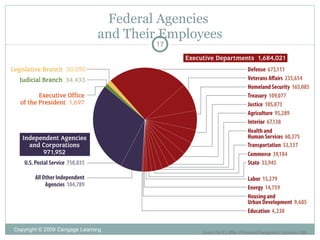
The document discusses Chapter 13 on the bureaucracy. It provides an overview of the key topics in the chapter, including why Congress allows bureaucratic rulemaking, potential conflicts with this system, models of bureaucracy like the Weberian model, and modern attempts at bureaucratic reform through initiatives like deregulation, privatization, and whistleblower protections. It also addresses the size and organization of the federal bureaucracy along with congressional control over bureaucratic agencies and departments.