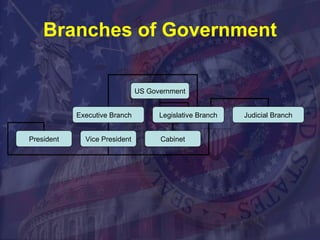
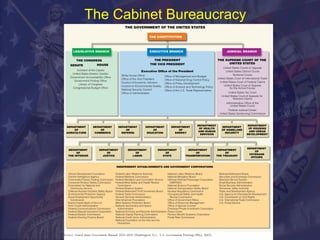
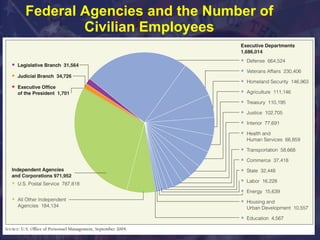
The document discusses the roles and powers of the President and executive branch, including the President's roles as chief of state, diplomat, executive, legislator, commander-in-chief, and party leader. It also covers the Vice President, Cabinet, and various executive agencies. The size of the federal bureaucracy is discussed, with over 2.7 million civilian employees working across different departments and agencies.