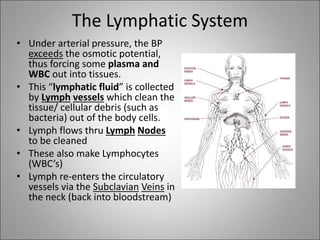
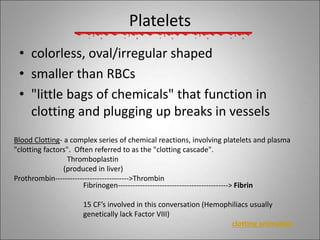
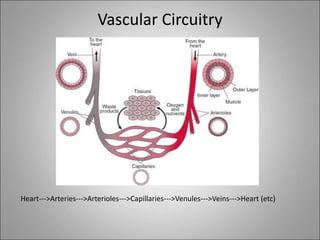
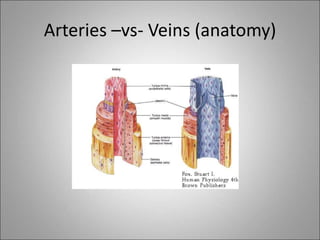
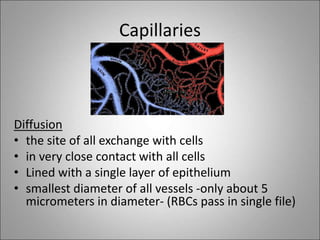
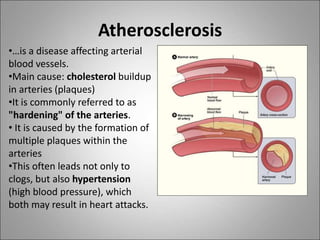
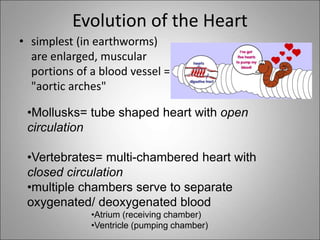
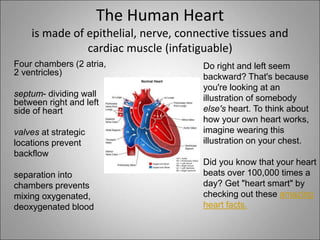
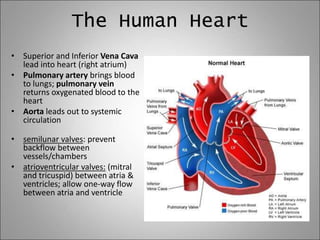
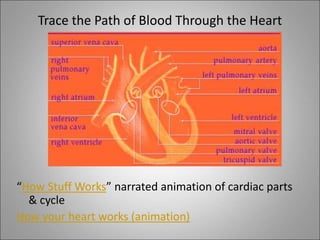
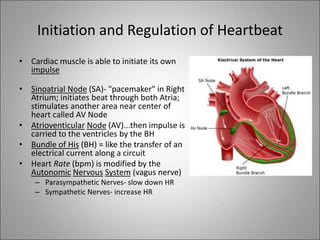
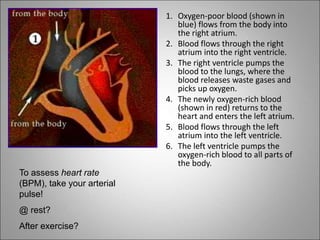
The circulatory system transports blood, nutrients, oxygen, hormones, and waste products throughout the body. Blood contains plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. The heart pumps blood through a closed loop system of arteries, veins, and capillaries. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart while veins return deoxygenated blood back to the heart. The lymphatic system drains lymph fluid and waste from tissues and returns it to the blood.








![How much blood does the heart
pump?
• The heart pumps the equivalent of 5,000 to 6,000
quarts (about 6800 L) of blood each day!
• Total volume of blood pumped by heart per minute =
“cardiac output”
• Cardiac Output = Heart Rate x Stroke volume
• (L/min) = (BPM) x (L/beat)
• [ex: 72 BPM x 0.07 L/beat = 5 L/min.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5786327-230131190423-28603abd/85/5786327-ppt-21-320.jpg)