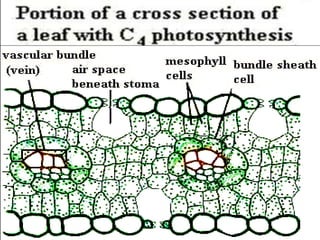
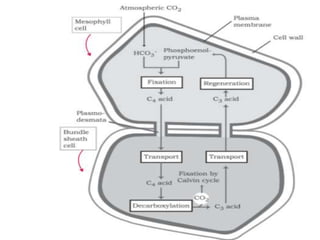
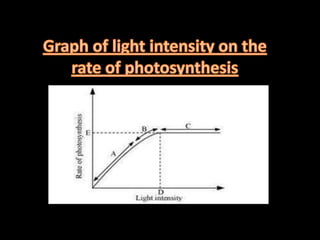
C4 plants differ from C3 plants by having specialized leaf anatomy, higher temperature tolerance, and an absence of photorespiration, which leads to greater biomass productivity. The C4 pathway involves the conversion of phospho-enol-pyruvate to oxaloacetic acid, facilitating efficient CO2 fixation without the wastefulness associated with photorespiration found in C3 plants. Photosynthesis rates in plants are influenced by multiple internal and external factors, including light intensity, CO2 concentration, and temperature, with certain factors acting as limiting agents dictated by Blackman's law of limiting factors.