Embed presentation
Downloaded 1,936 times








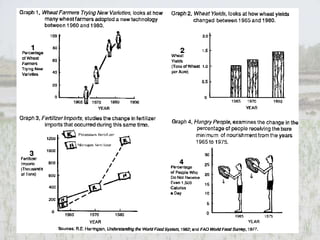








The Green Revolution in India aimed to address food shortages through high-yielding crop varieties that required intensive chemical use. This transition from traditional to industrial agriculture had significant social, political, and environmental consequences. It increased tensions by prioritizing large farms, exacerbating inequalities. Over-application of chemicals degraded soils while dependence on external inputs rose. Ultimately, declining returns sparked unrest among small farmers and added to regional ethnic/religious conflicts, such as the crisis in Punjab between Sikh farmers and the central government.















