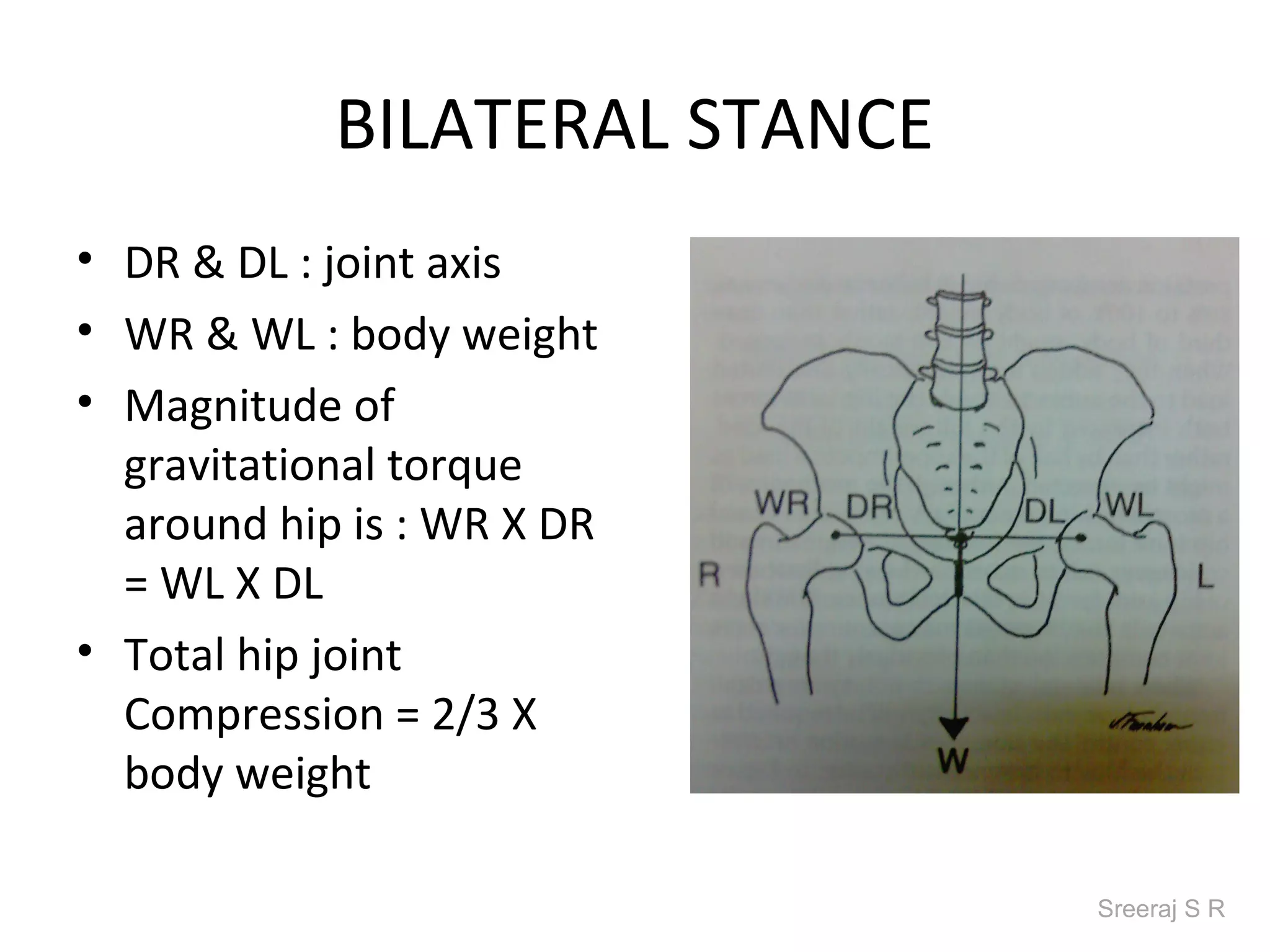
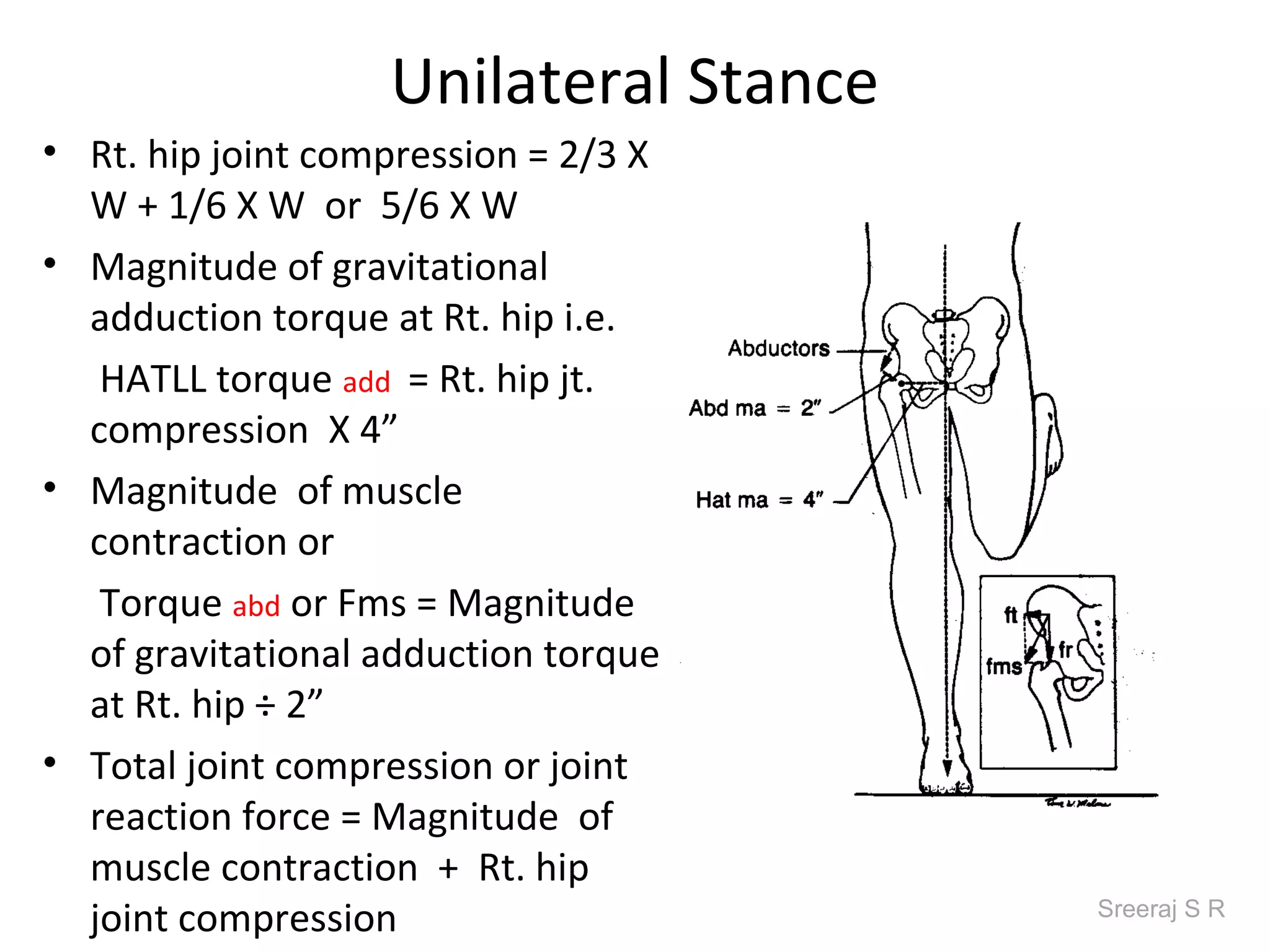
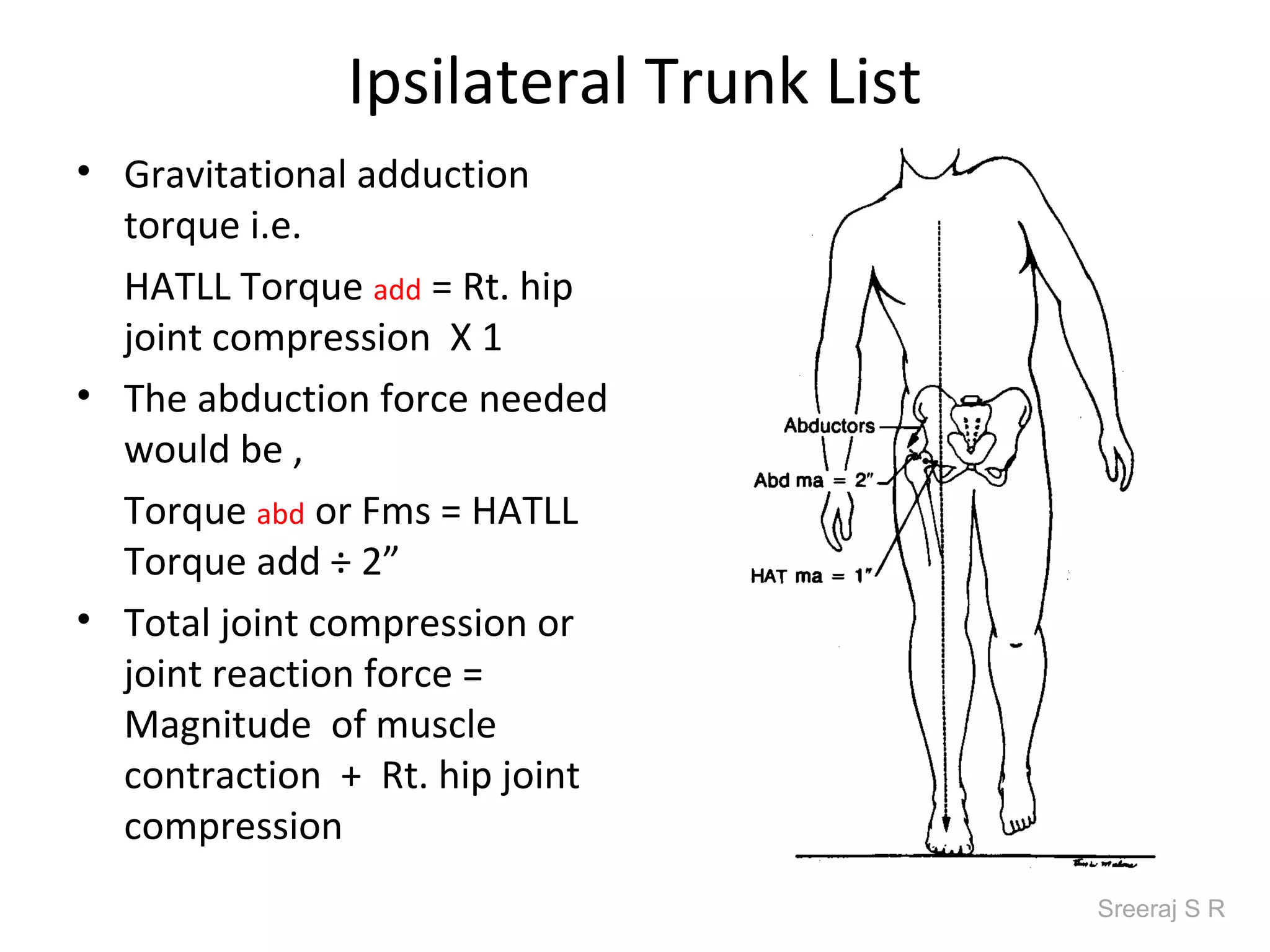
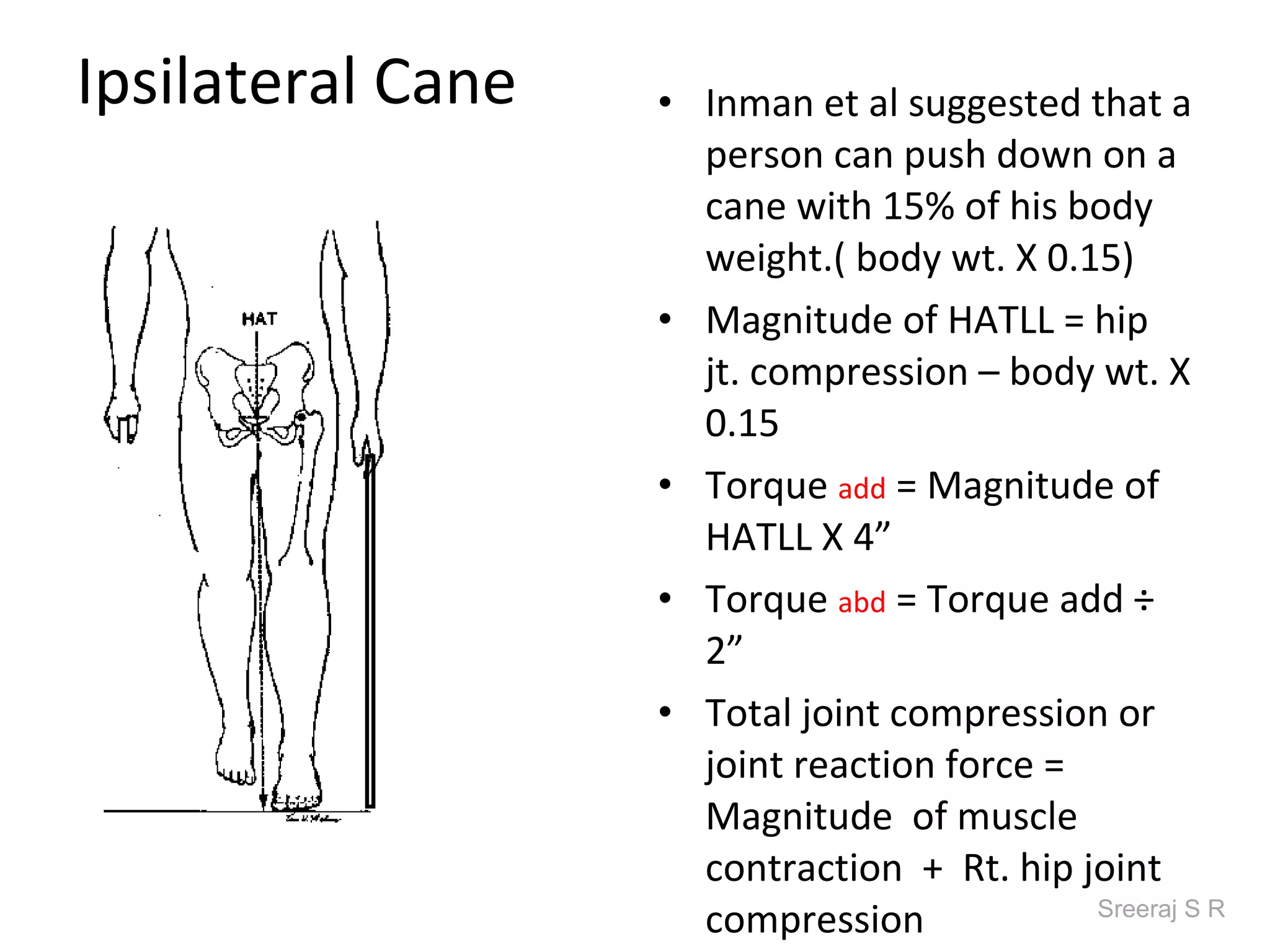
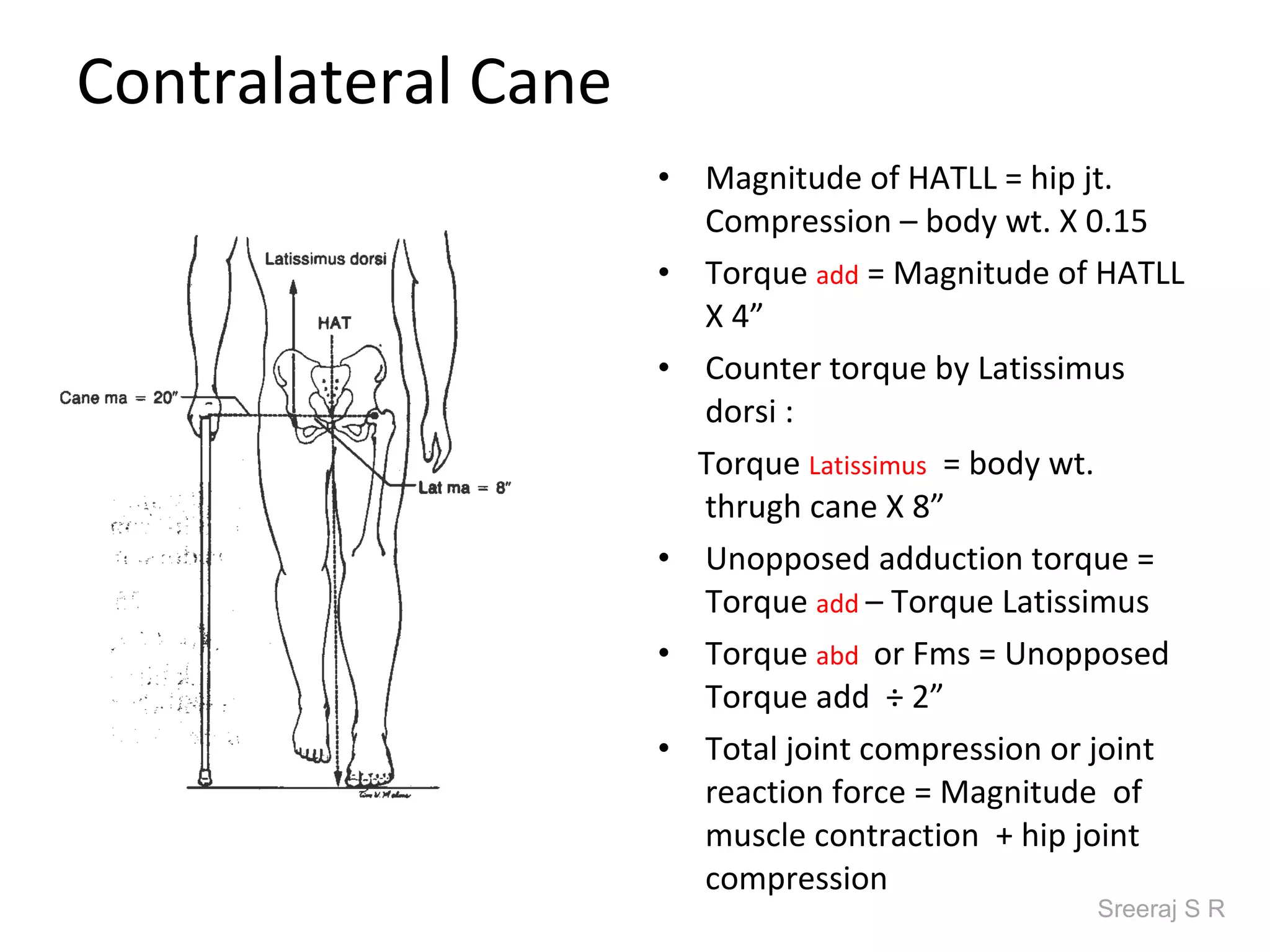
The document discusses the biomechanics of the hip complex, including its articulations, angles, ligaments, musculature, and kinematics. Key points include descriptions of the proximal and distal articular surfaces, angles of inclination and torsion, capsular ligaments, weight bearing structures, and osteokinematics of the femur and pelvis during motions like flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation. Gait and stance mechanics are analyzed, such as bilateral stance, unilateral stance, and trunk listing with calculations of joint torques and forces.