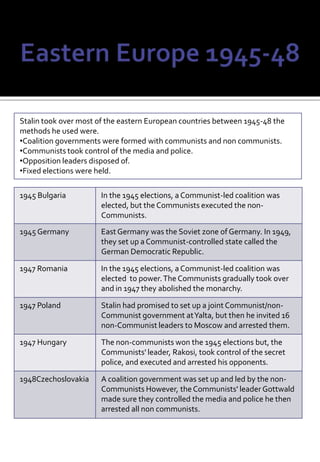
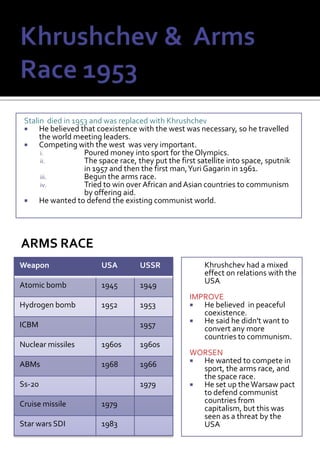
The document provides a timeline of key events during the Cold War between 1945-1991. It begins with the Yalta and Potsdam conferences in 1945 where the Allied powers agreed to divide Germany and Berlin into occupation zones but tensions were rising between the US and USSR. The timeline then lists major events in the escalating arms race and conflicts between the US and Soviet-led communist bloc, including various crises and wars, until the decline and fall of the Soviet Union in 1991 marking the end of the Cold War.