Smooth muscle contraction.pptx
- 3. The smooth muscle of each organ is distinctive from that of most other organs in several ways: (1) physical dimensions (2) organization into bundles or sheets (3) response to different types of stimuli (4) characteristics of innervation (5) function
- 4. TYPES OF SMOOTH MUSCLE FIBERS Smooth muscle fibers are of two types: 1. Single-unit smooth muscle or unitary smooth muscle or visceral smooth muscle or syncytial smooth muscle 2. Multiunit smooth muscle fibers.
- 6. Single-unit smooth muscle fibers Muscle fibers are arranged in sheets or bundles Mainly non-nervous stimuli (hormonal stimuli) Cell membrane of adjacent fibers fuses at many points to form gap junctions. a functional syncytium is developed. The syncytium contracts as a single unit. In this way, the visceral smooth muscle resembles cardiac muscle Show spontaneous contractions.
- 8. It is also called visceral smooth muscle because it is found in the walls of most viscera of the body, including gastrointestinal tract bile ducts ureters uterus blood vessels.
- 9. Multiunit smooth muscle 1. . Muscle fibers are individual fibers 2. Each muscle fiber is innervated by a single nerve ending 3. Each muscle fiber are covered by a thin layer of basement membrane-a mixture of fine collagen and glycoprotein that helps insulate the separate fibers from one another 4. Each fiber contract independently 5. Control of these muscle fibers is mainly by nerve signals 6. These smooth muscle fibers donot have interconnecting gap junctions 7. These smooth muscle fibers resemble the skeletal muscle fibers in many ways. 8. Does not show spontaneous contraction
- 11. Distribution of Multiunit Smooth Muscle Fibers : Multiunit muscle fibers are in ciliary muscles of the eye iris of the eye Piloerector muscles that cause erection of the hairs
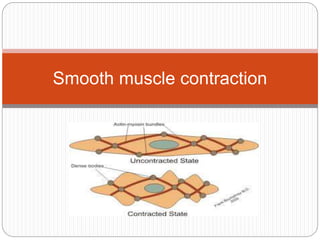
- 13. Structure of Smooth Muscle Lacks visible cross-striations Actin and myosin-II are present but not arranged in regular arrays Actin 5-10 times more than Myosin Dense bodies instead of Z lines Actin filaments attach to dense bodies Contains tropomyosin, but troponin absent Regulatory protein is calmodulin instead of troponin
- 14. Sarcoplasmic reticulum not well developed Few mitochondria Mononucleate cells Far smaller fibers Calveoli is present Involuntary
- 15. Smooth muscle contraction is prolonged tonic contraction, sometimes lasting hours or even days. Slow cycling of the myosin cross bridge Low energy utilization Less ATPase activity One molecule of ATP is required for each cycle Total contraction time is 1 to 3 sec Slow onset of contraction but prolonged contraction Maximum force of contraction is greater than skeletal muscle
- 17. Myosin filaments have “sidepolar” cross- bridges Arranged so that bridges on one side hinge in one direction and those on other side hinge in opposite direction Allows myosin to pull an actin filament in one direction on one side while simultaneously pulling another actin filament in the opposite direction on the other side Allows smooth muscle cells to contract as much as 80% of their length instead of 30% (skeletal muscle)
- 21. LATCH MECHANISM Latch mechanism is that it can maintain prolonged tonic contraction in smooth muscle for hours with little use of energy. Little continued excitatory signal is required from nerve fibers or hormonal sources.
- 24. 1. Calcium concentration in the cytosolic fluid of the smooth muscle increases as a result of the influx of calcium from the extracellular fluid through calcium channels and/or release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. 2. The calcium ions bind reversibly with calmodulin. 3. The calcium-calmodulin complex then joins with and activates myosin light chain kinase. 4. One of the light chains of each myosin head, called the regulatory chain, becomes phosphorylated in response to this myosin kinase. When this chain is not phosphorylated, the attachment-detachment cycling of the myosin head with the actin filament does not occur.
- 28. When the calcium ion concentration falls below a critical level, the aforementioned processes automatically reverse, except for the phosphorylation of the myosin head. Reversal of this situation requires another enzyme, myosin phosphatase, located in the cytosol of the smooth muscle cell, which splits the phosphate from the regulatory light chain. Then the cycling stops, and contraction ceases.
- 30. Source of Calcium Ions That Cause Contraction the concentration of calcium ions in the extracellular fluid is greater than 10−3 molar, in comparison with less than 10−7 molar inside the smooth muscle cell; this causes rapid diffusion of the calcium ions into the cell from the extracellular fluid when the calcium channels open
- 32. • the vesicles of the autonomic nerve fiber endings contain acetylcholine and Norepinephrine. • the type of receptor determines whether the smooth muscle is inhibited or excited and also determines which of the two transmitters, acetylcholine or norepinephrine, is effective in causing the excitation or inhibition. • For example, norepinephrine inhibits contraction of smooth muscle in the intestine but stimulates contraction of smooth muscle in blood vessels.
- 36. MEMBRANE POTENTIALS AND ACTION POTENTIALS IN SMOOTH MUSCLE Membrane Potentials in Smooth Muscle. In the normal resting state, the intracellular potential is usually about −50 to −60 millivolts, which is about 30 millivolts less negative than in skeletal muscle.
- 38. Calcium Channels Are Important in Generating the Smooth Muscle Action Potential. • The smooth muscle cell membrane has far more voltage-gated calcium channels than skeletal muscle but few voltage-gated sodium channels. • Ca++ channels open more slowly and also remain open much longer for plateau • Another important feature of calcium ion entry into the cells during the action potential is that the calcium ions act directly on the smooth muscle contractile mechanism to cause contraction. Thus, the calcium performs two tasks at once
- 39. Threshold potential for smooth muscle is -30 to- 35 mv
- 40. EFFECT OF LOCAL TISSUE FACTORS ANDHORMONES TO CAUSE SMOOTH MUSCLECONTRACTION WITHOUT ACTION Two types of non-nervous and nonaction potential stimulating factors often involved are (1) local tissue chemical factors (2) various hormones
- 41. Smooth Muscle Contraction in Response to Local Tissue Chemical Factors Lack of O2 ExcessCO2 Increased H+ Adenosine, lactic acid increased K+ diminished Ca2+ increased body temperature can all cause local vasodilatation.
- 42. Effects of Hormones on Smooth Muscle Contraction. Norepinephrine epinephrine acetylcholine Angiotensin Endothelin Vasopressin Oxytocin Serotonin histamine