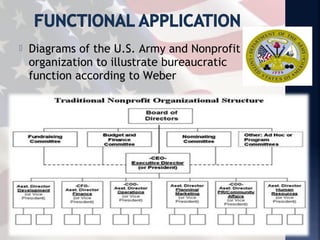
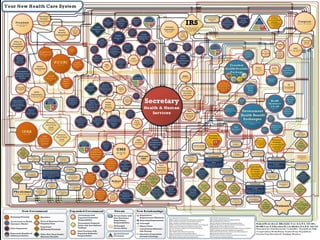
This document provides an overview of the key topics covered in the BUS 4010 Introduction to Public Administration course. The course covers the history and functions of public administration, the rulemaking process, bureaucratic red tape, the influence of politics, and the advantages and disadvantages of bureaucracy. It also examines Max Weber's theory of bureaucracy and the characteristics of bureaucratic organizations, such as hierarchical authority, task specialization, extensive rules, and impersonality. Common criticisms of bureaucracy like red tape are also discussed.