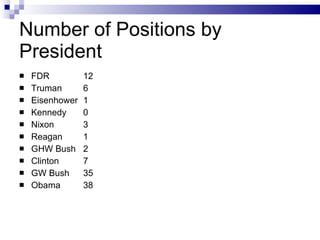
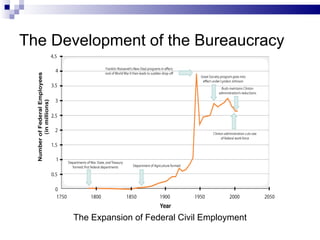
The document discusses the structure and characteristics of bureaucracy in the United States government. It defines bureaucracy as large specialized organizations with clearly defined hierarchies. It describes the organizational structure of federal bureaucracy, including cabinet departments, independent agencies, independent regulatory commissions, and government corporations. It also discusses the advantages and disadvantages of bureaucracy, including standardization and expertise versus a lack of popular sovereignty and potential for political overreach.