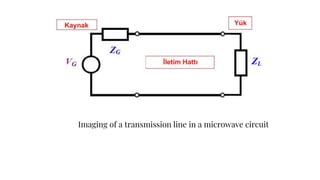
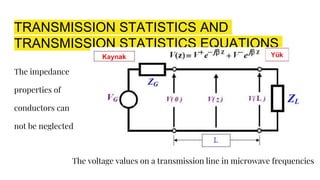
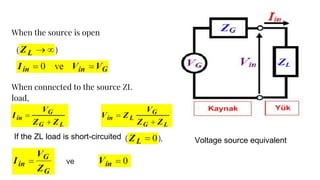
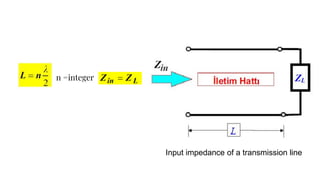
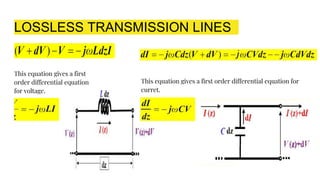
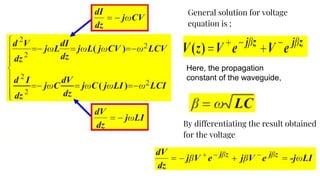
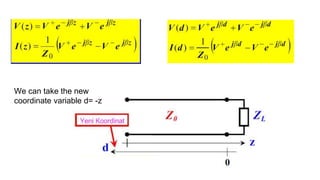
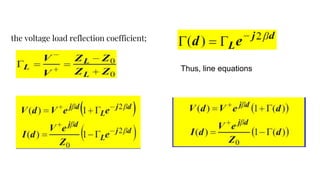
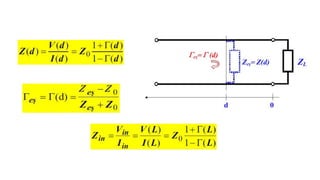
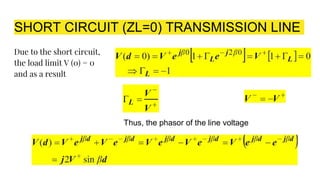
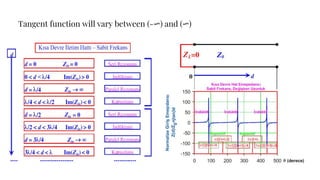
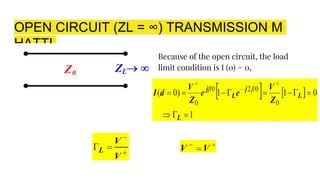
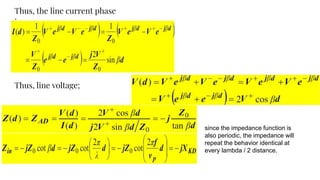
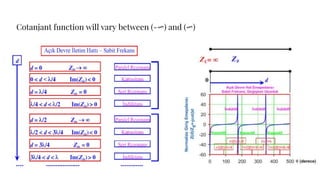
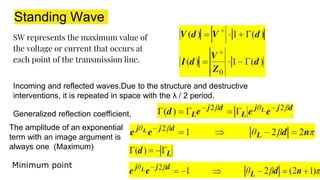
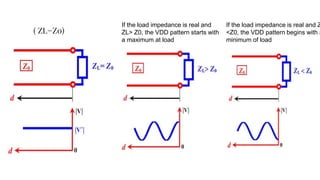
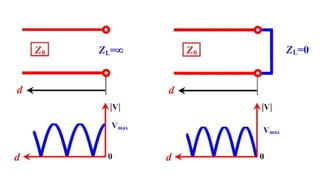
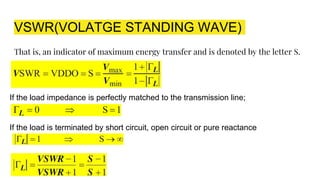
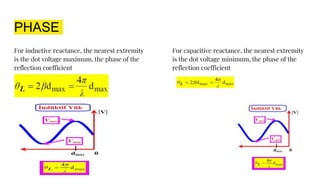
The document discusses parameters plotted on the Smith Chart such as reflection coefficient magnitude and phase, transmission line length, VSWR, and input impedance. It examines voltage and current on transmission lines for different load conditions like open circuit, short circuit, and matched loads. Equations are presented for voltage and current on lossless transmission lines, and for calculating standing wave ratios and reflection coefficients. The behavior of voltage standing wave patterns and phase are described depending on the load impedance characteristics.