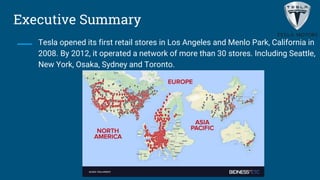
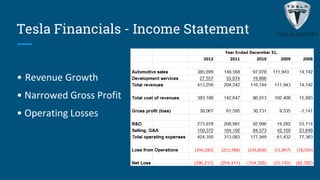
Tesla aims to accelerate sustainable transportation through mass market electric vehicles. It introduced the Roadster in 2008 and Model S in 2012, operating over 30 retail stores globally by 2012. While Tesla has strengths in innovation and leadership, it faces challenges from delays, supply constraints, and lack of charging infrastructure abroad. The document evaluates expanding to China due to its large auto market and environmental concerns, though government subsidies are not guaranteed. It recommends Tesla expand internationally to gain global presence and target developed EV markets.