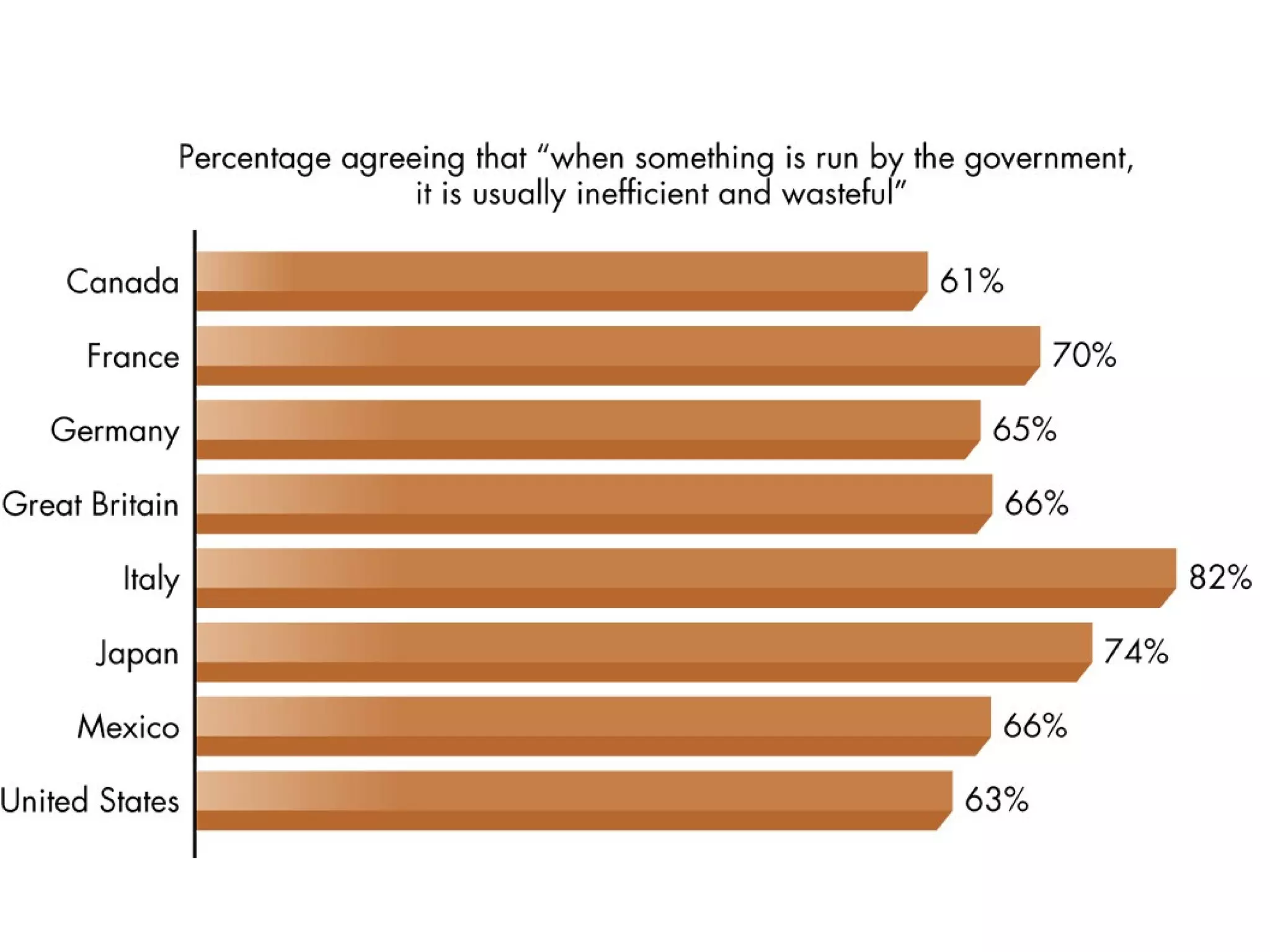
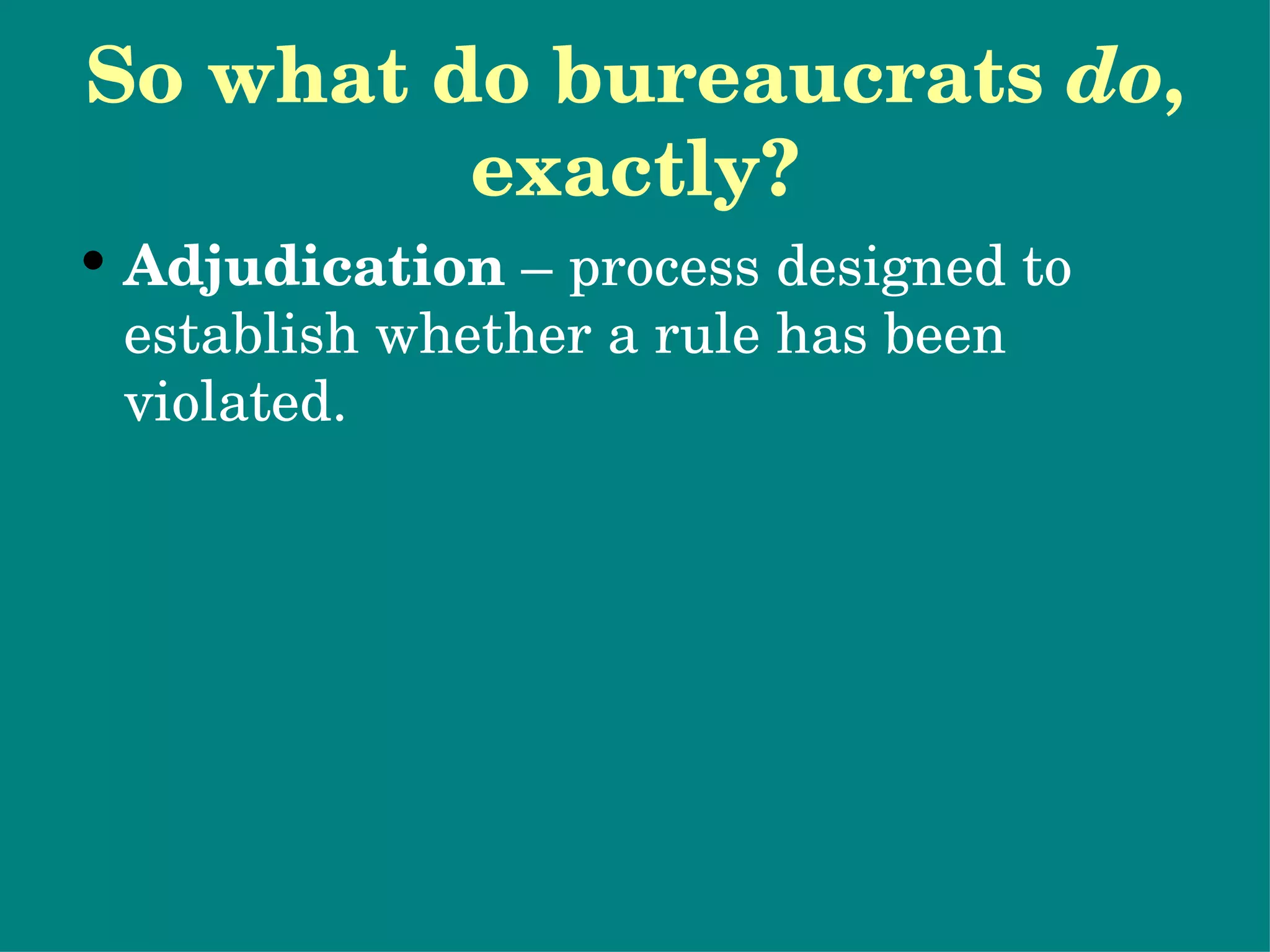
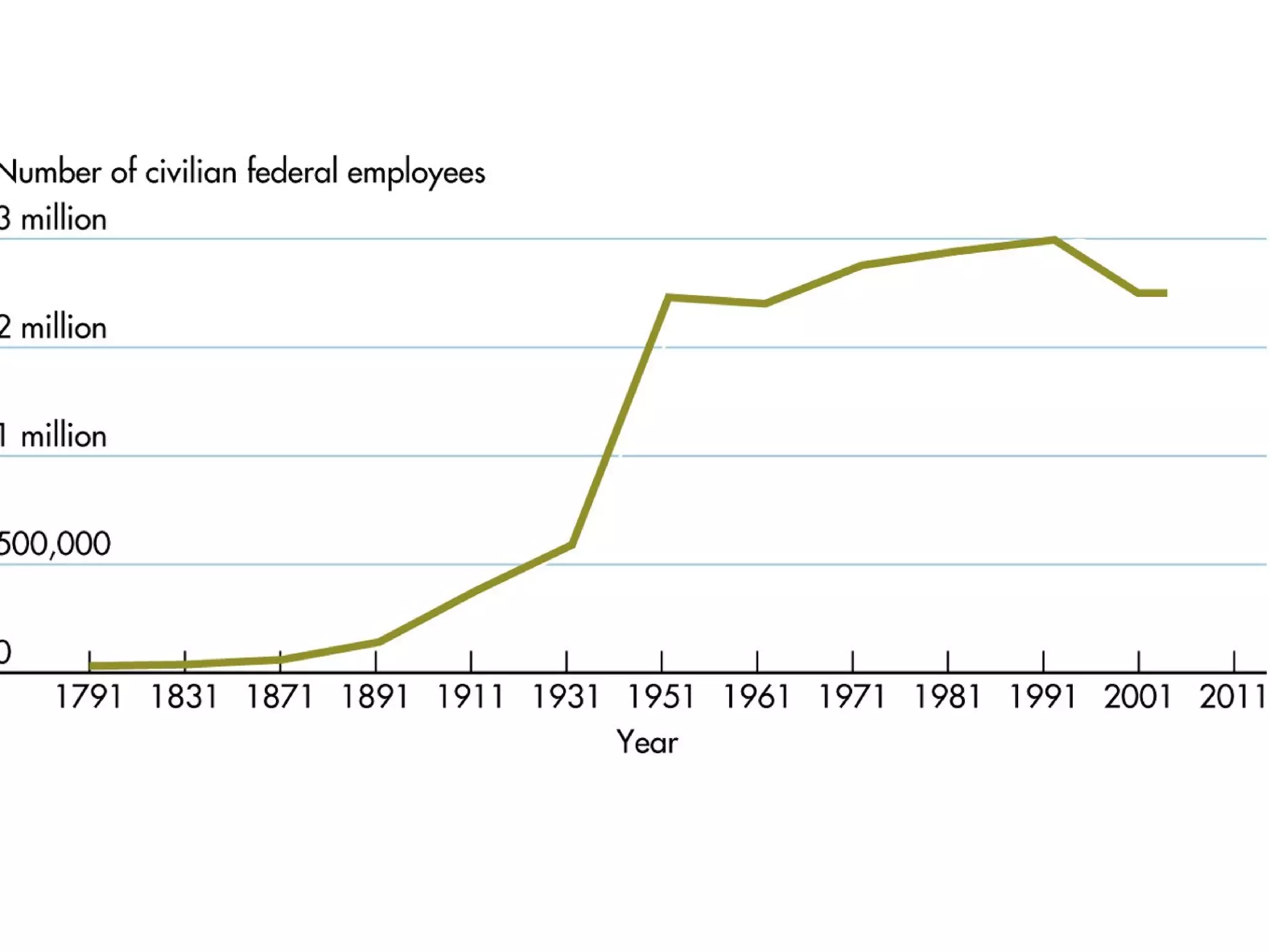
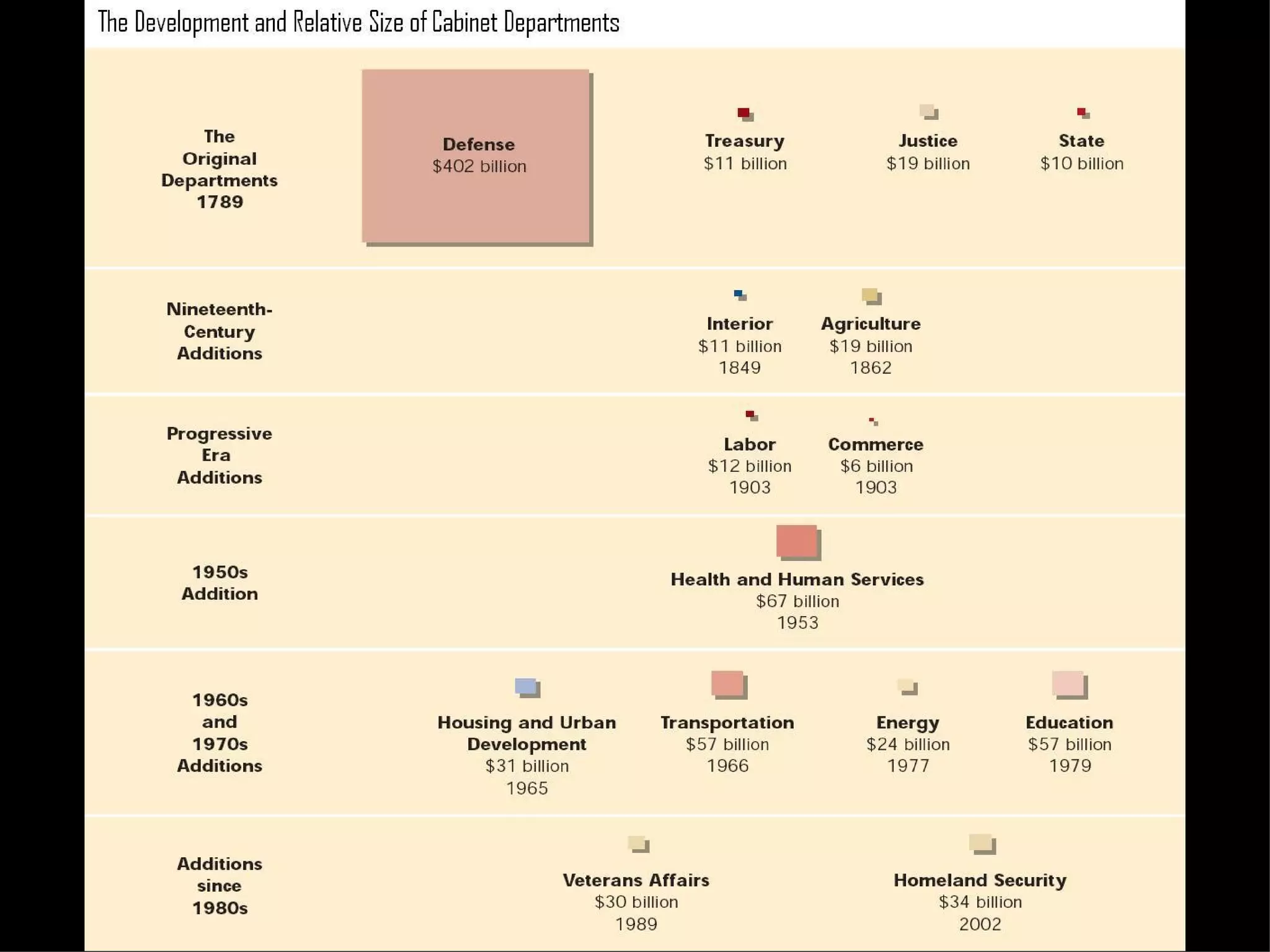
The document provides an overview of bureaucracy, defining it as a large organization where specialized knowledge is organized in a hierarchy. It discusses the merits and disadvantages of bureaucratic structures, focusing on characteristics such as division of labor and formal rules, as well as the differences between the merit system and spoils system. The document also outlines the roles of bureaucrats, including executing laws, rulemaking, and adjudication, and highlights potential issues with bureaucratic policymaking.