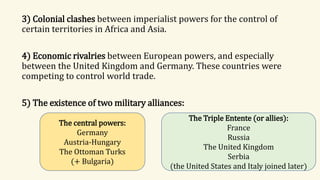
World War I began in 1914 due to increasing tensions between European powers resulting from imperialism, military alliances, and nationalism. The immediate cause was the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary by a Serbian nationalist. This led Austria-Hungary to declare war on Serbia, drawing in allies on both sides through a system of entangling alliances. The war became total war as whole societies were mobilized. It was fought mostly in trench warfare until the United States joined the Allies in 1917, shifting momentum and leading Germany to surrender in 1918. Over 10 million soldiers and civilians lost their lives in the war.