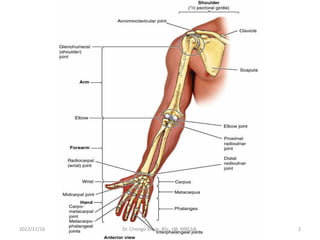
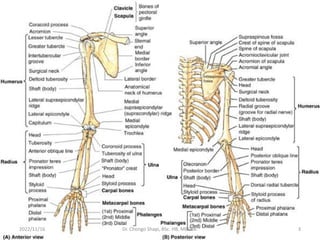
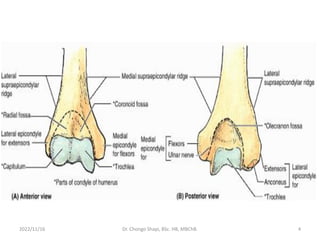
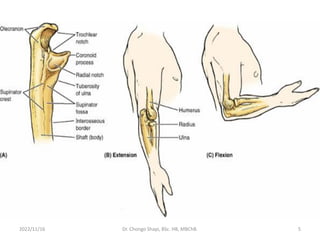
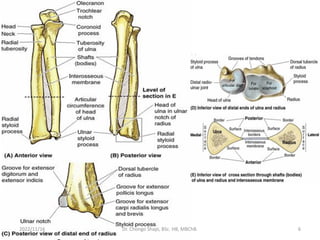
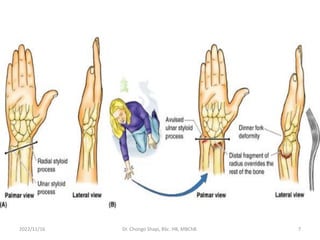
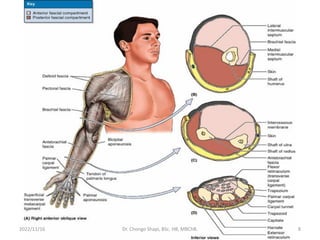
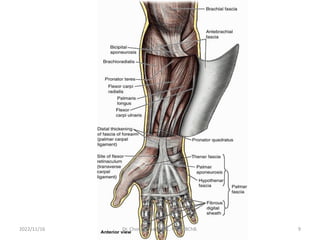
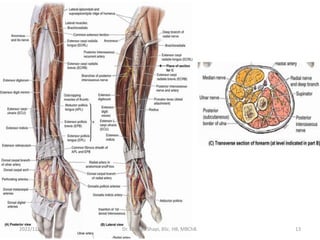
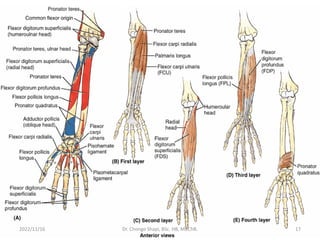
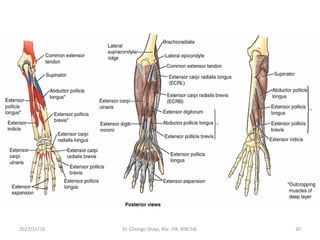
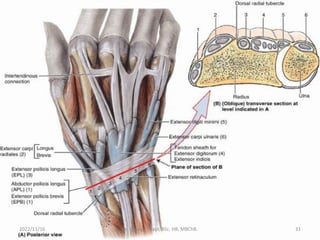
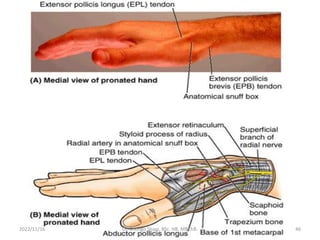
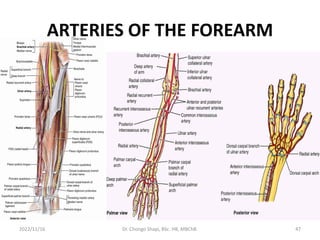
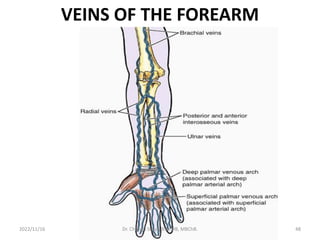
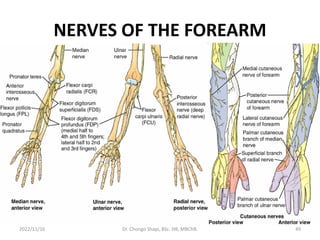
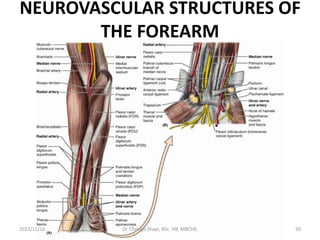
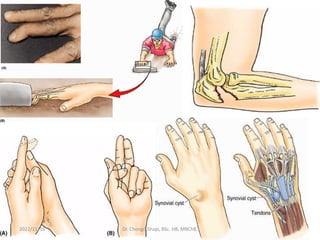
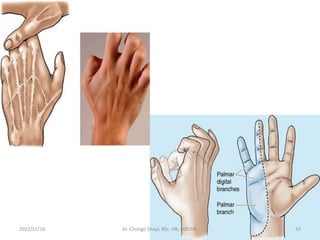
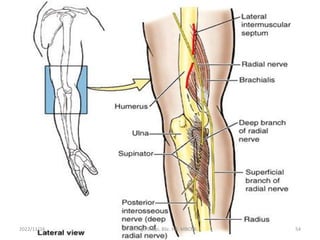
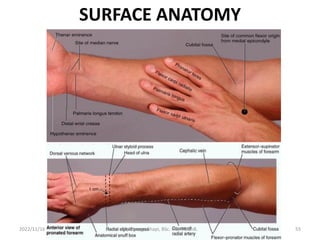
The document provides a detailed overview of the anatomy of the forearm, including the functions and divisions of flexor and extensor muscles. It discusses specific muscles involved, their movements, innervation, and testing procedures to assess their function. The text highlights the significance of anatomical structures in surgical considerations and functional activities of the upper limb.