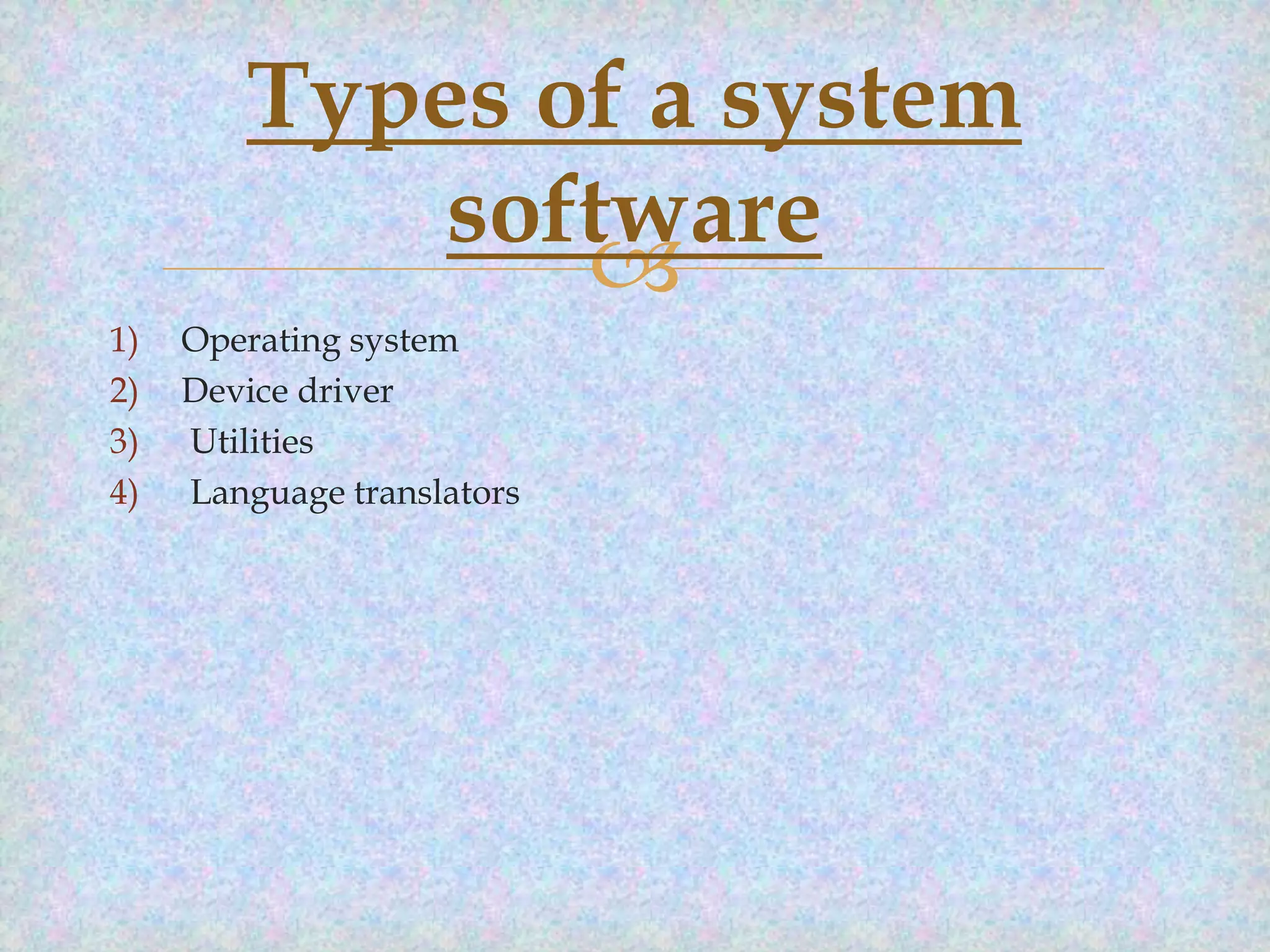
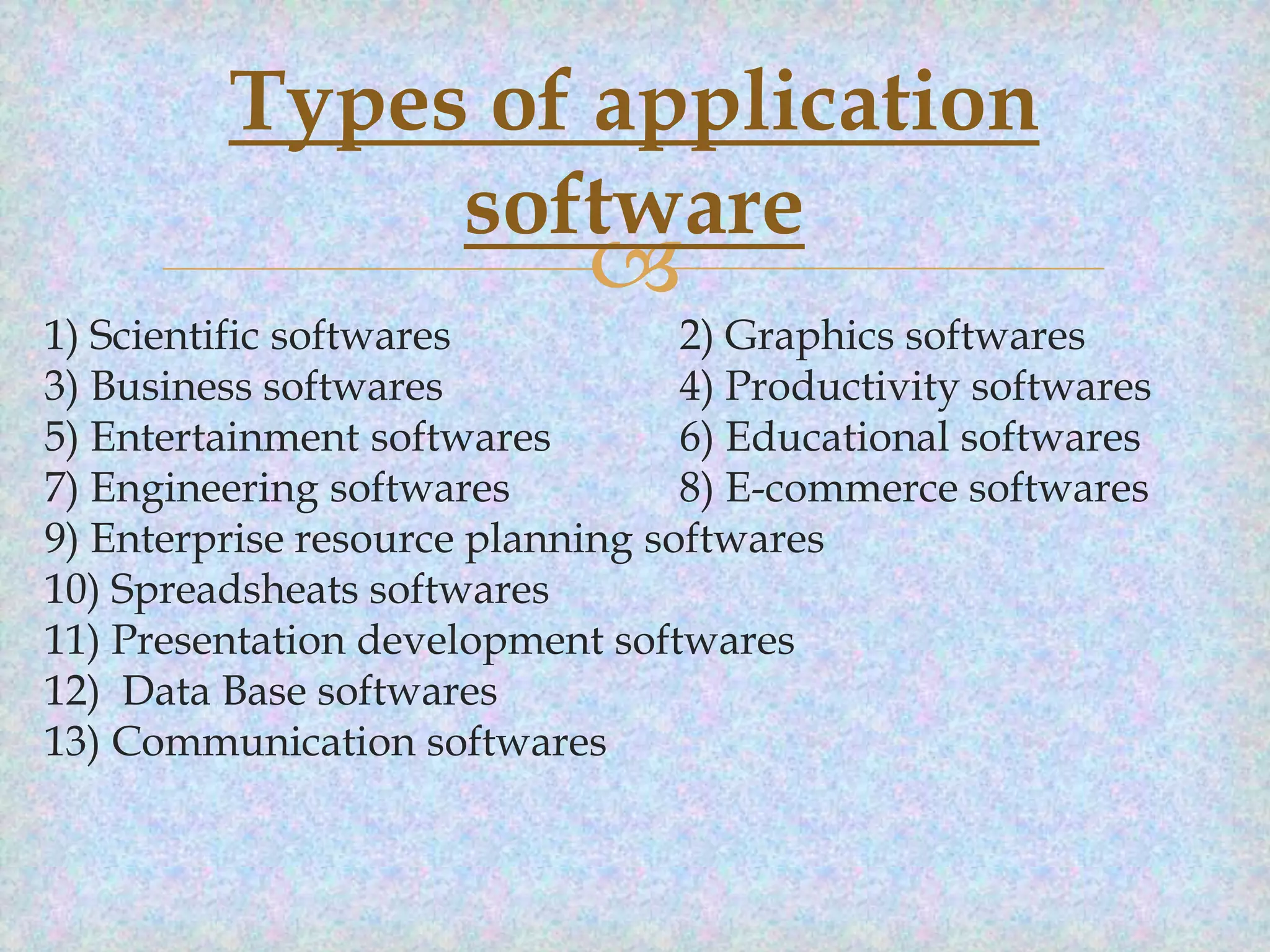
The document provides an overview of computer software, defining it as a set of instructions necessary for hardware operation. It categorizes software into system software, which includes operating systems and device drivers, and application software, which serves various user needs including productivity and educational purposes. Examples of different types of software are listed, showcasing their specific functions and applications.