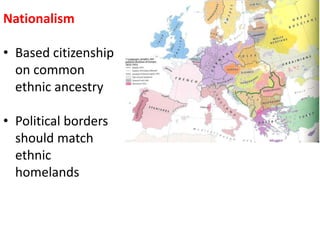
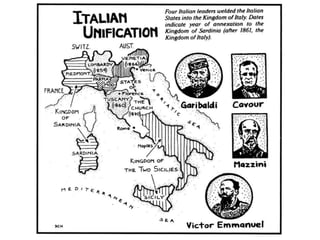
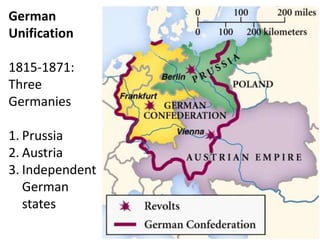
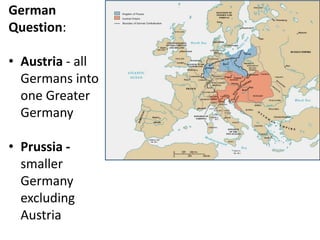
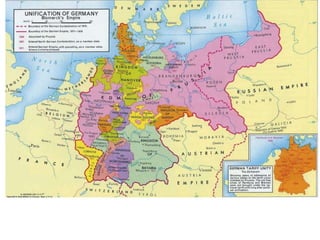
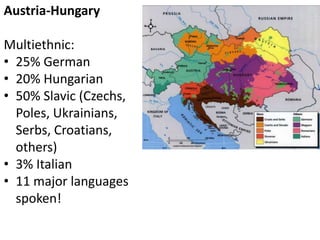
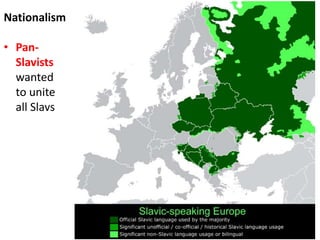
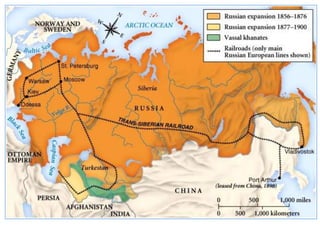
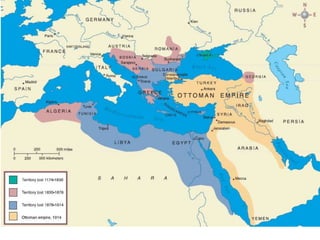
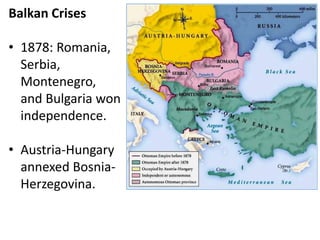
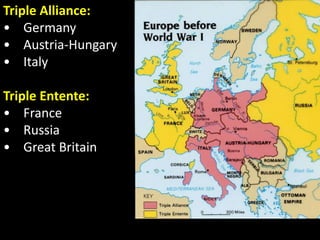
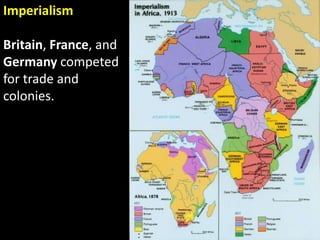
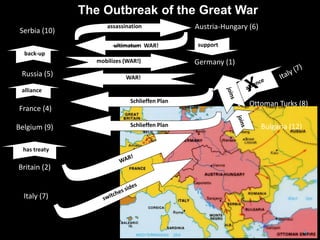
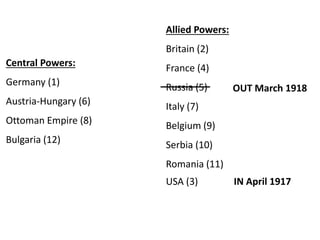
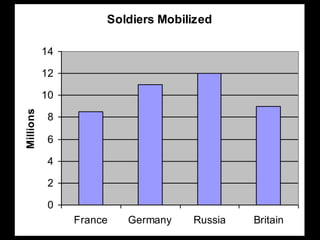
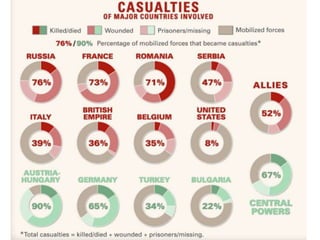
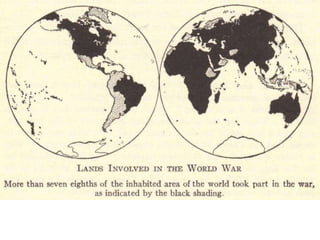
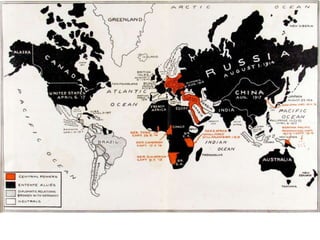
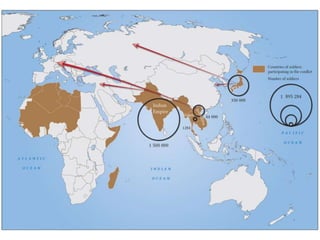
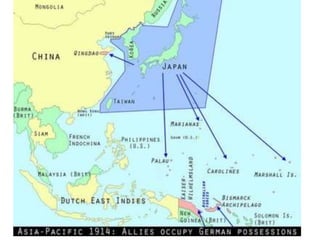
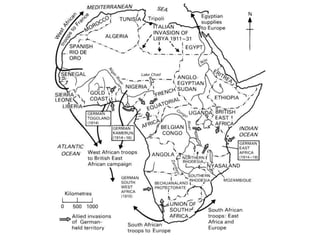
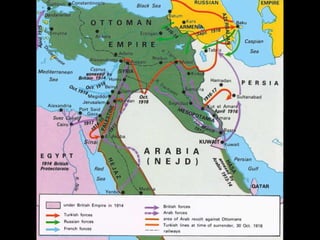
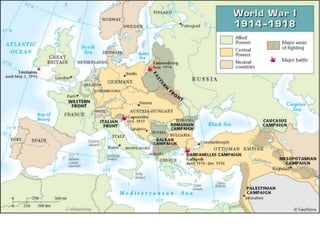
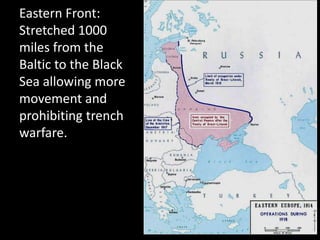
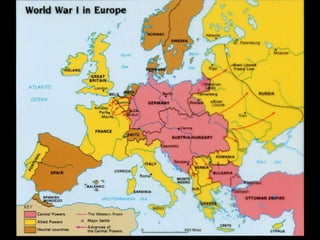
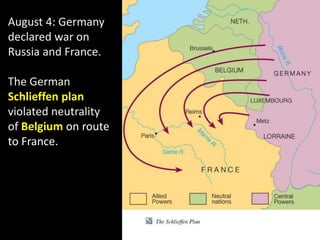
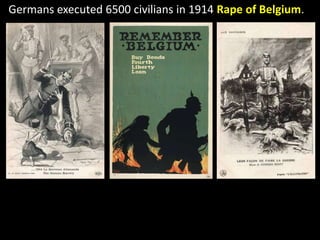
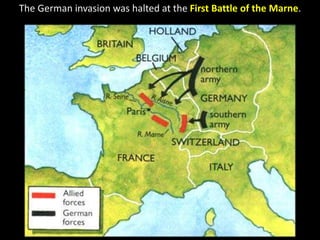
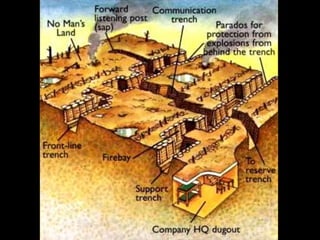
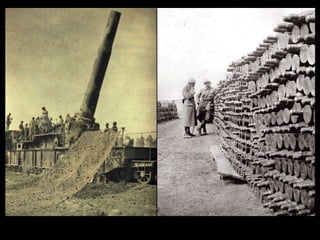
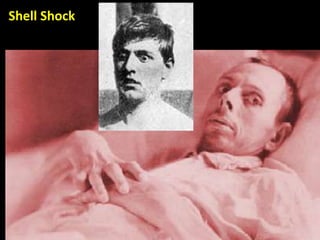
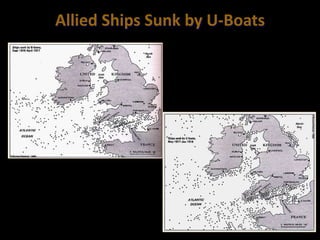
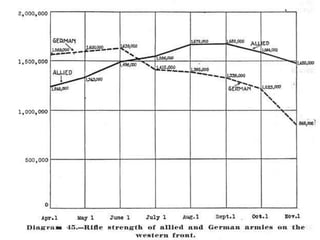
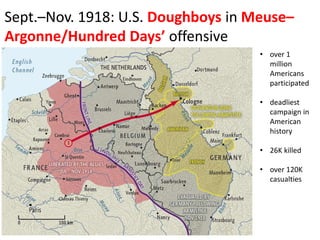
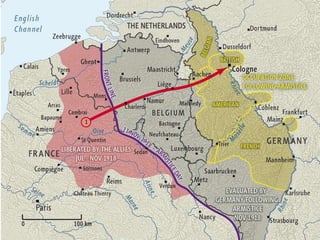
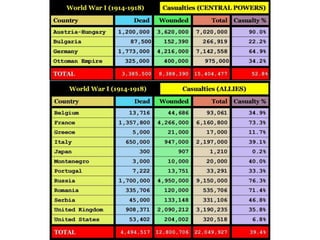
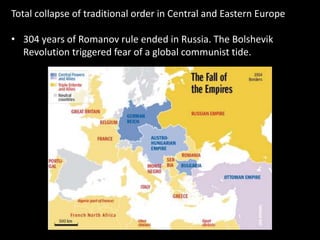
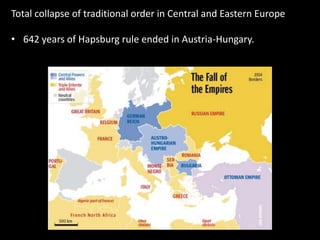
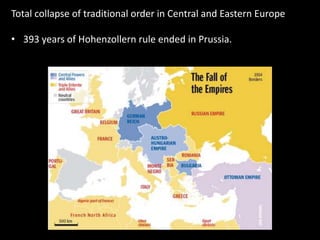
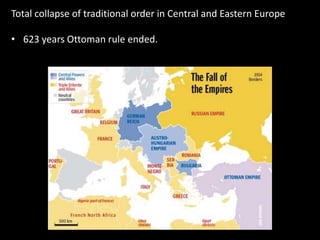
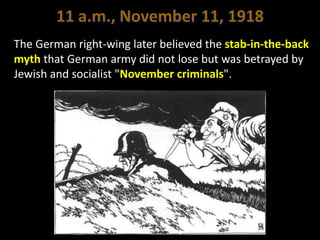
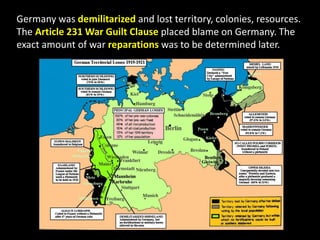
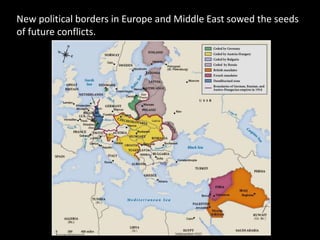
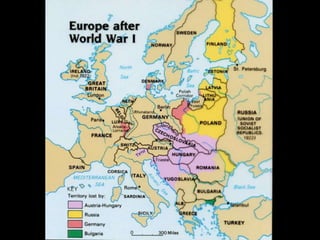
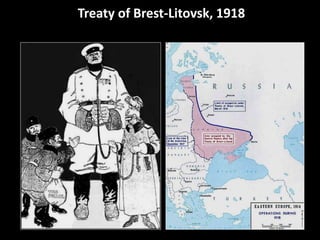
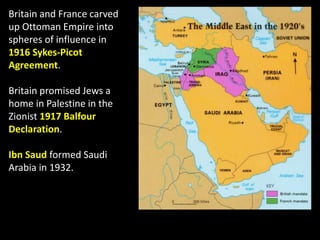
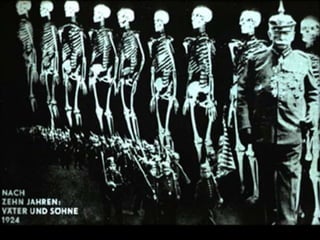
The document summarizes the causes and course of World War 1. It discusses the rise of nationalism, militarism, imperialism and alliances in Europe which contributed to tensions prior to 1914. It then describes the key events that triggered the war, including the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, and outlines the major battles and use of new weapons technology on the Western and Eastern fronts between 1914-1918. It concludes by noting the enormous human and political costs of the war, and how the peace settlement laid the groundwork for future conflicts.