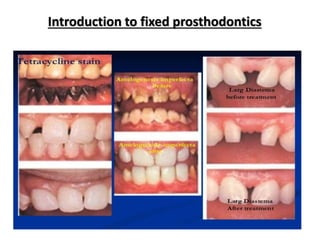
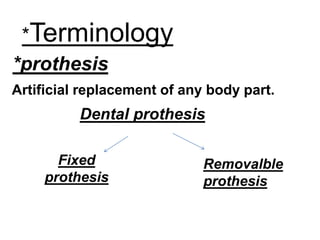
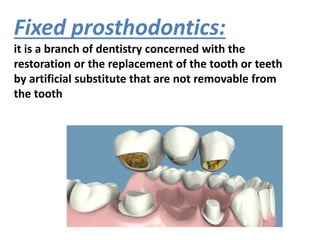
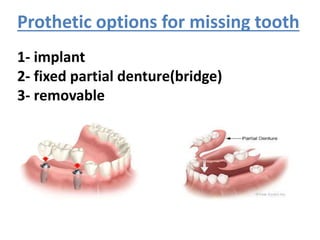
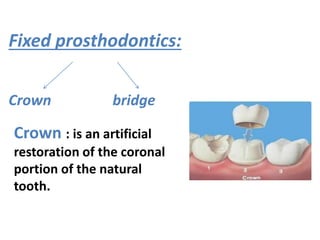
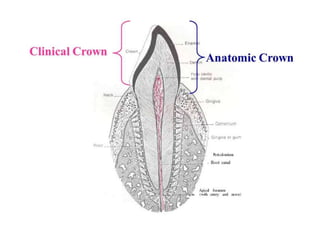
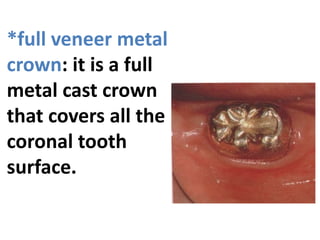
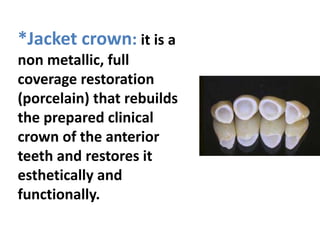
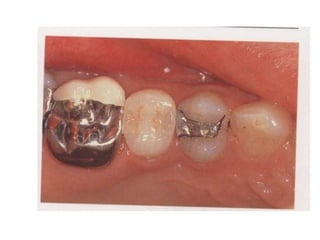
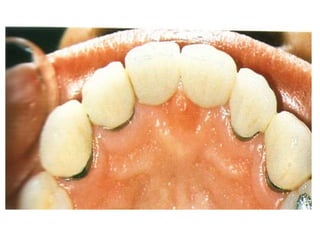
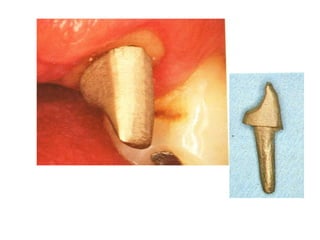
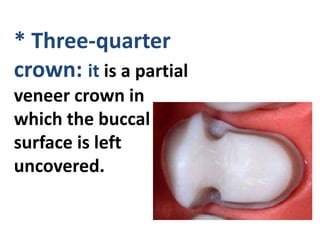
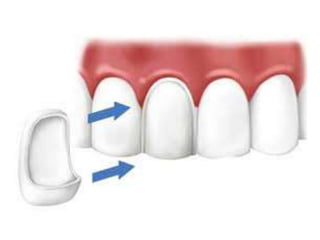
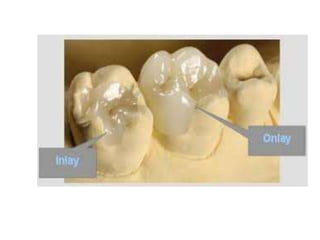
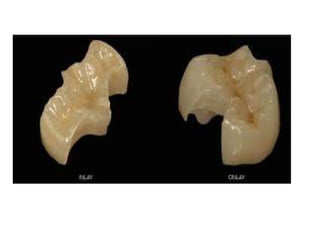
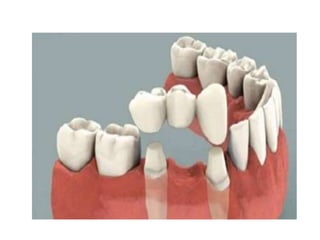
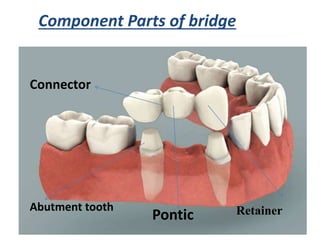
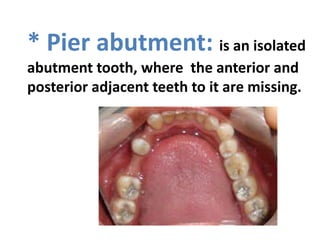
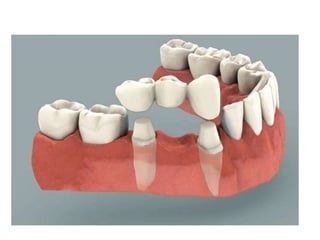
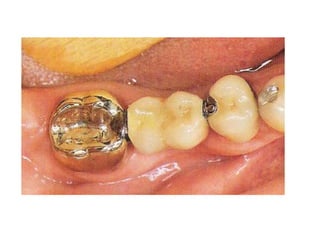
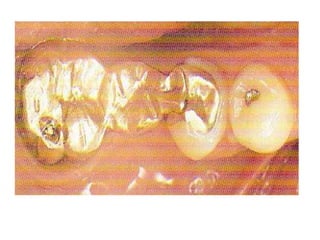
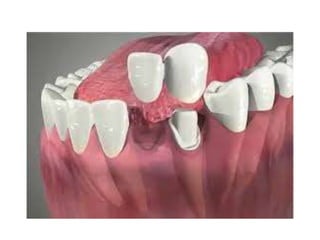
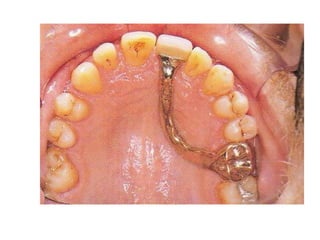
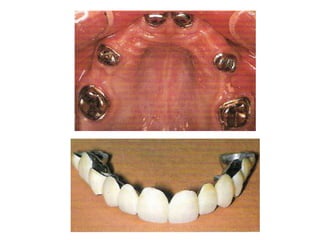
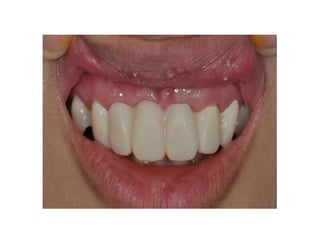
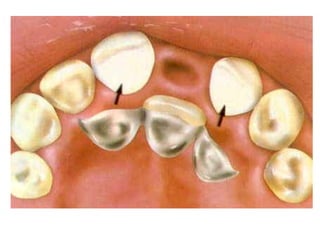
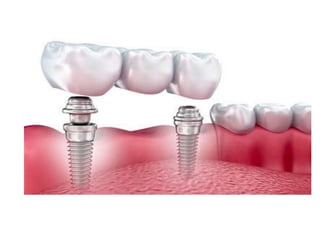
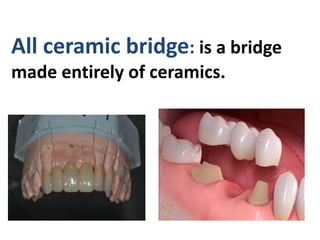
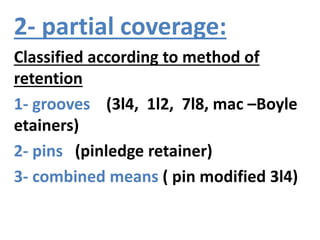
This document provides an introduction to fixed prosthodontics, including terminology, classifications of crowns and bridges, and types of prosthetics. It defines fixed prosthodontics as the replacement of missing teeth by artificial substitutes that are not removable. Crowns are described as restorations that replace the coronal portion of a tooth, and can be full or partial coverage. Bridges are fixed prostheses used to replace one or more missing teeth, consisting of retainers, pontics, and sometimes connectors. Bridges are classified based on retention, materials used, and location in the mouth.