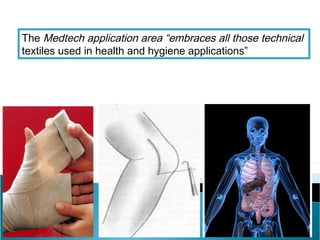
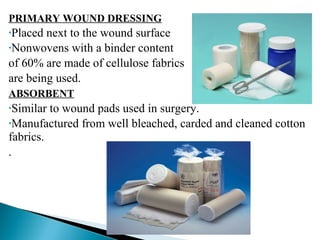
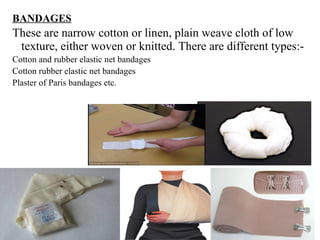
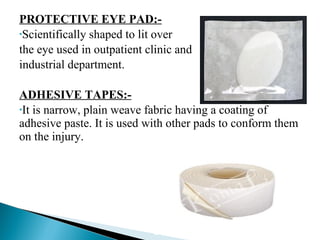
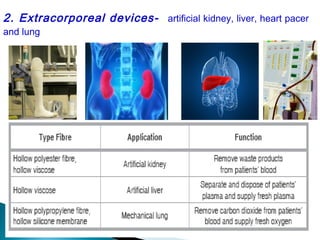
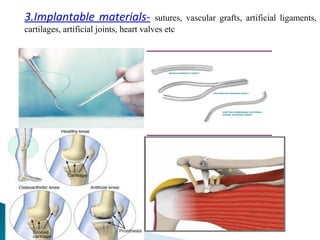
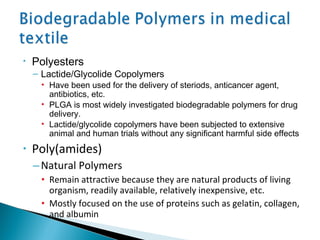
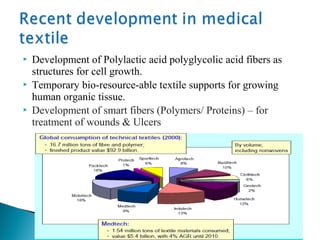
This document discusses medical textiles. It begins by defining medical textiles as textile materials engineered to meet medical needs where strength, flexibility, moisture permeability are required. There are four main categories of medical textiles: non-implantable materials like bandages; extracorporeal devices like artificial organs; implantable materials like sutures and grafts; and healthcare/hygiene products like gowns and bedding. The document outlines properties required for different medical textiles and common fiber types used. It also discusses manufacturing processes and recent developments in the field.