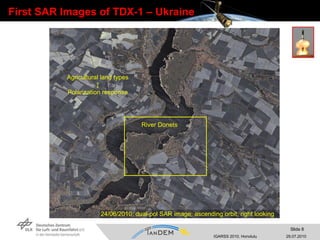
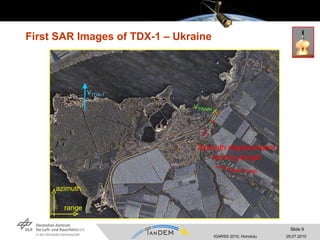
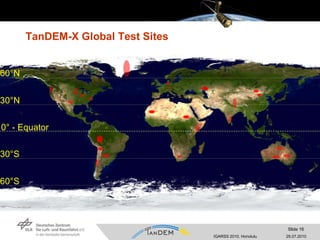
- The TanDEM-X mission involves coordinating two satellites, TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X, flying in close formation to generate a high-quality global digital elevation model (DEM).
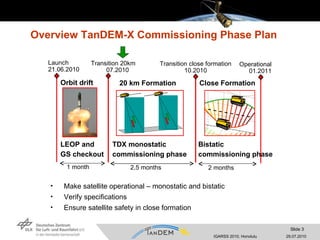
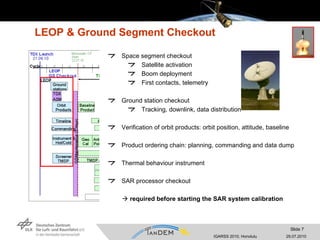
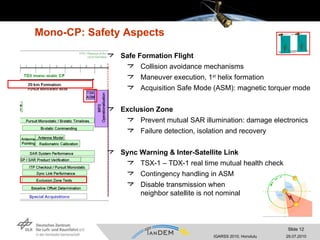
- The commissioning phase involved making the satellites operational for monostatic and bistatic data acquisition, verifying specifications, and ensuring safety during close formation flying.
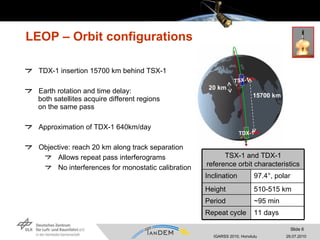
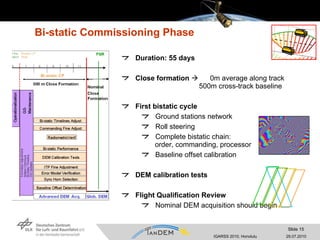
- Key activities included satellite checkout, early orbit operations, monostatic calibration with a 20km separation, and a 55-day bistatic phase with a 500m cross-track baseline to calibrate the bistatic data chain.