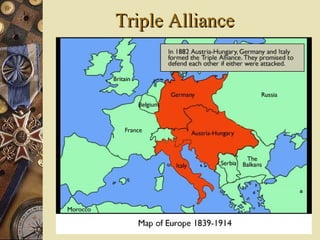
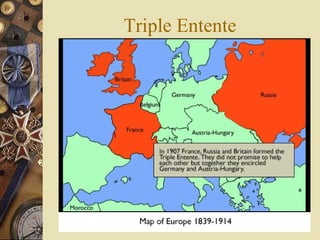
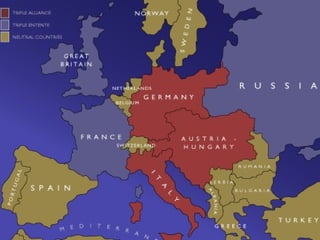
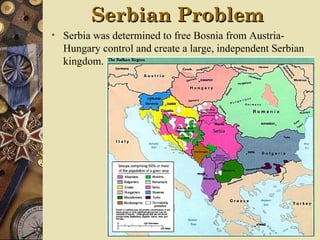
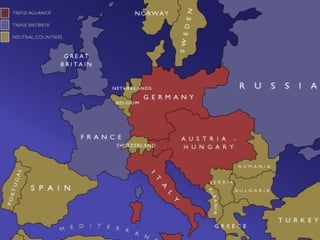
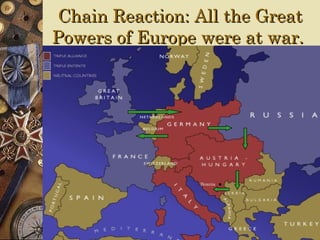
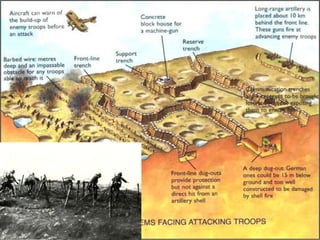
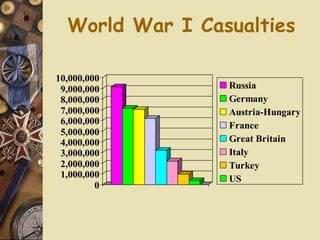
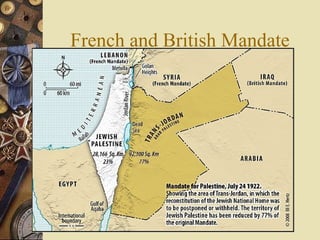
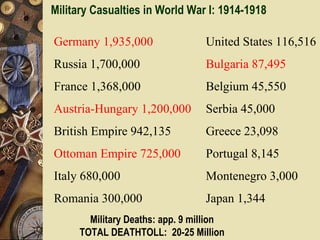
The document provides background information on World War I and its aftermath. It discusses the various causes of WWI, including nationalism, militarism, and alliances. It then describes how the assassination of Archduke Ferdinand led countries to take sides and declare war on each other. The war resulted in millions of casualties and heavy fighting in trenches. After huge costs, the war ended in 1918 and led to the restructuring of Europe and collapse of empires. The Treaty of Versailles imposed punishments on Germany but was ultimately unsatisfying and contributed to tensions.