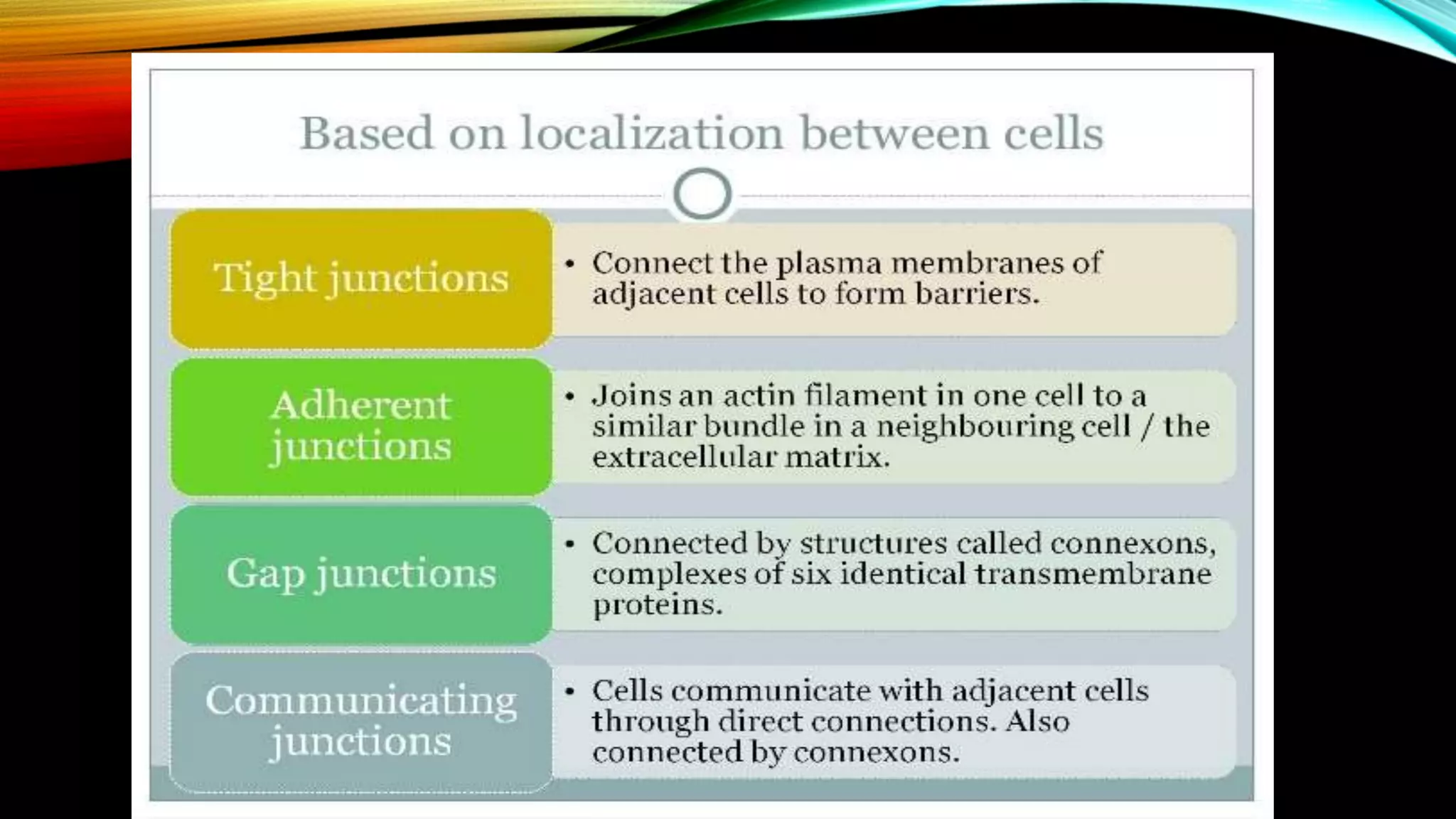
Cell junctions are multiprotein complexes that provide contact between adjacent animal cells and help hold tissues together. The main types are anchoring junctions, which attach cells to surrounding matrix and each other; gap junctions, which allow direct communication between cells; and tight junctions, which form barriers between epithelial layers. Cell junction molecules like selectins, cadherins, integrins, and the immunoglobulin superfamily mediate cell-cell adhesion through calcium-dependent and calcium-independent binding of domains on neighboring cell surfaces. Cell junctions are essential for tissue structure, cell signaling, and barrier functions in the body.