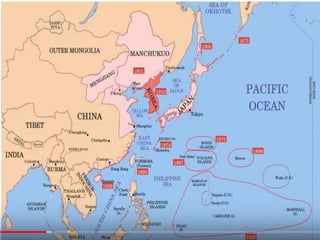
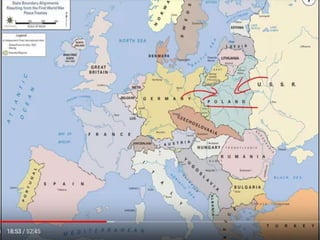
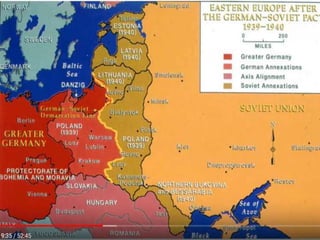
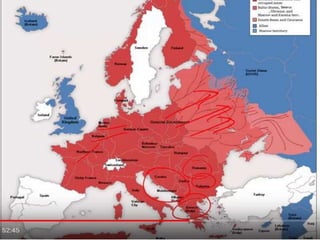
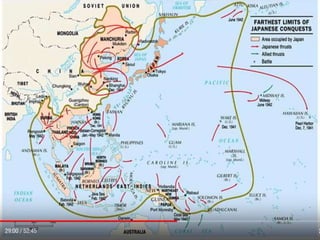
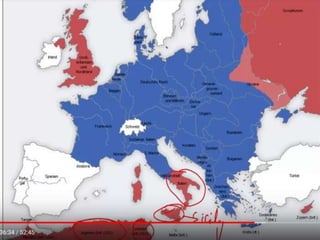
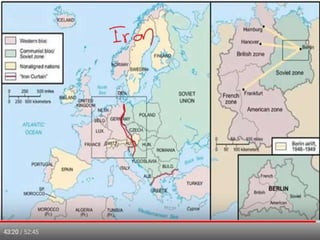
World War 2 was a global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved two opposing military alliances: the Allies (UK, France, USA, USSR, China, and others) and the Axis powers (Nazi Germany, Italy, Japan, and others). Over 60 million people were killed, making it the deadliest conflict in history. The war began with Germany's invasion of Poland in 1939. Germany conquered much of continental Europe while Japan conquered territories in Asia and the Pacific. The tide turned in favor of the Allies in 1942; by 1945 the Allies had defeated the Axis powers with Germany surrendering in Europe and the US dropping atomic bombs on Japan.