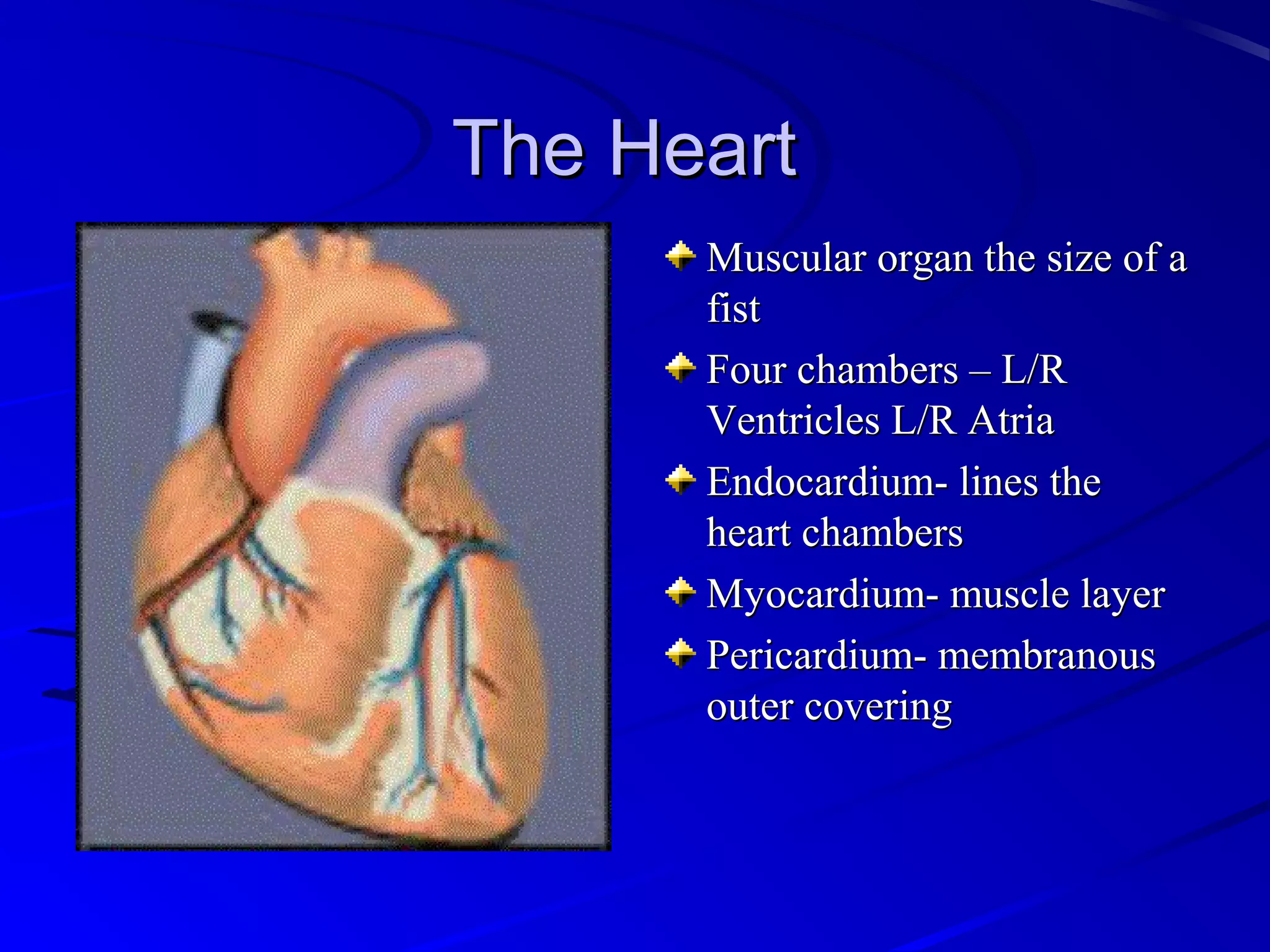
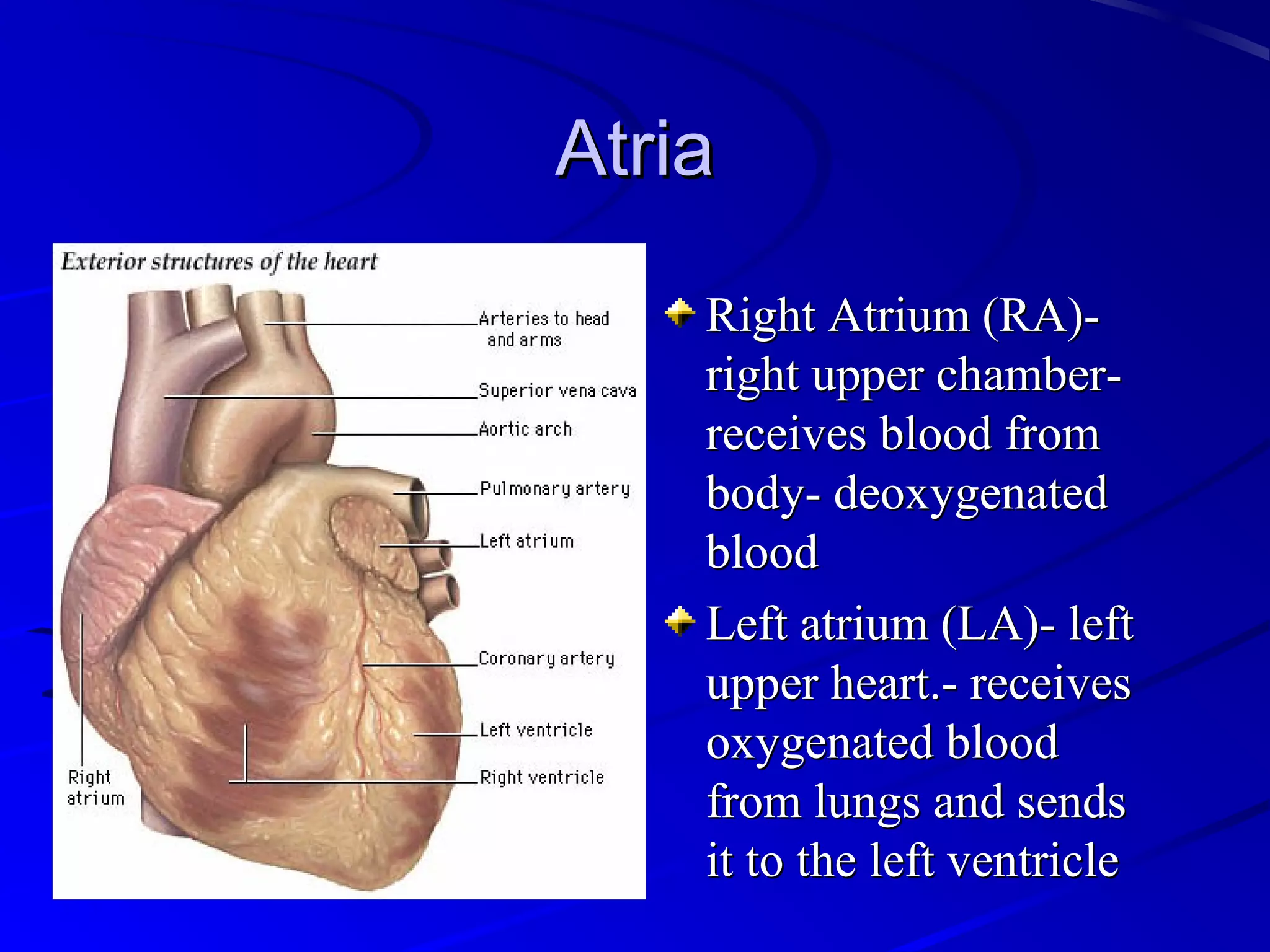
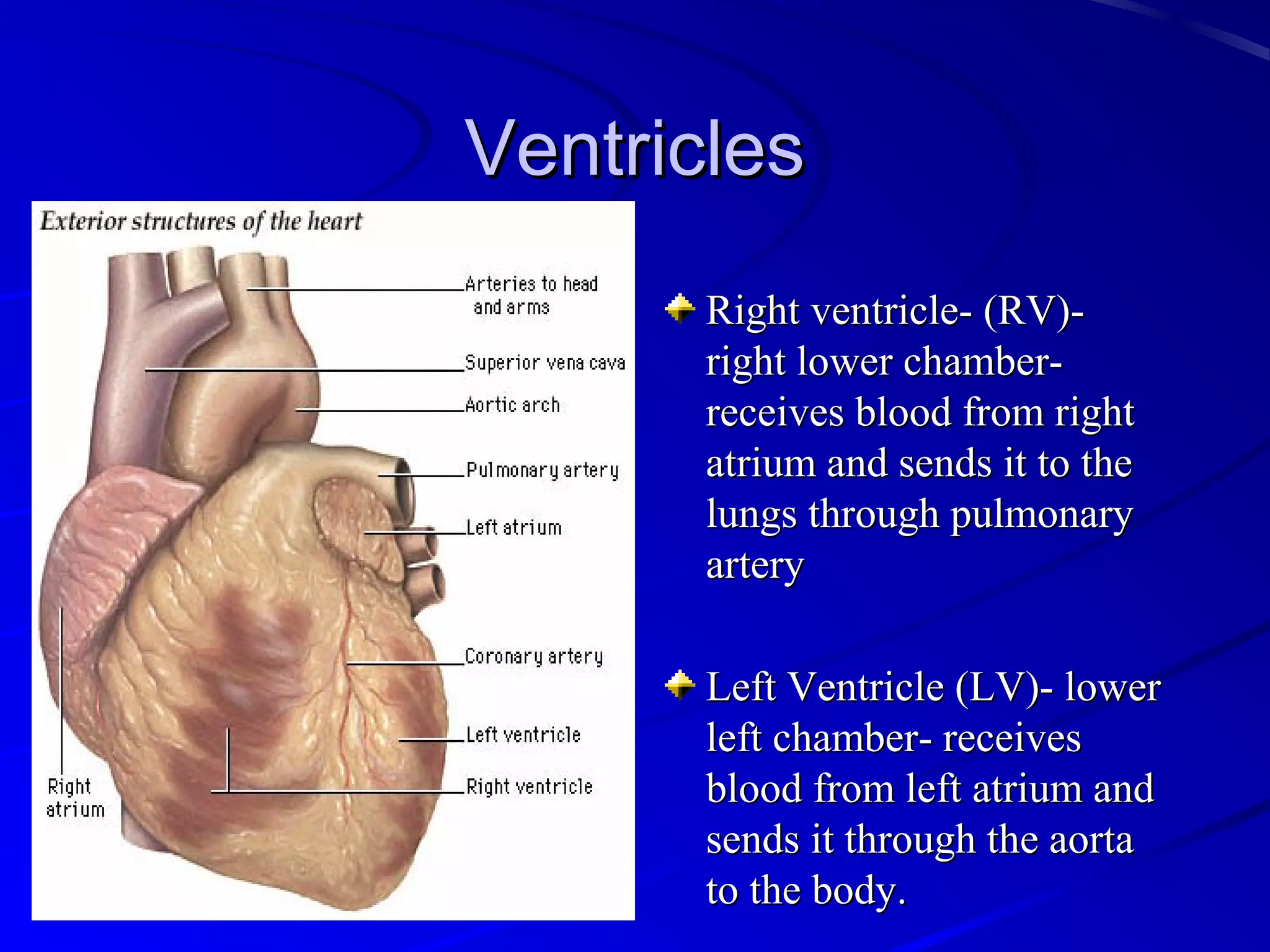
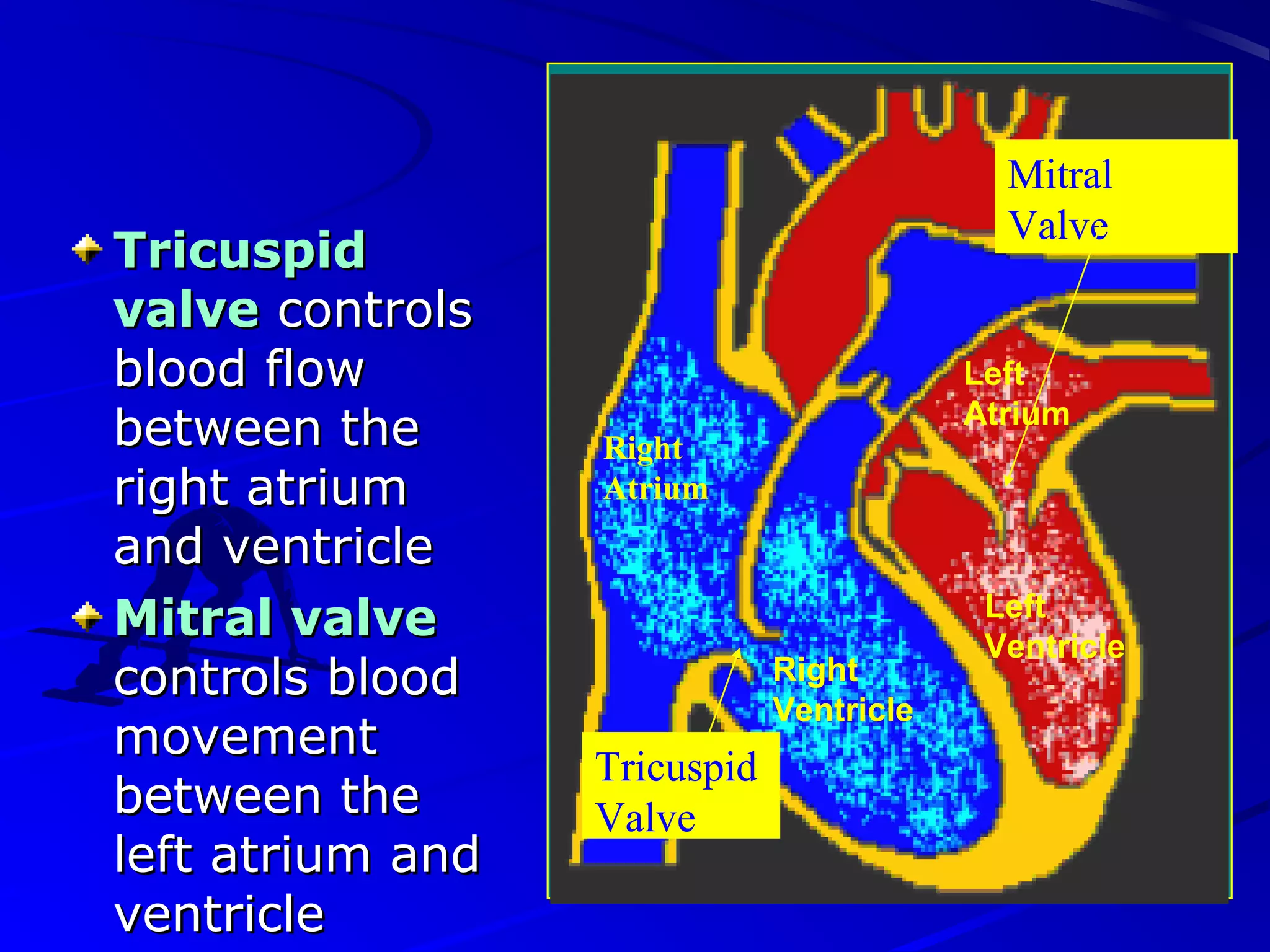
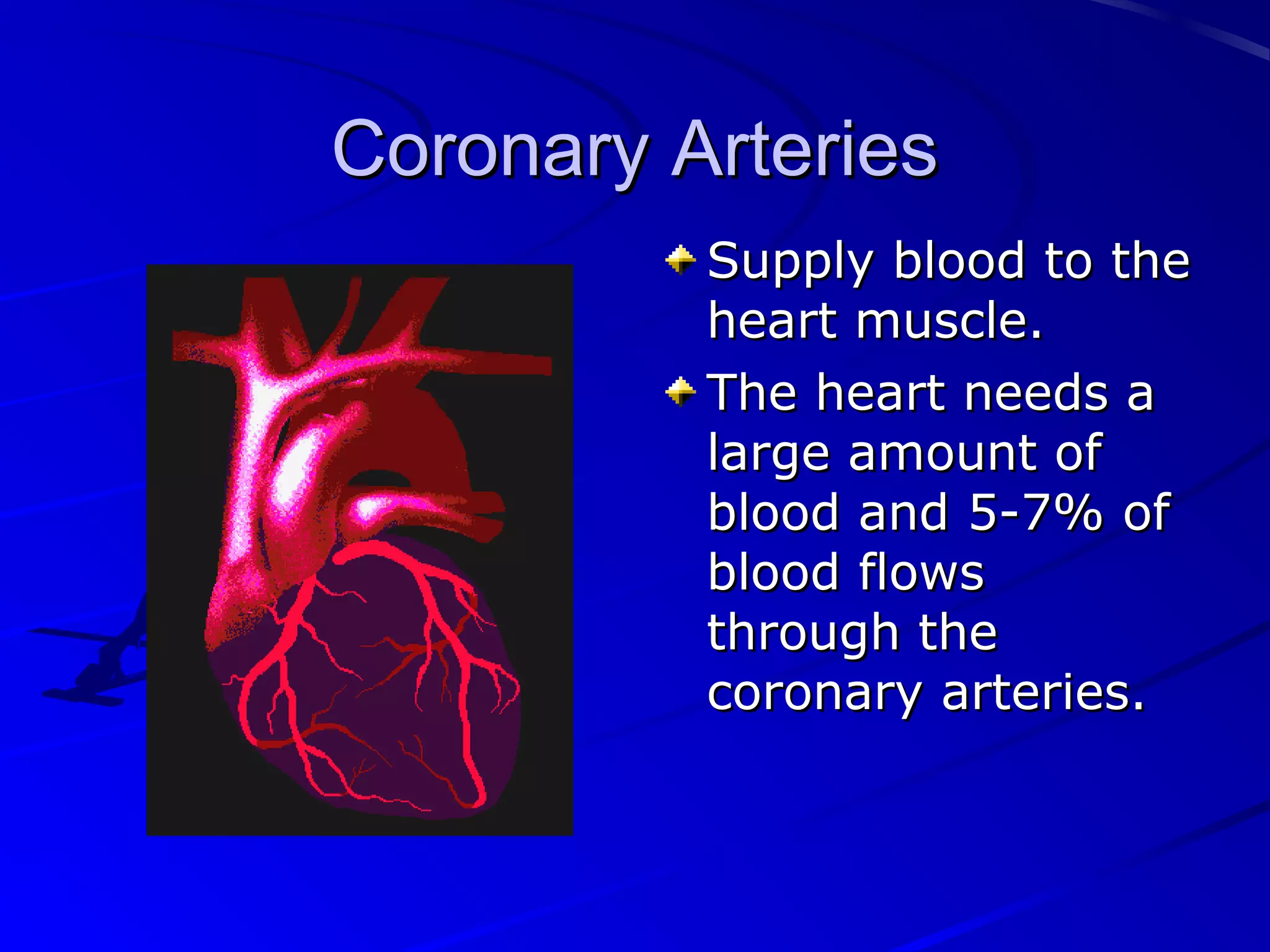
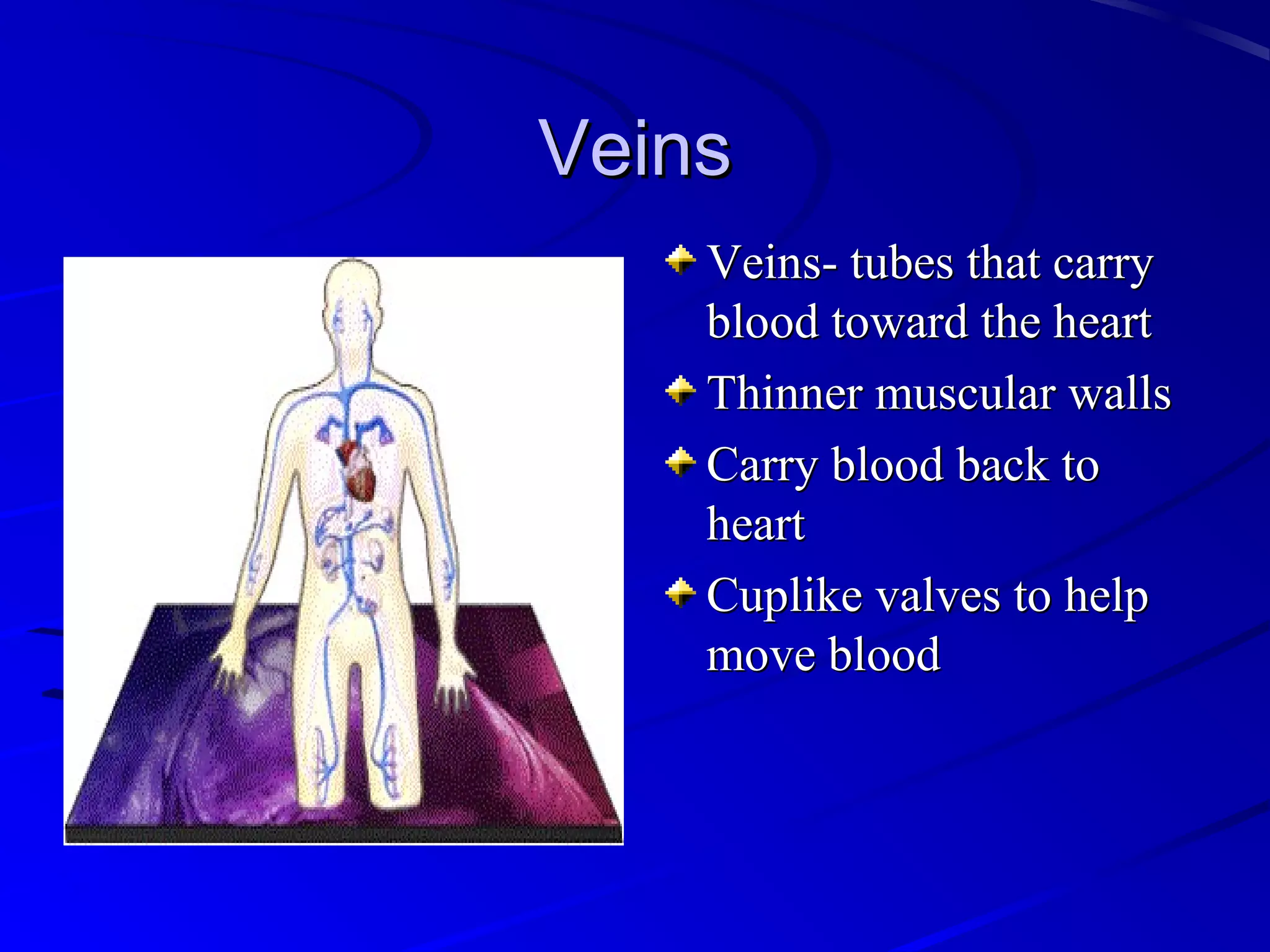
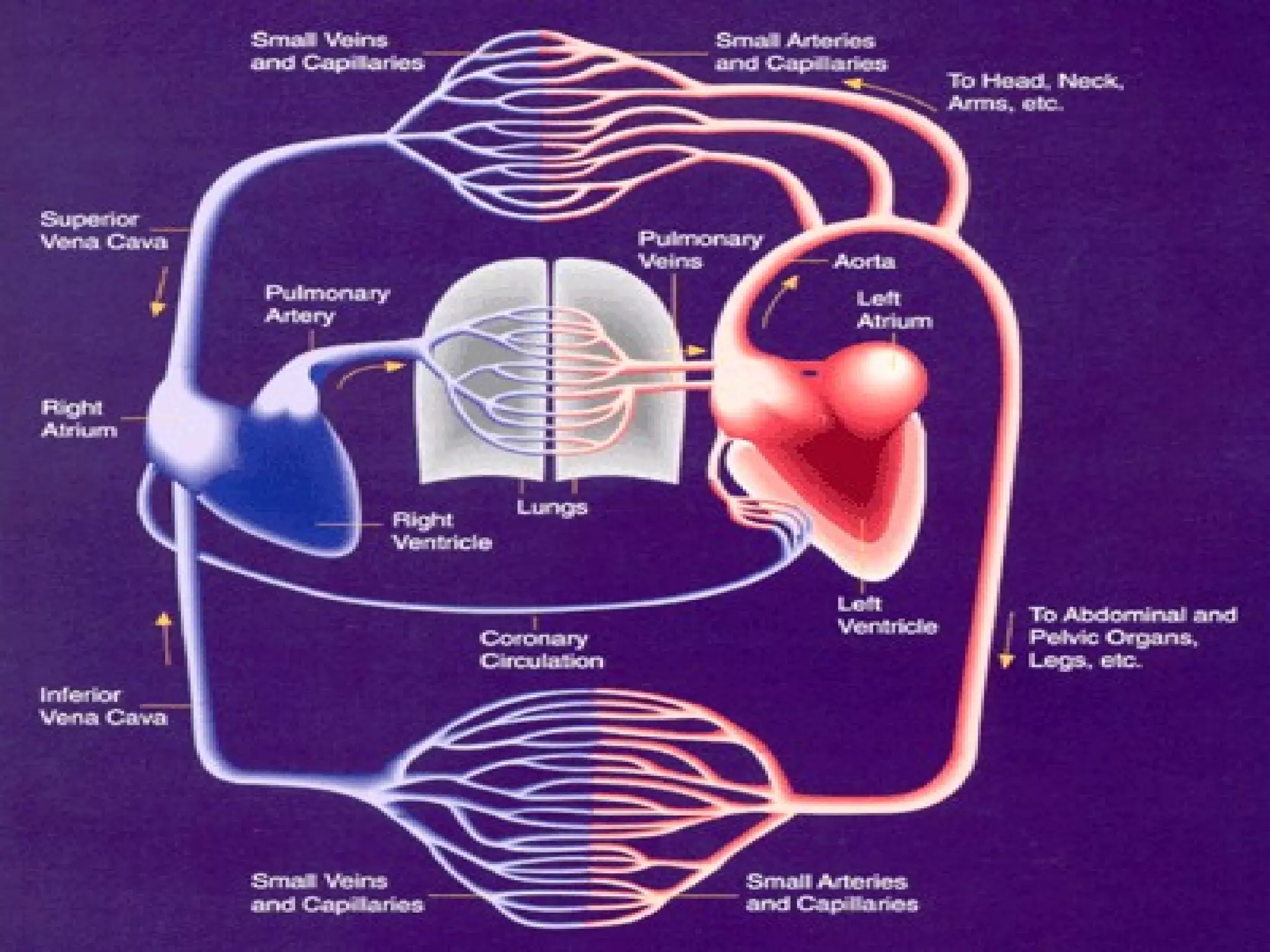
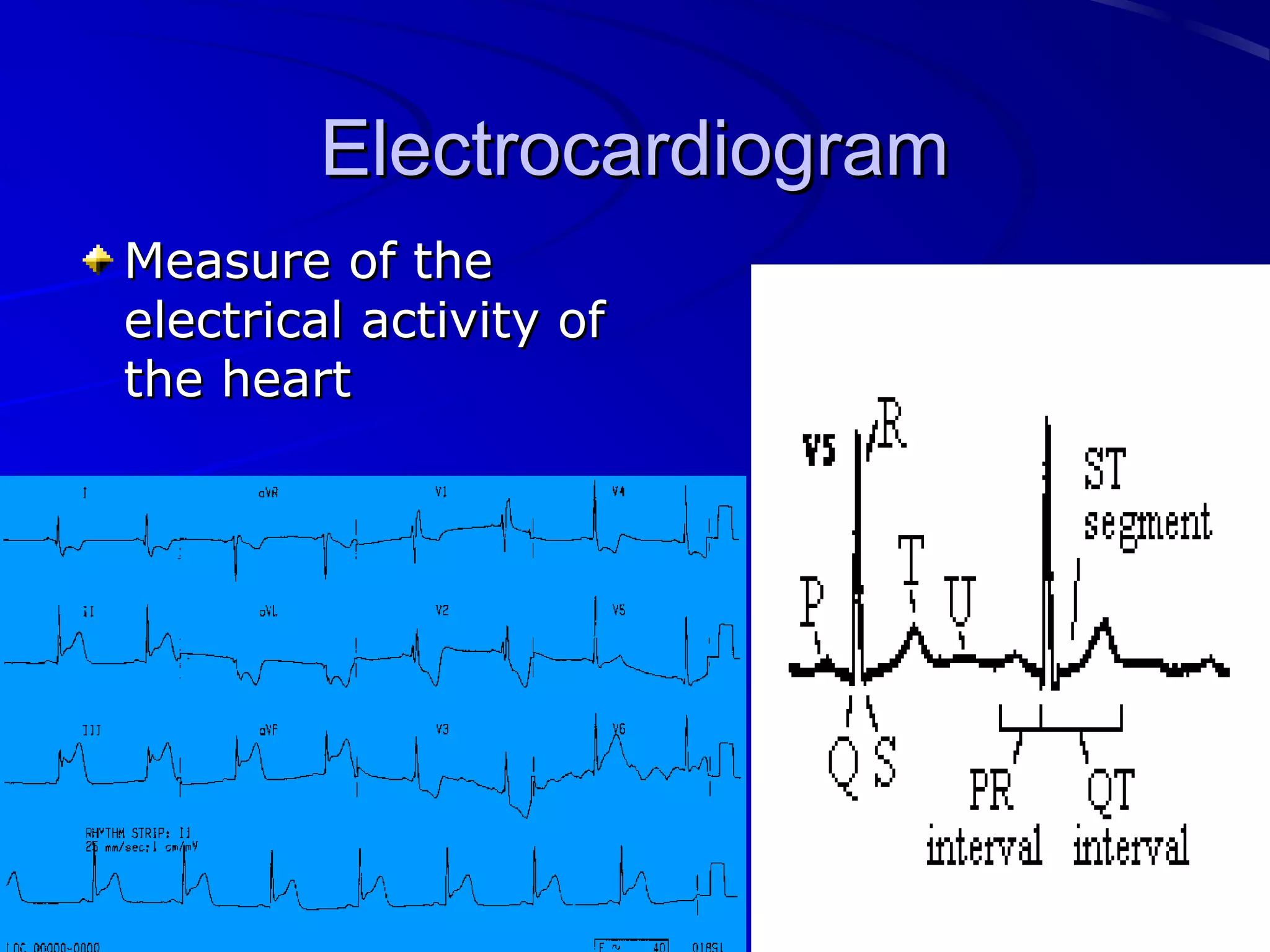
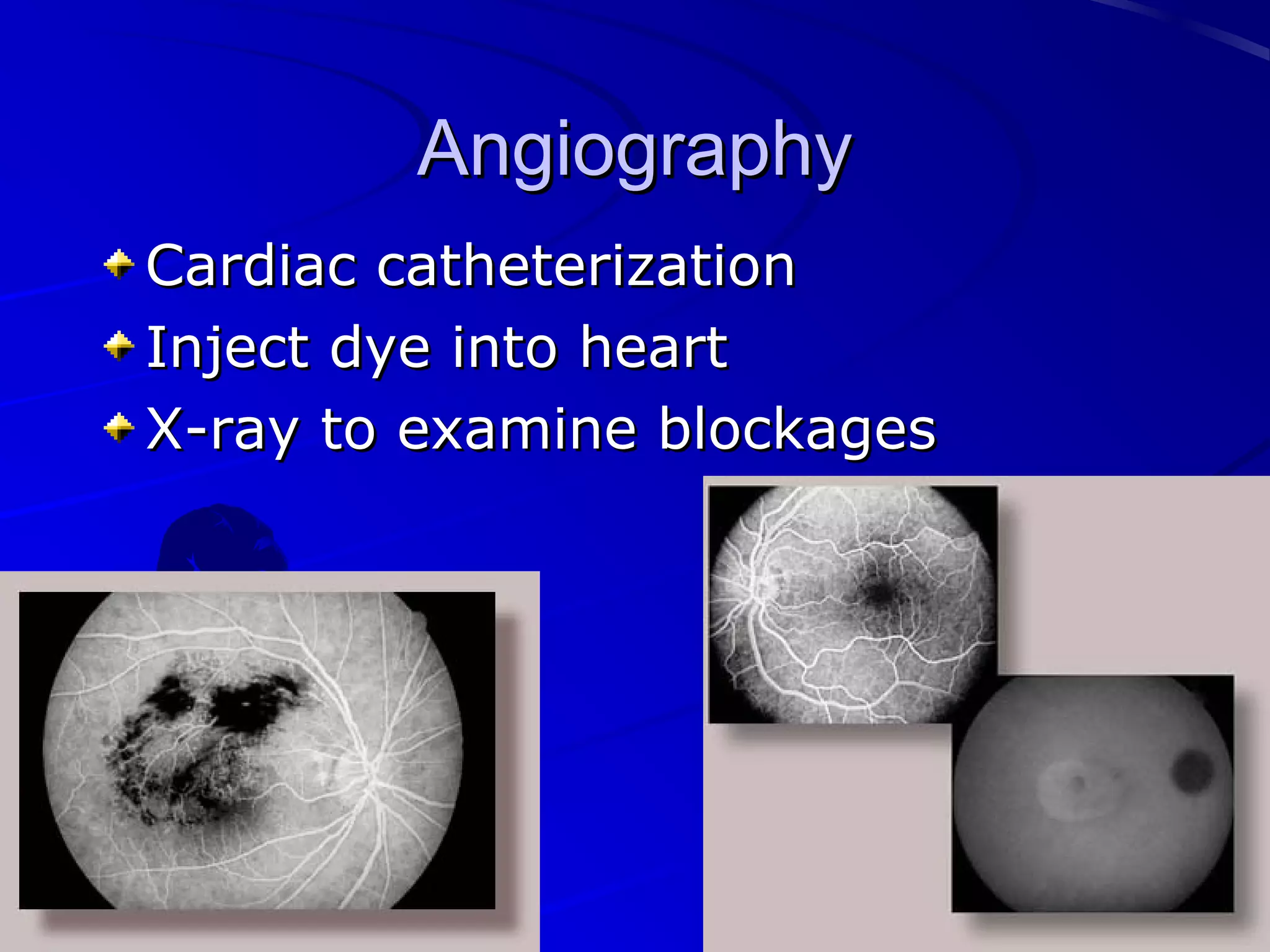
The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and blood vessels that circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is a muscular organ made of four chambers that pump blood into two main circuits - the pulmonary circuit pumps blood to the lungs, and the systemic circuit pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body. Blood pressure, electrocardiograms, stress tests, and angiography are common ways to measure cardiac function and identify issues like blockages. The cardiovascular system works continuously to supply oxygen and nutrients to tissues and remove carbon dioxide and wastes.