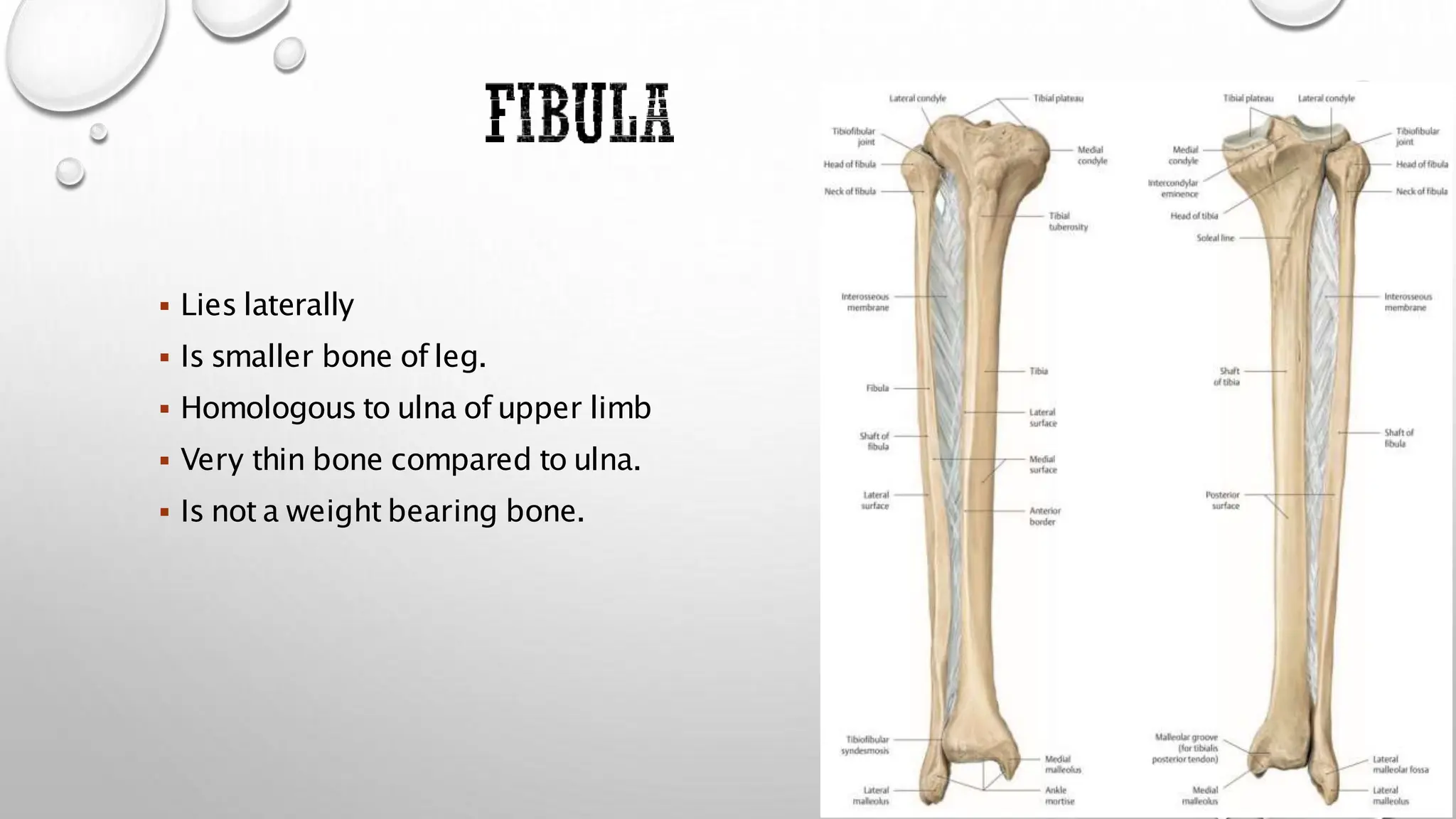
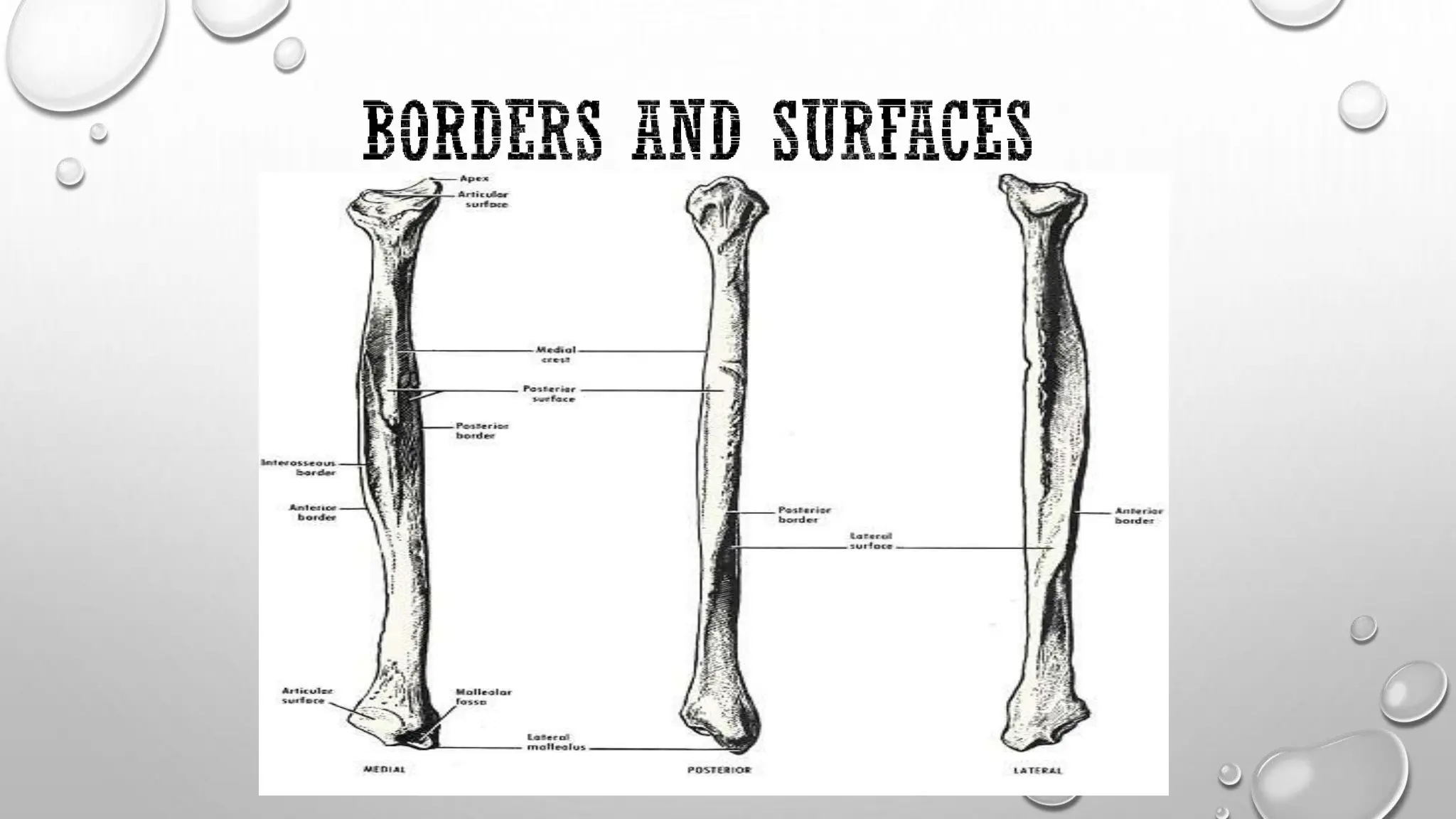
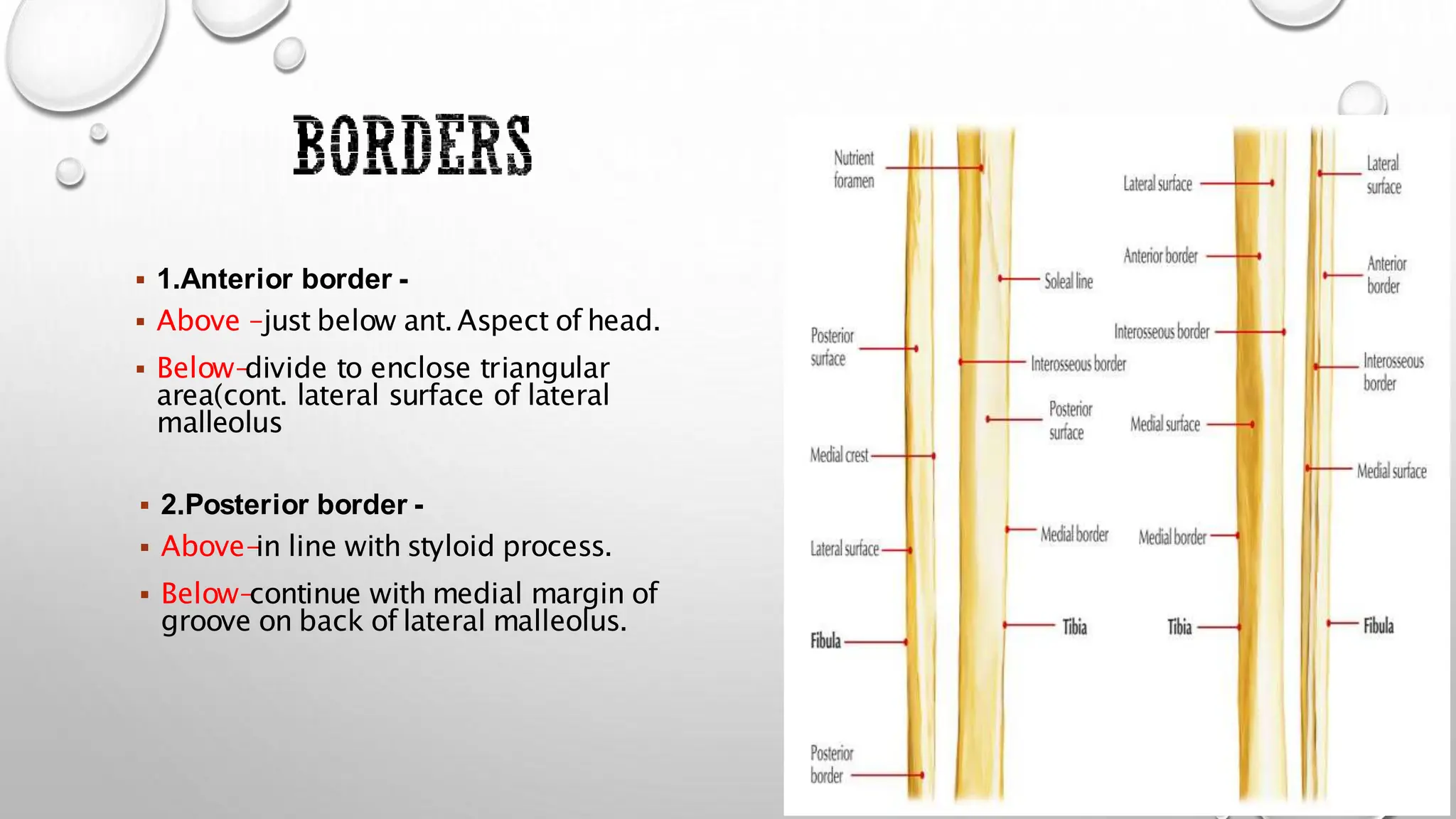
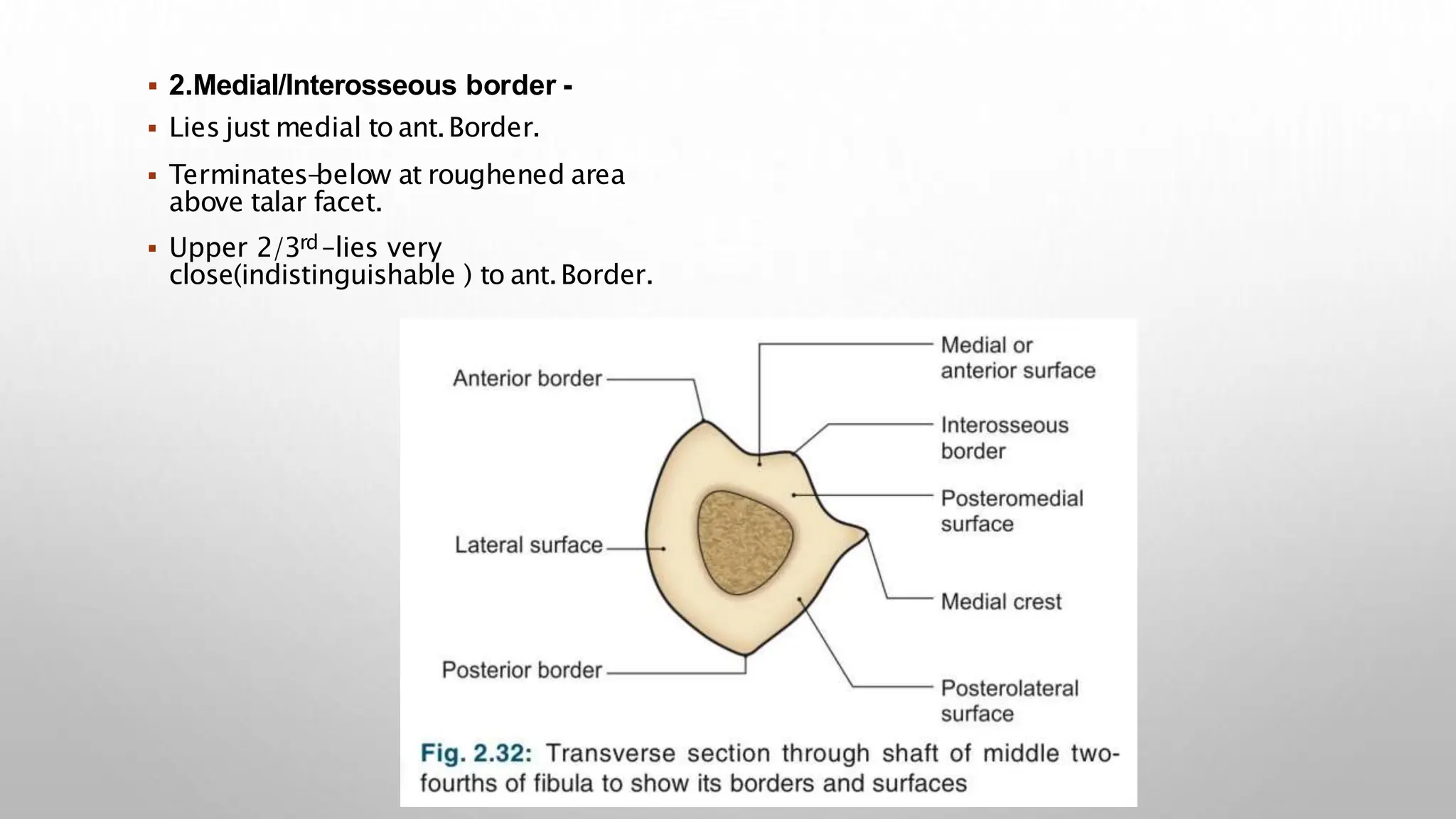
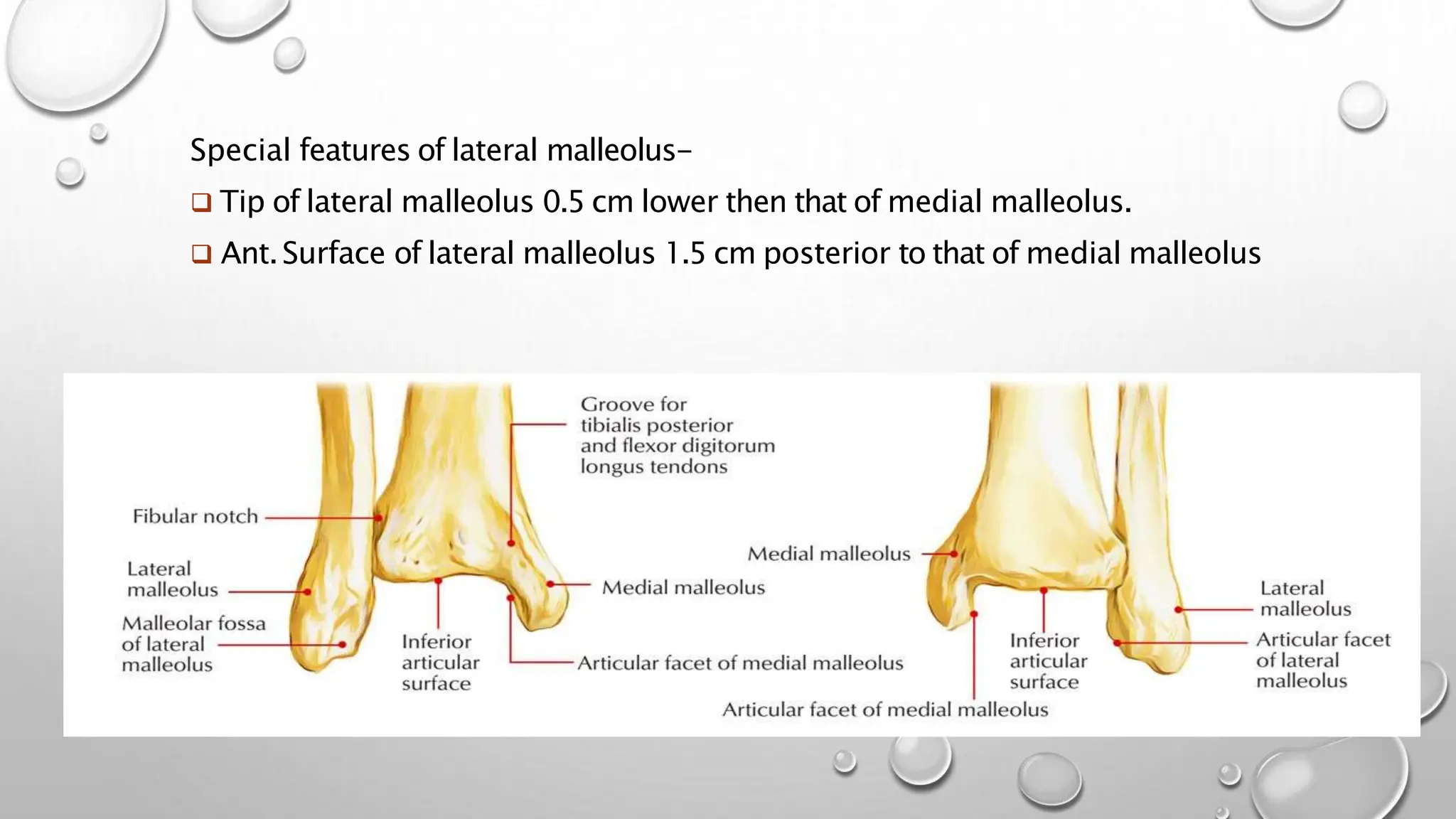
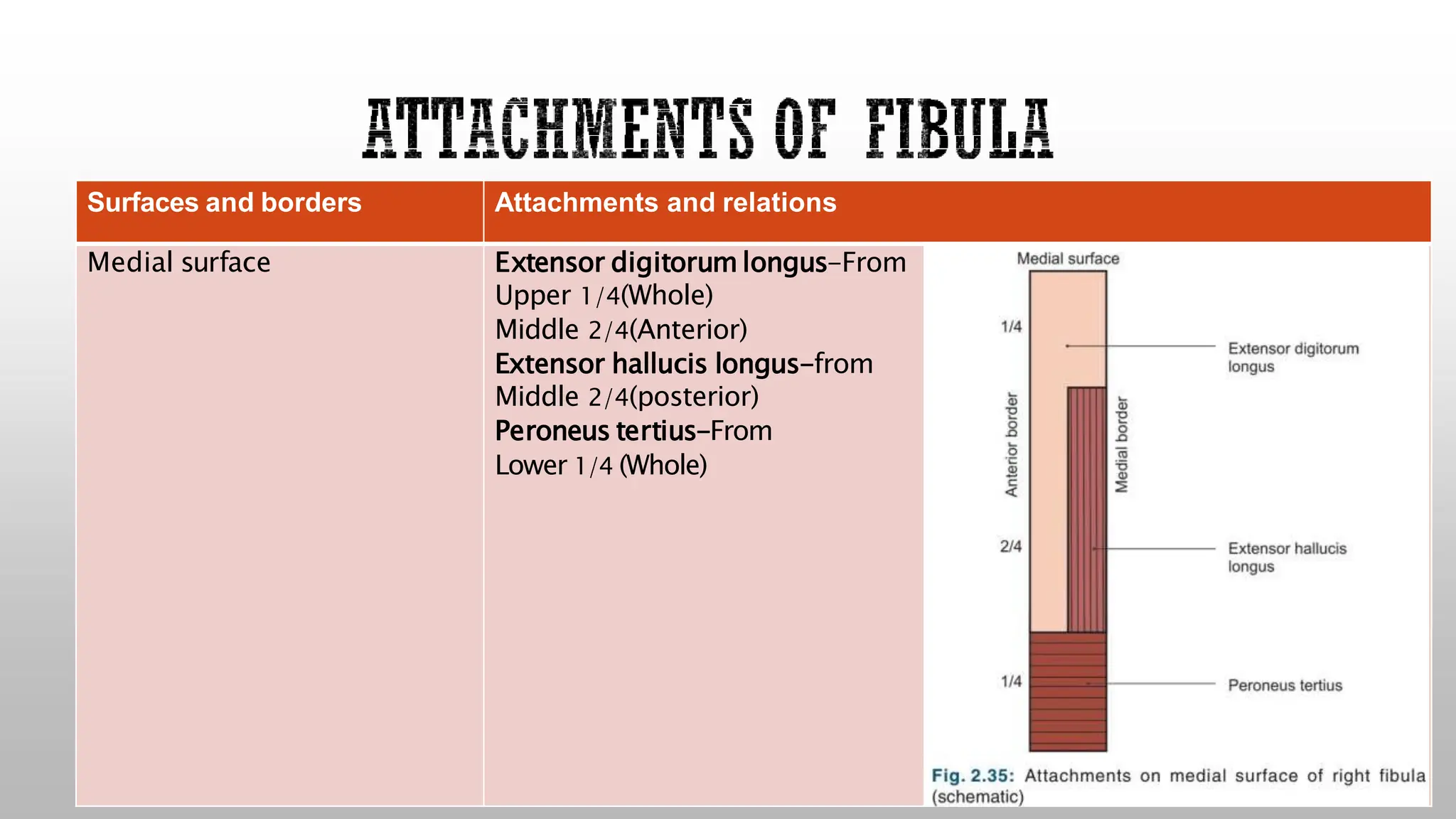
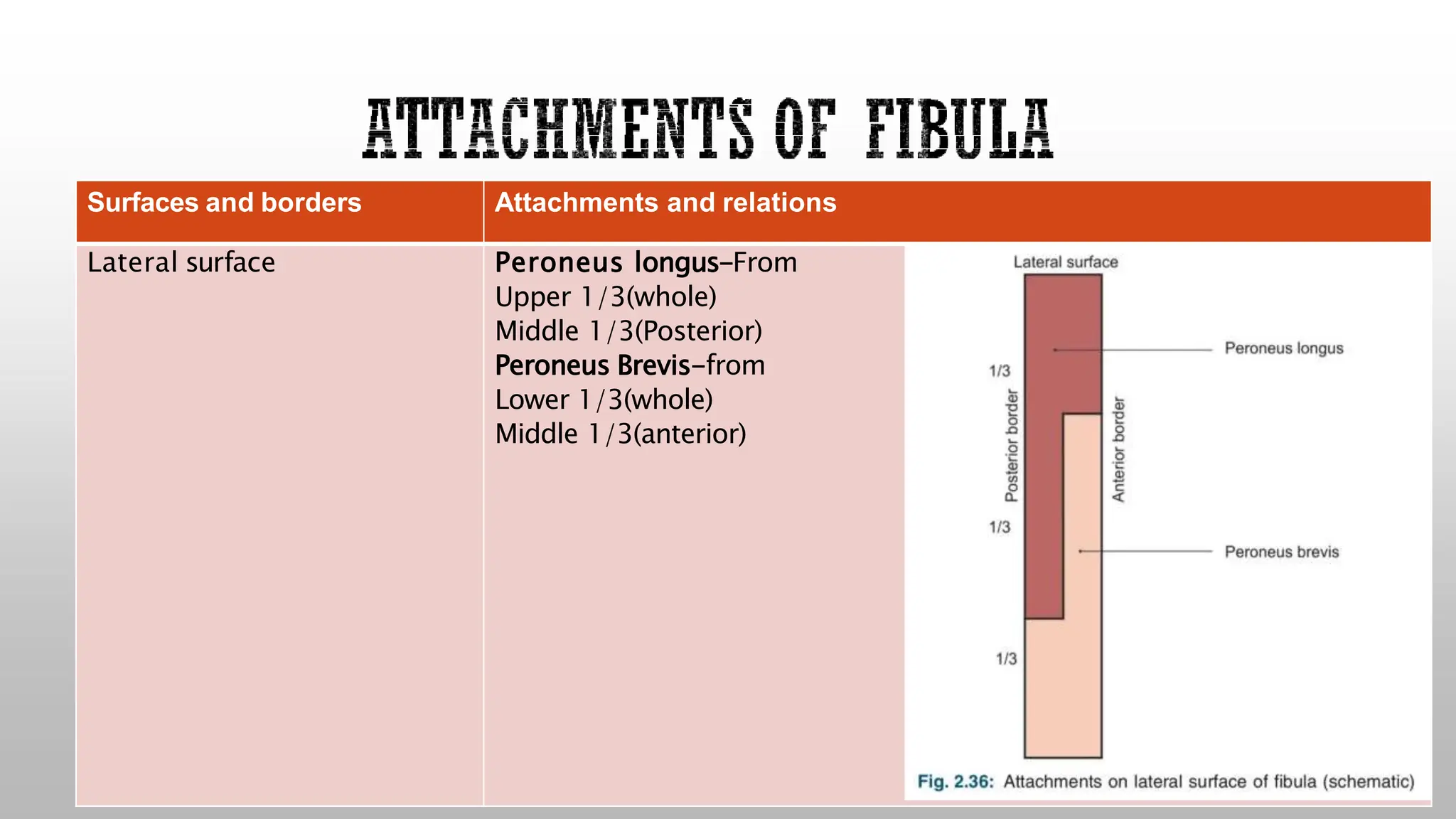
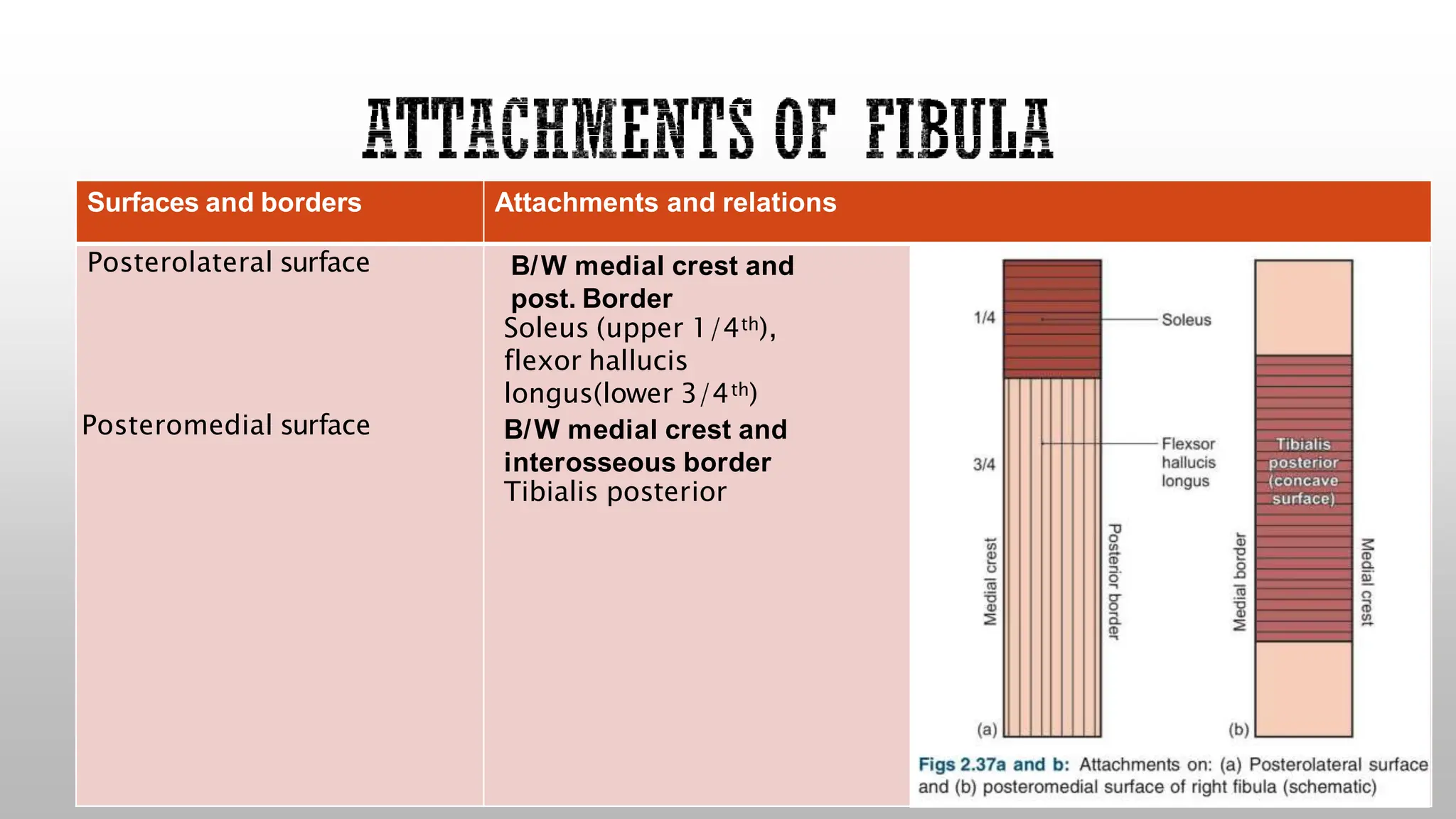
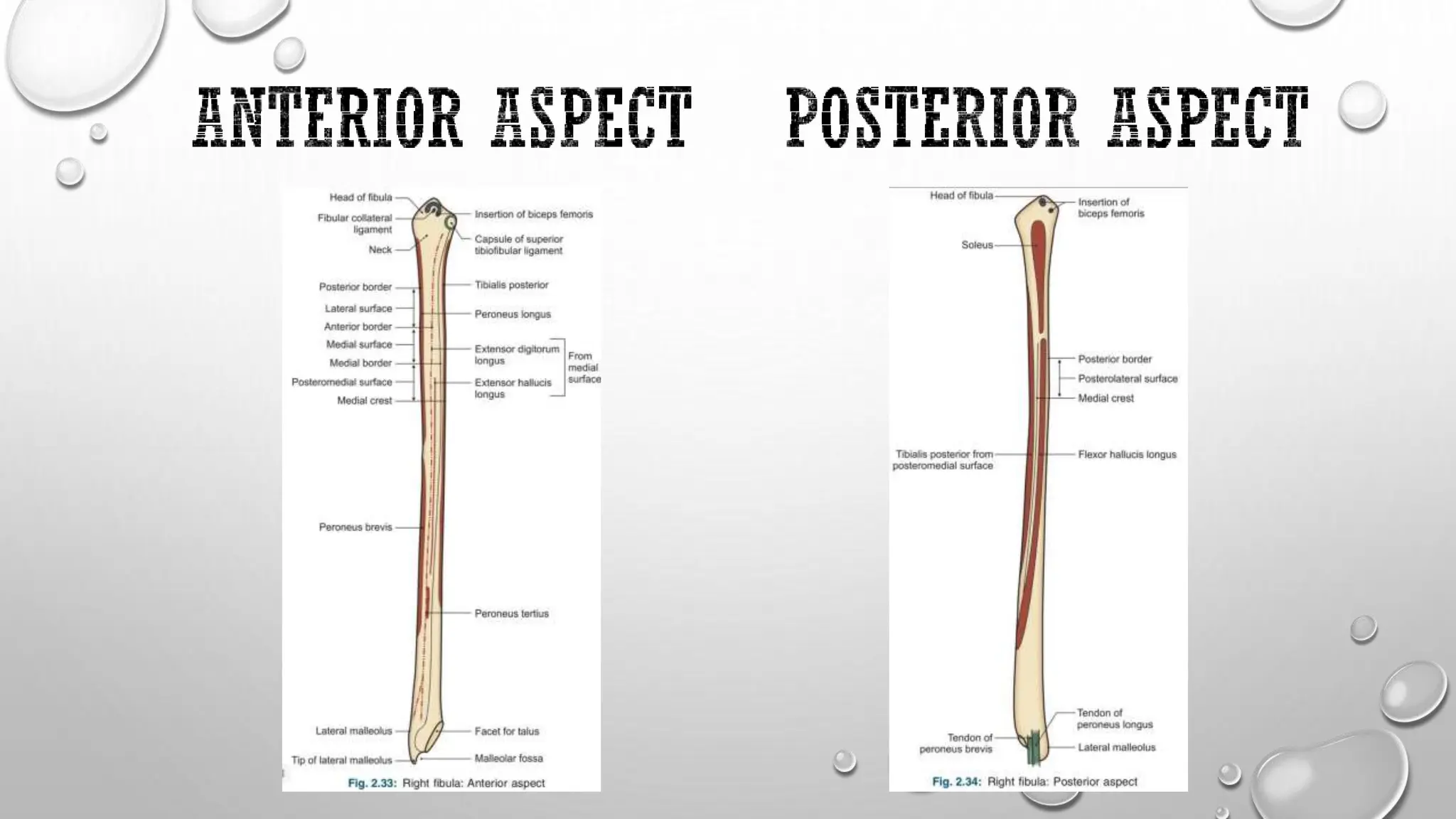
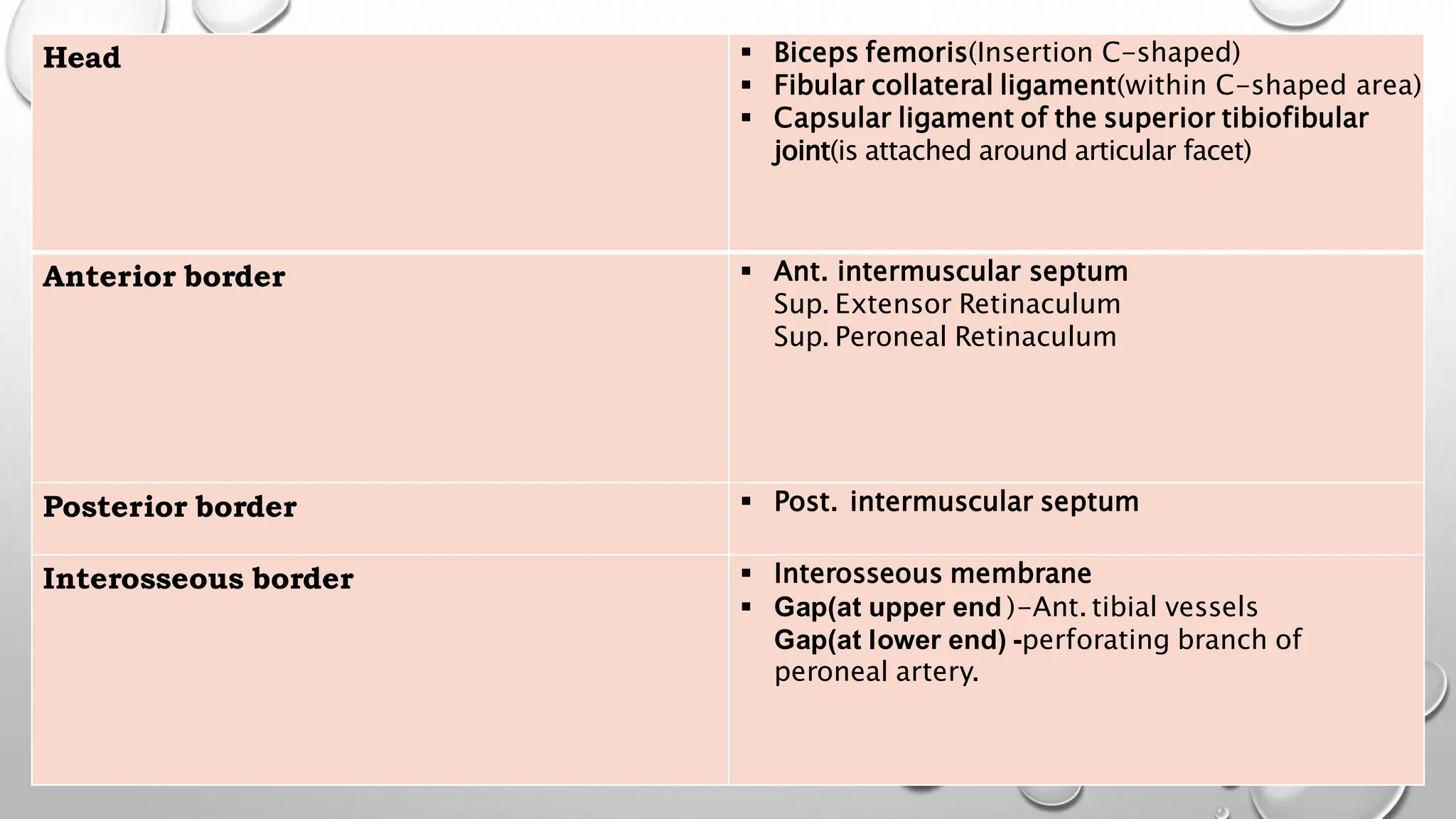
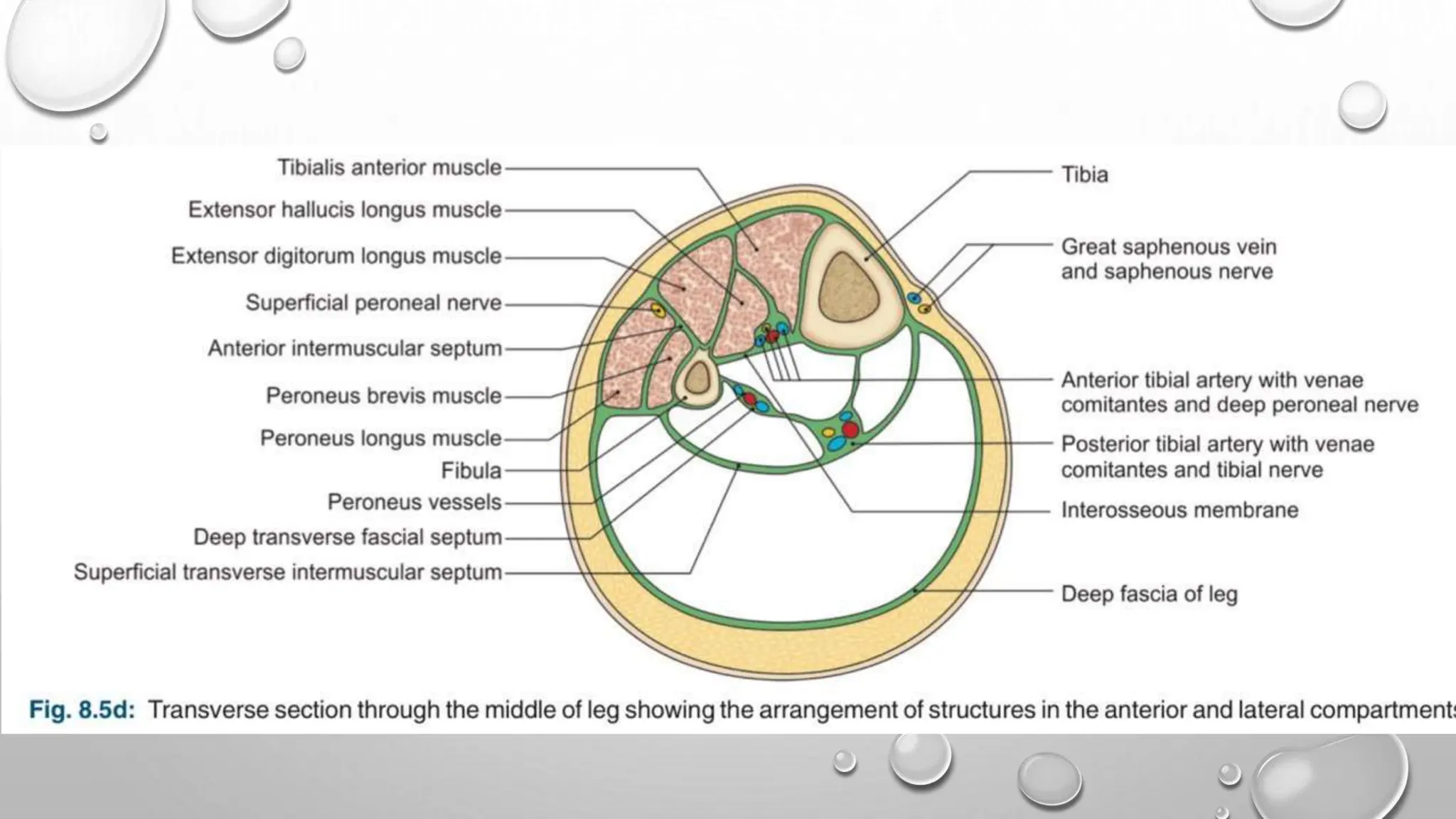
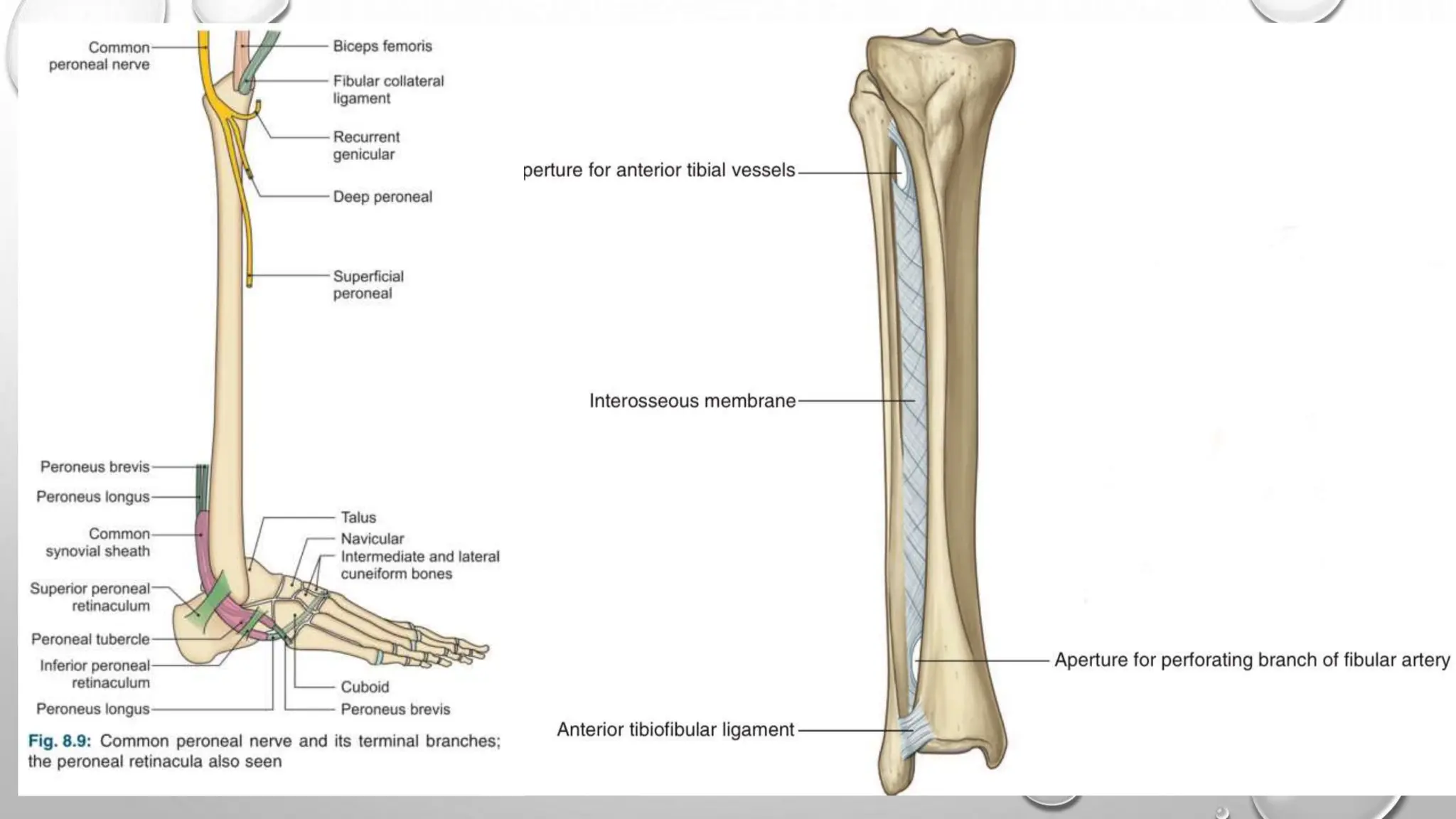
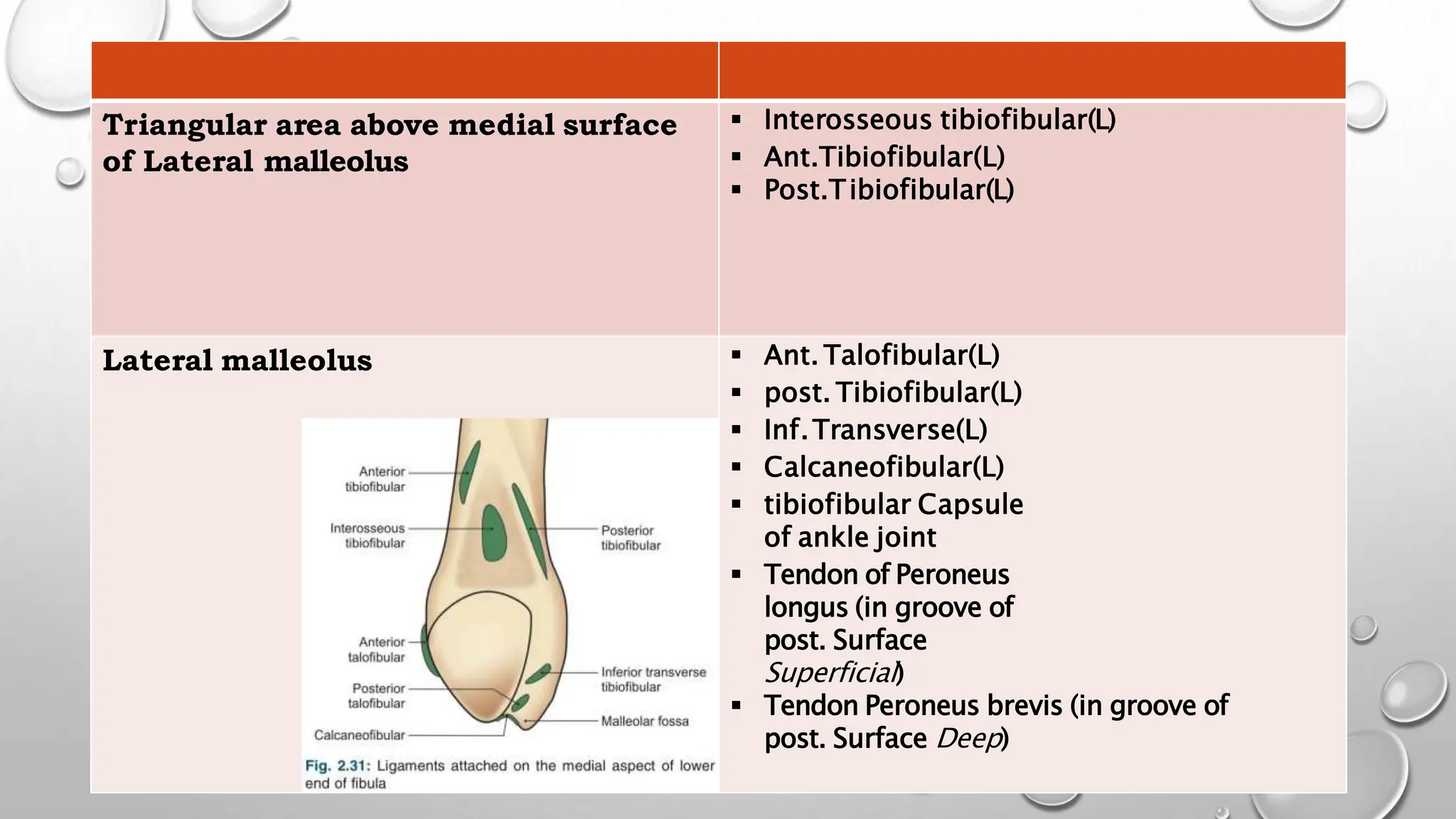
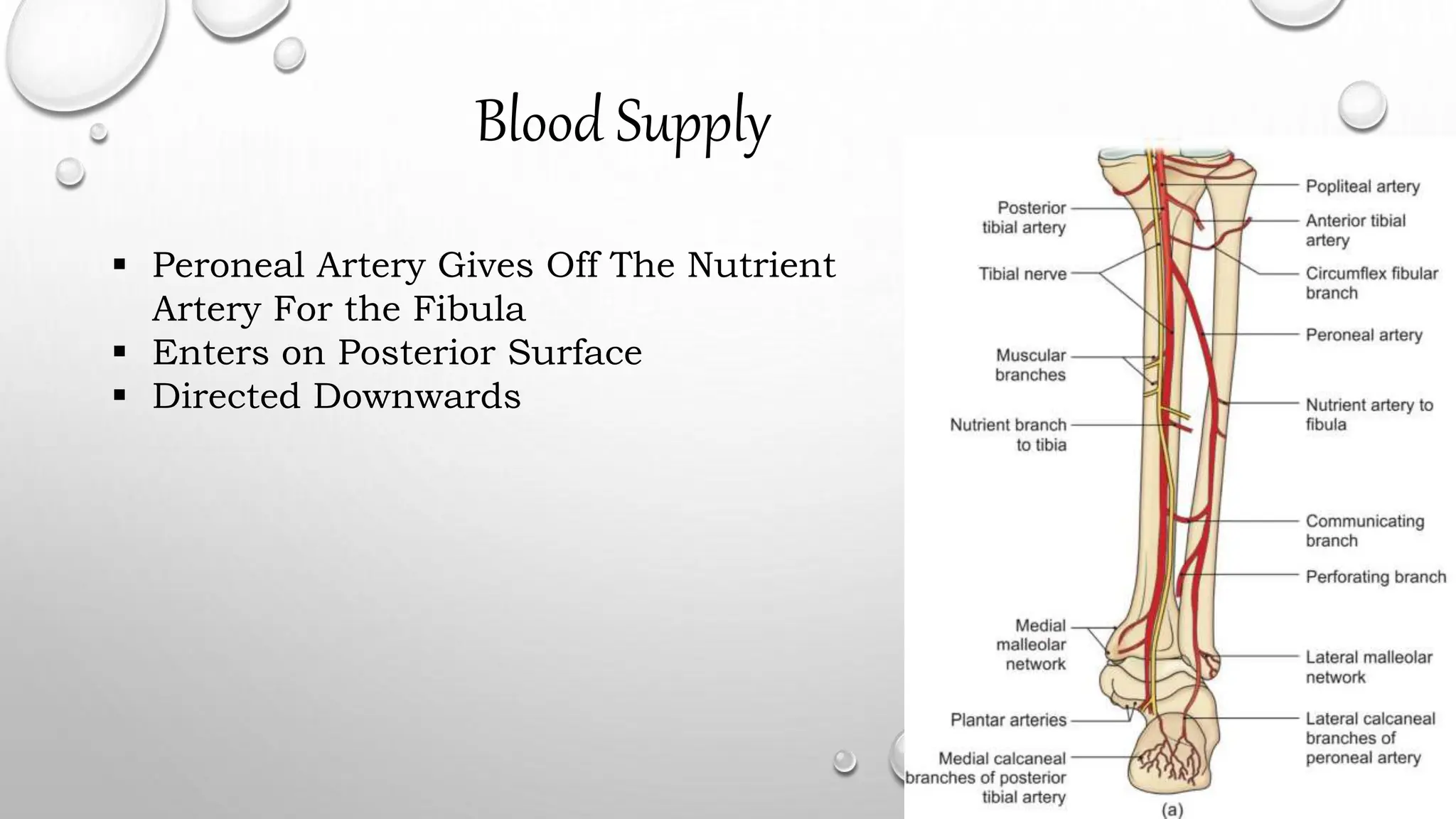
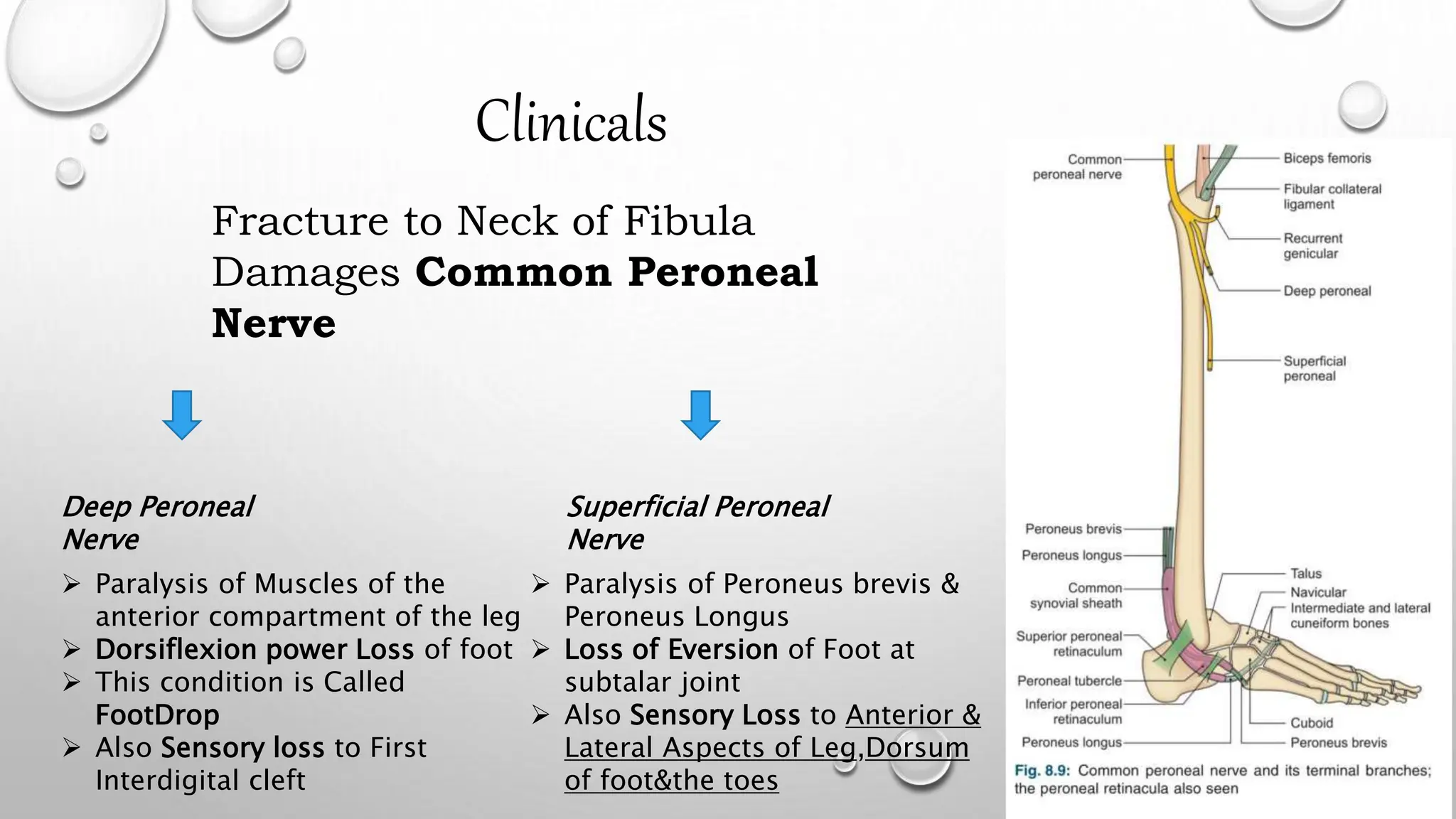
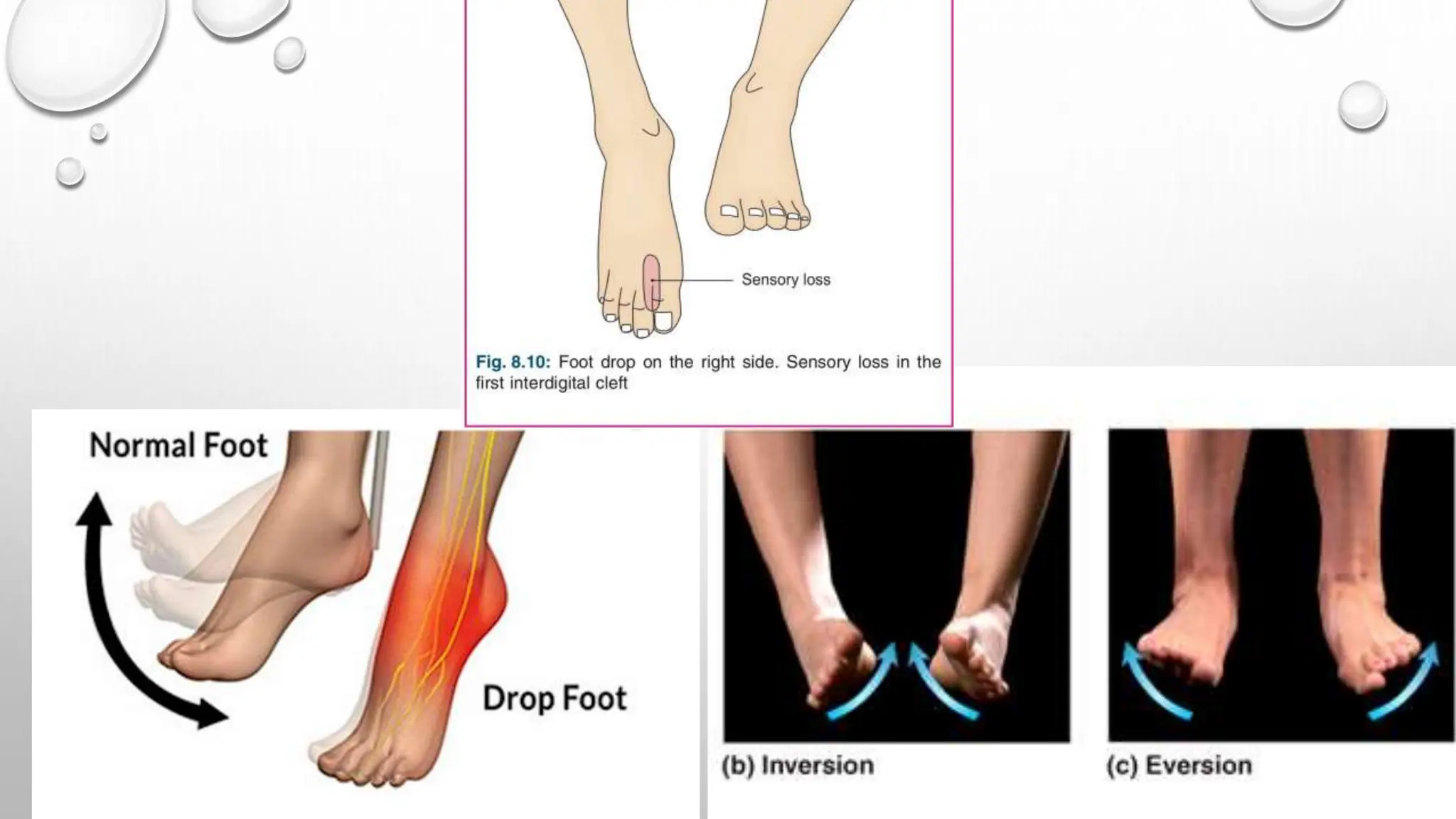
This document summarizes the anatomy of the fibula bone. It identifies the fibula and describes its parts including the head, neck, shaft, and lower end. It discusses the borders and surfaces of the fibula and how to determine its side. The document outlines the attachments of ligaments and muscles to the fibula including the peroneal muscles. It also provides clinical notes on fractures to the fibula neck damaging the common peroneal nerve and resulting in foot drop.