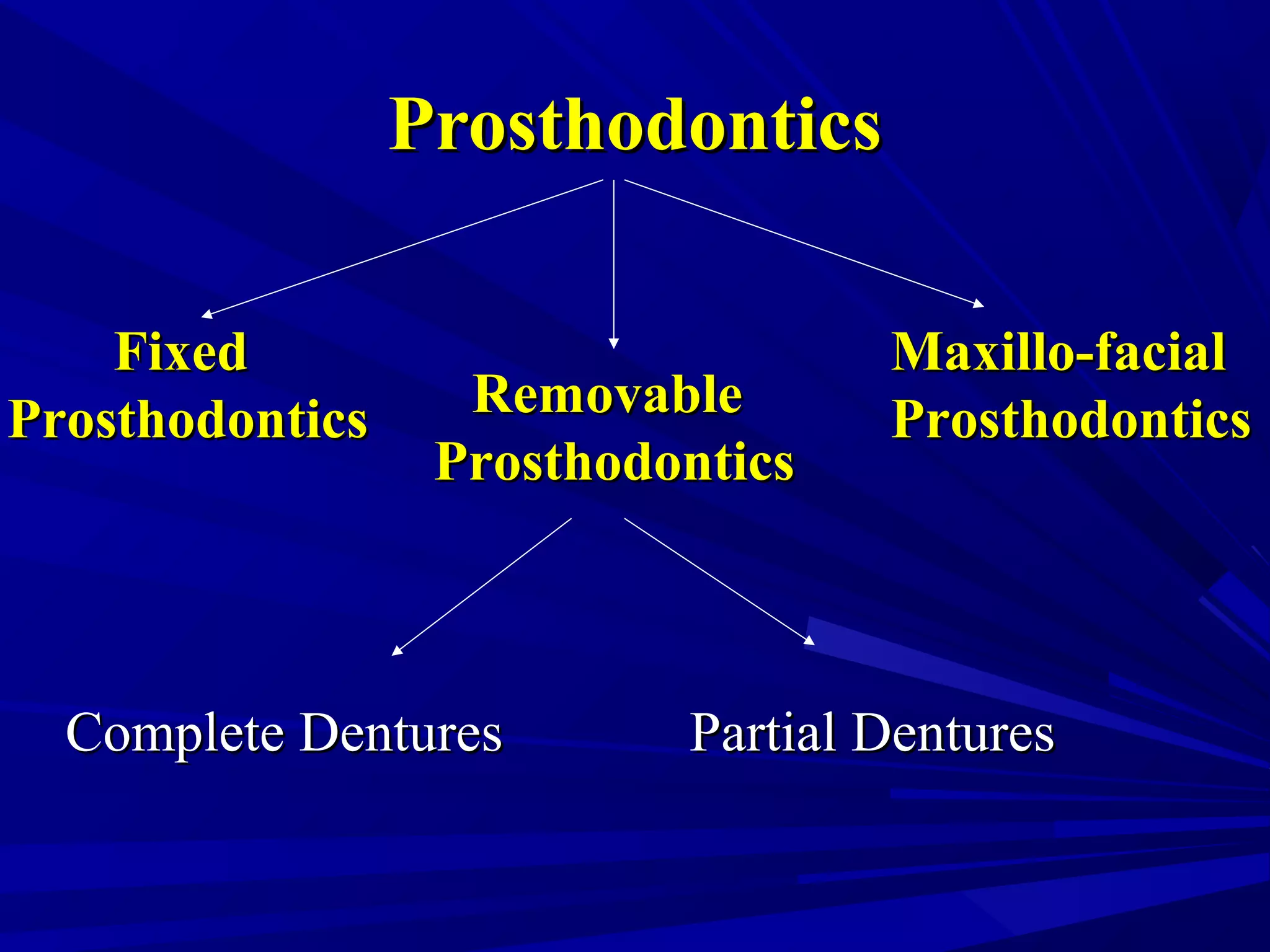
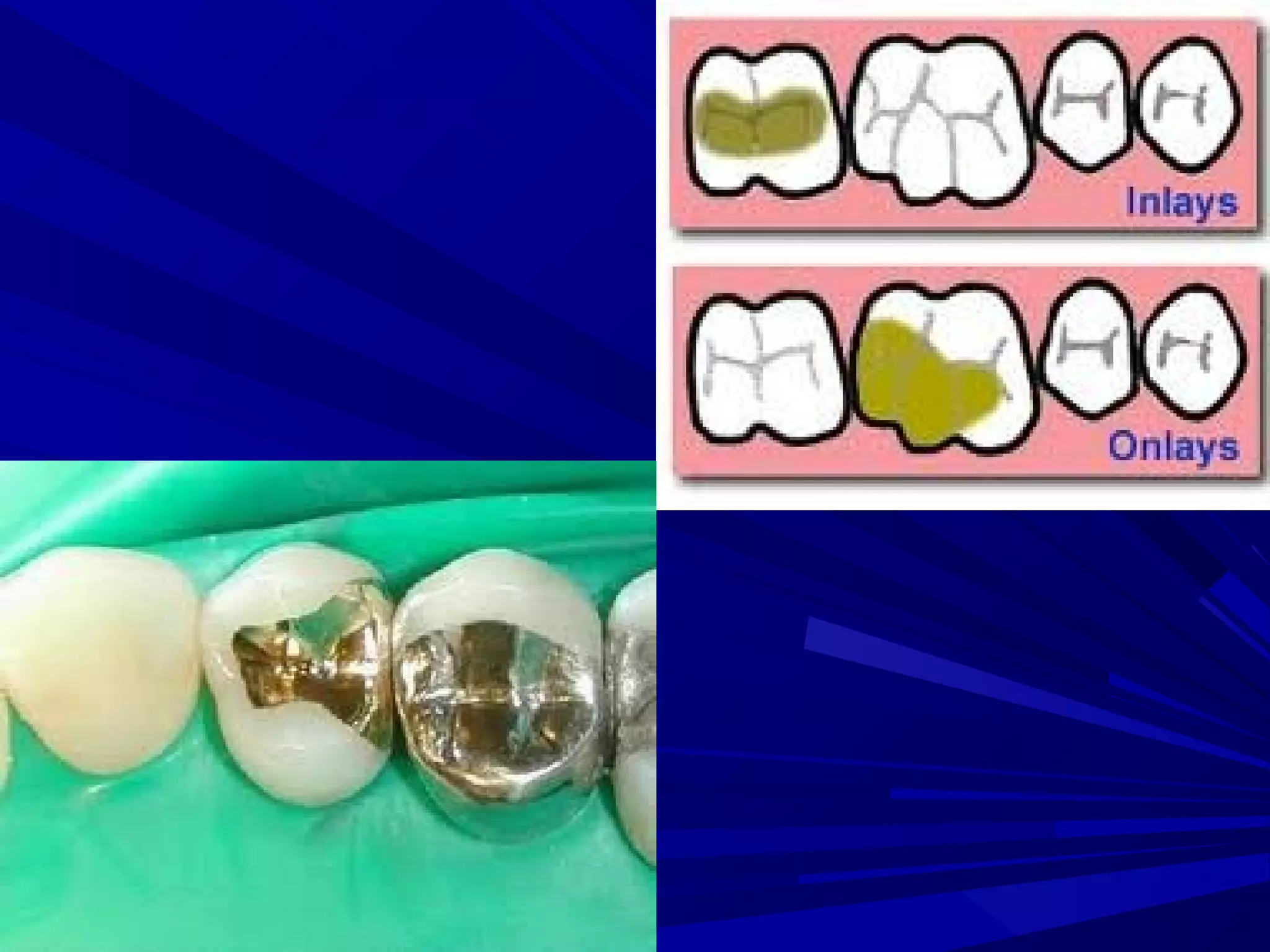
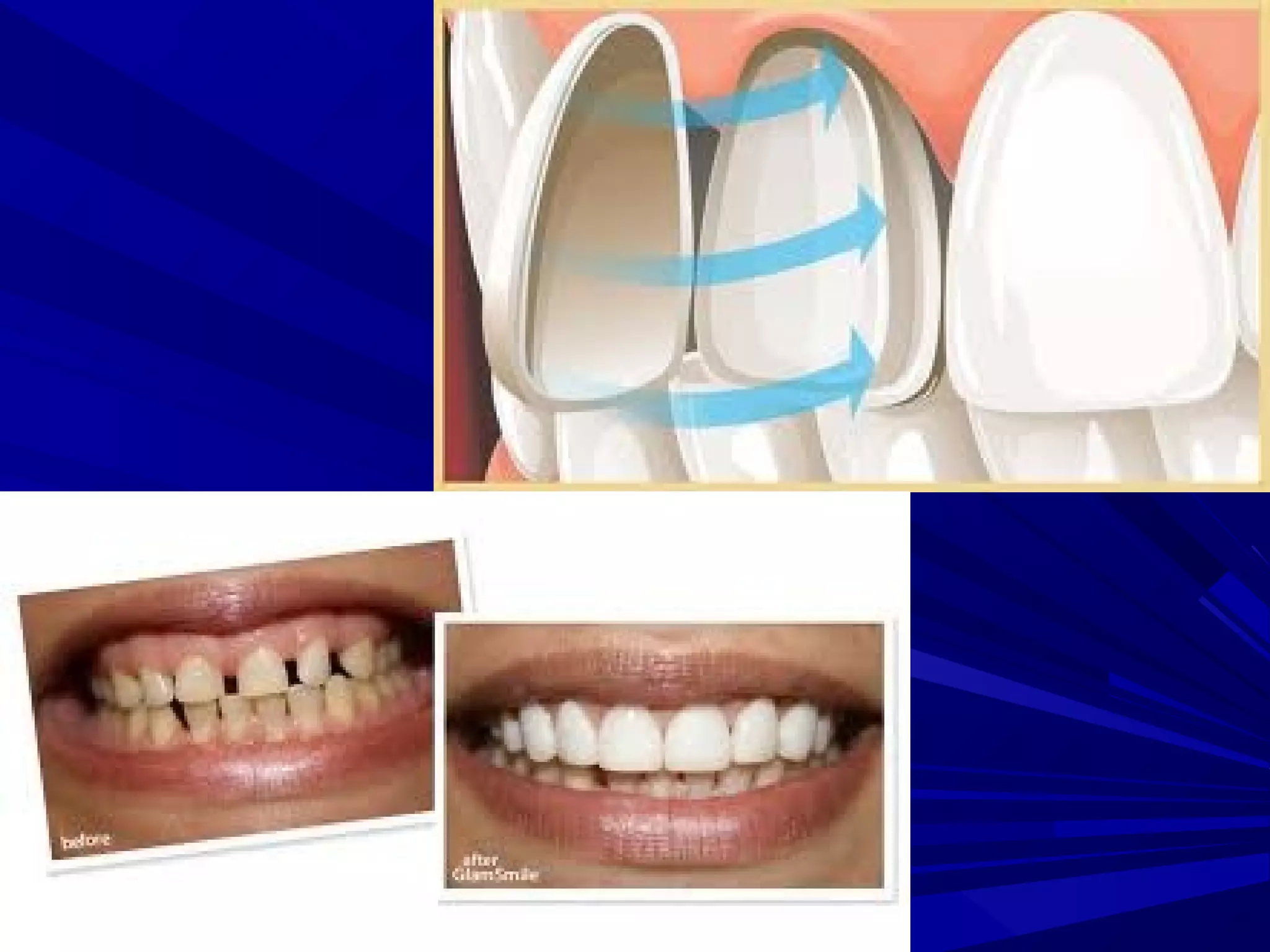
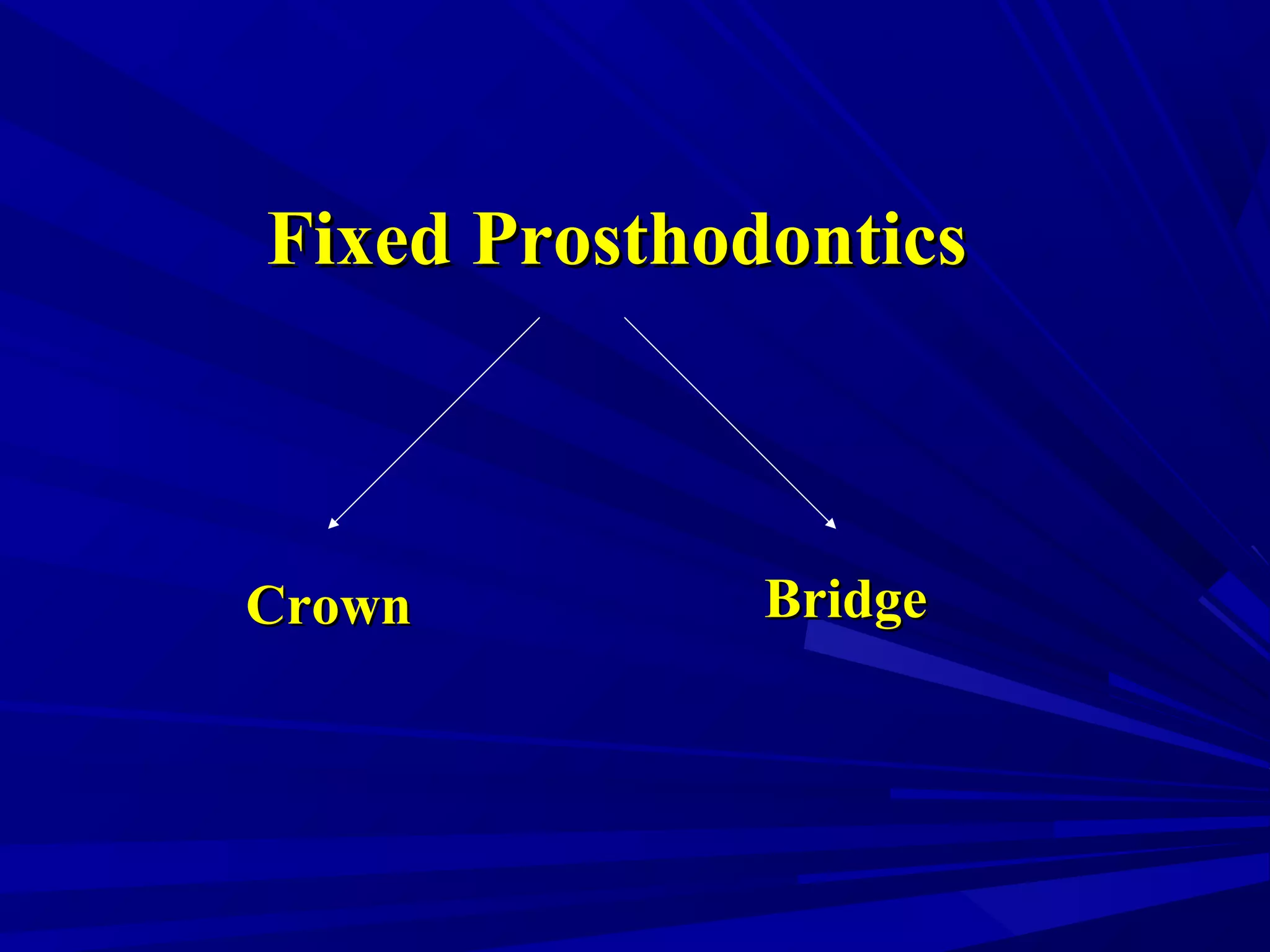
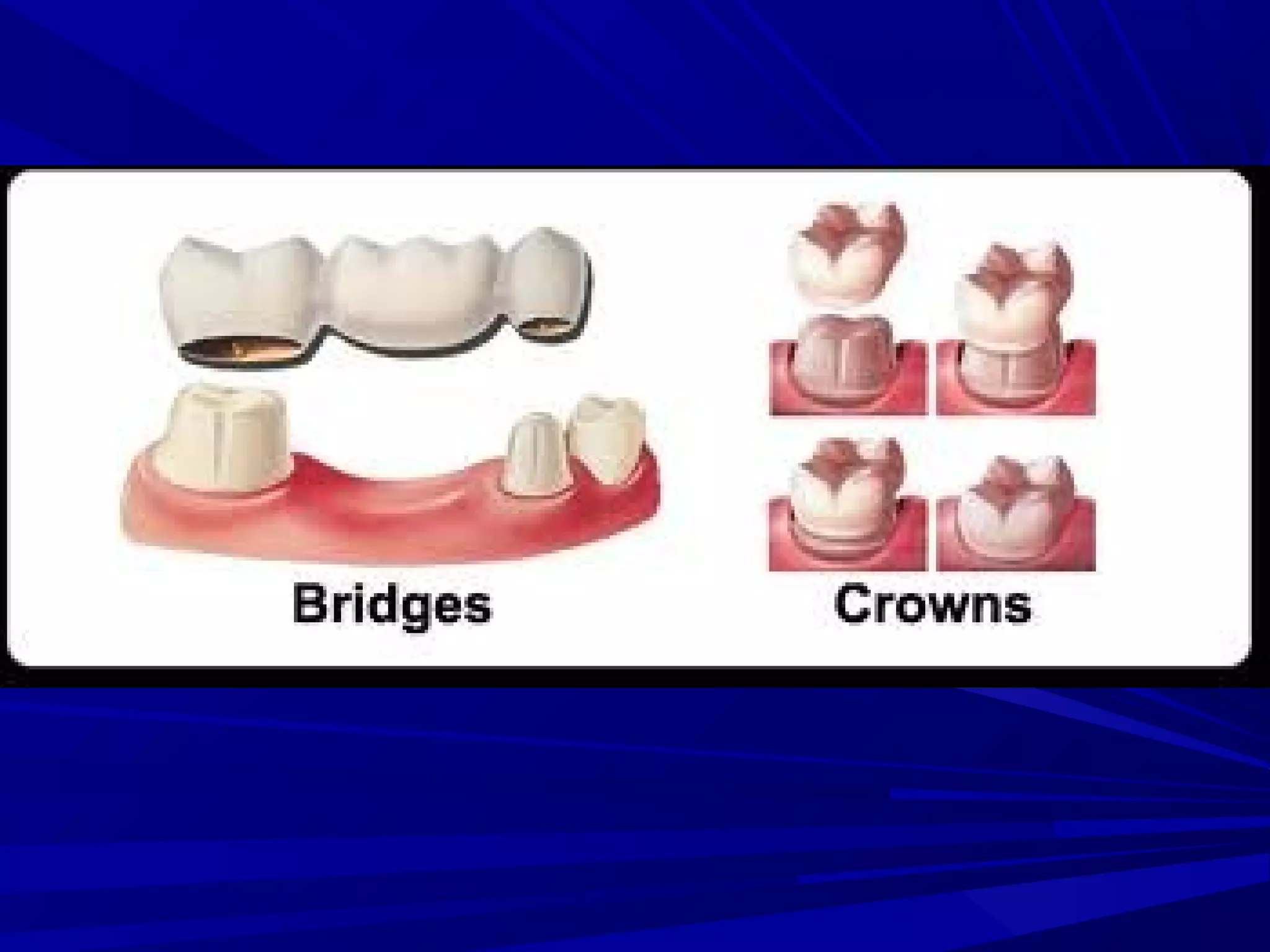
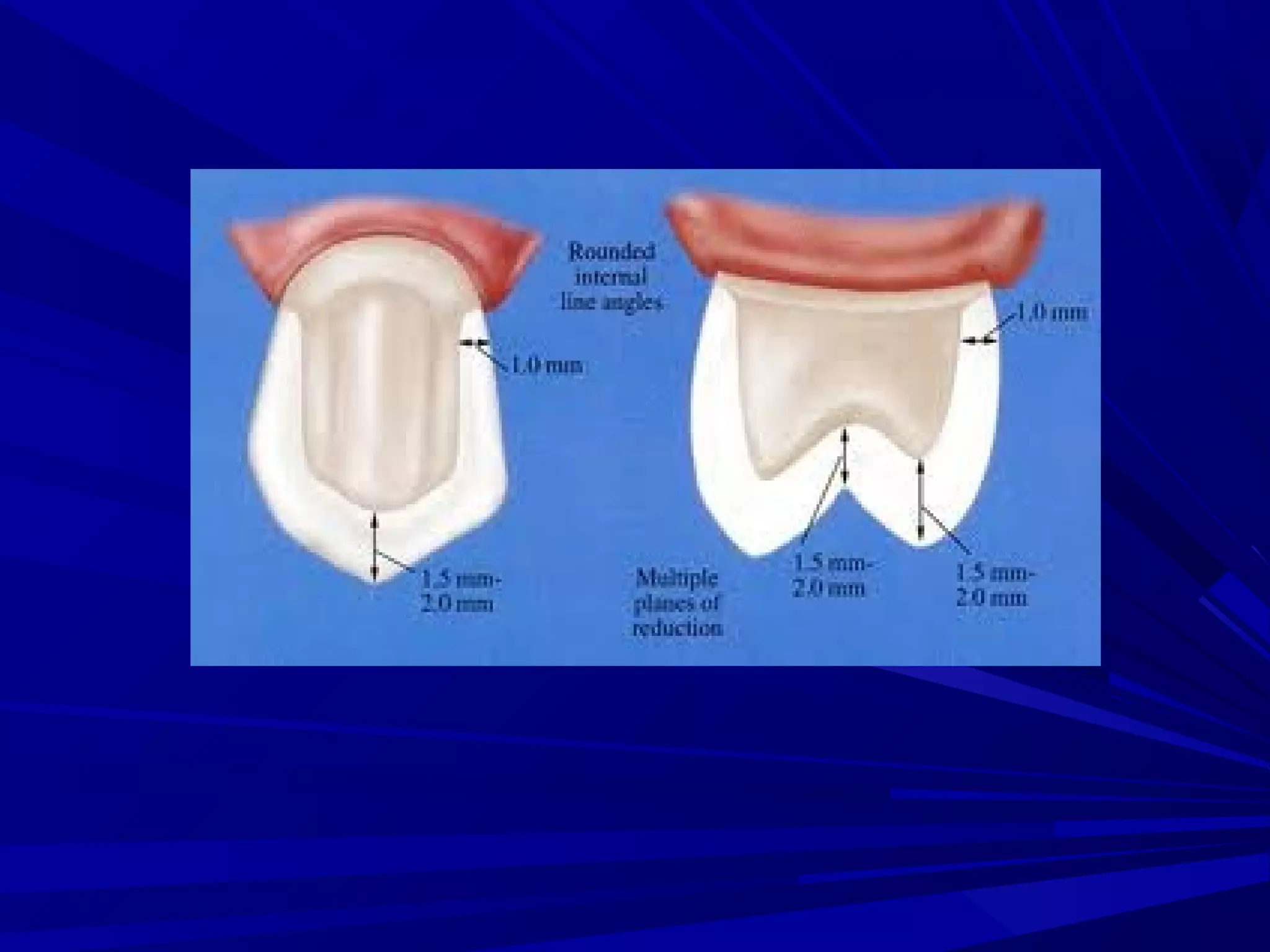
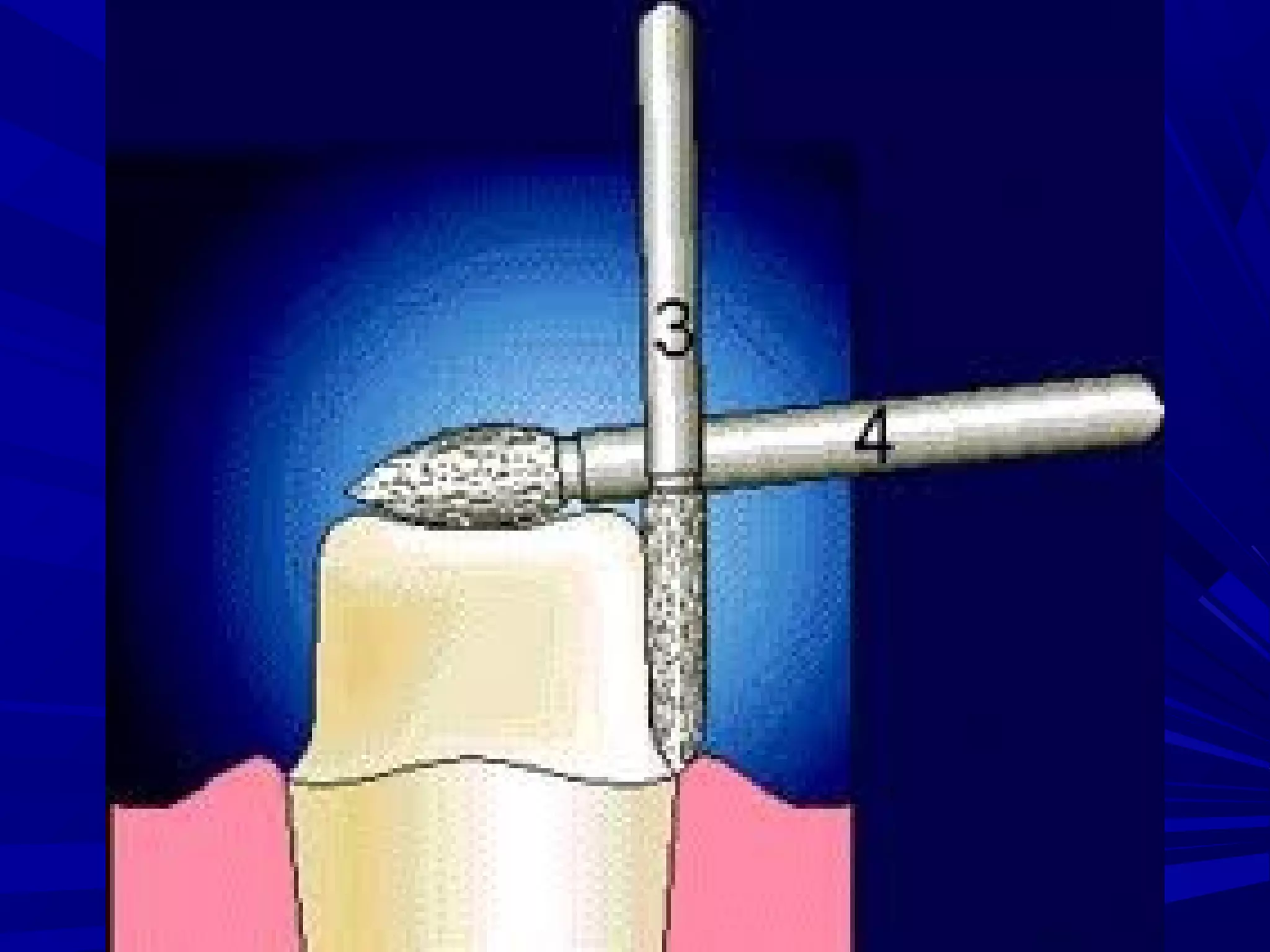
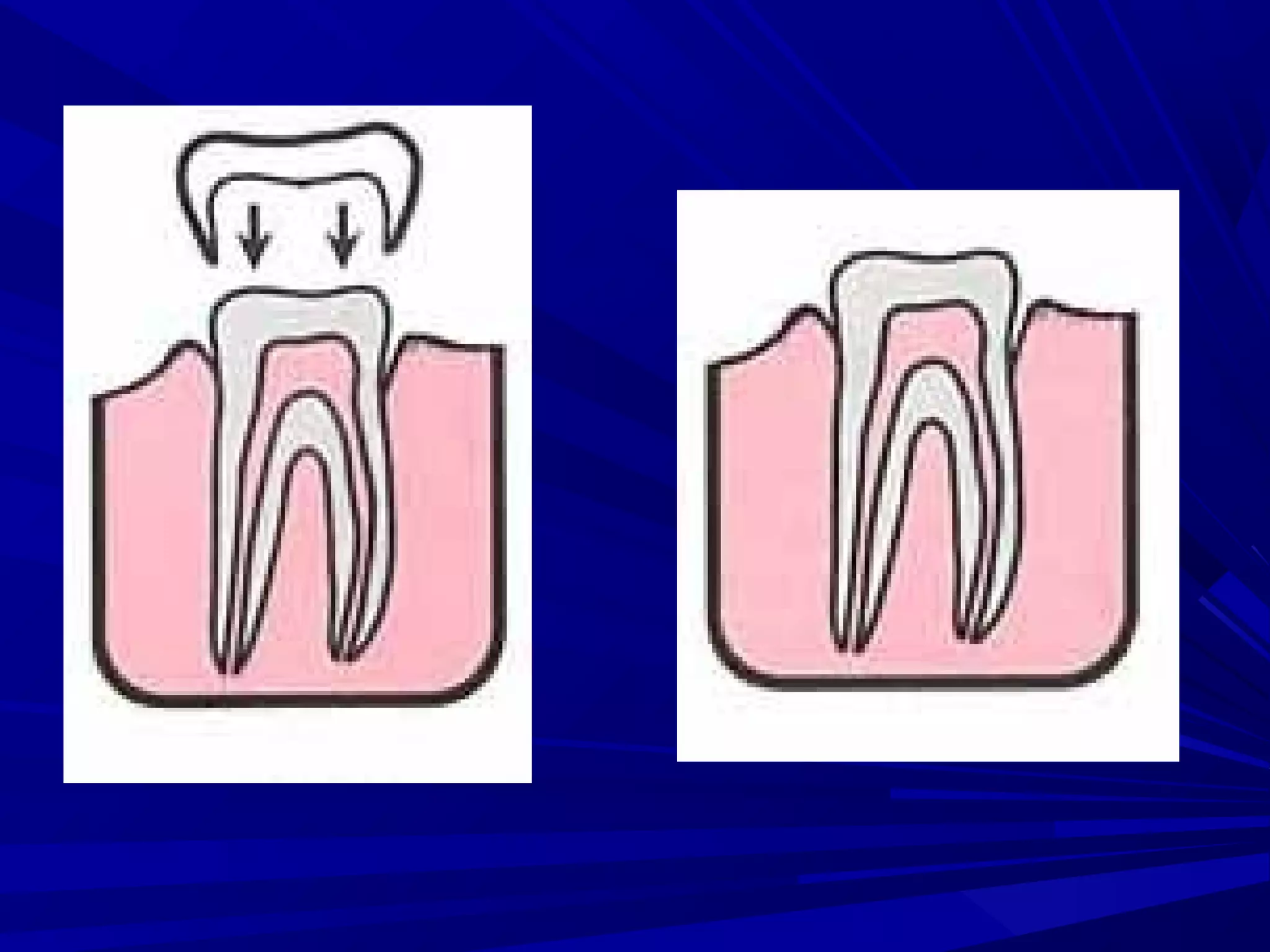
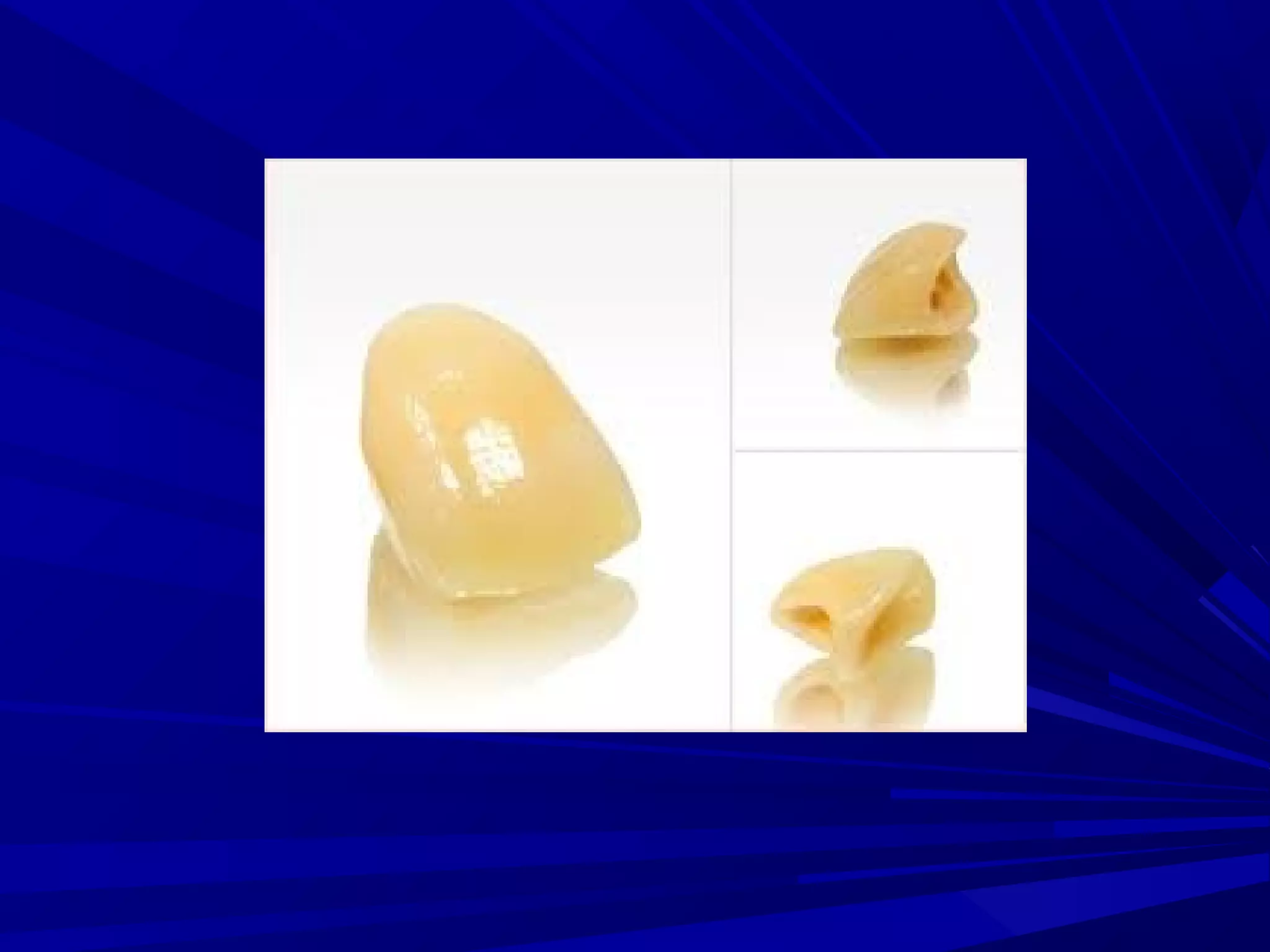
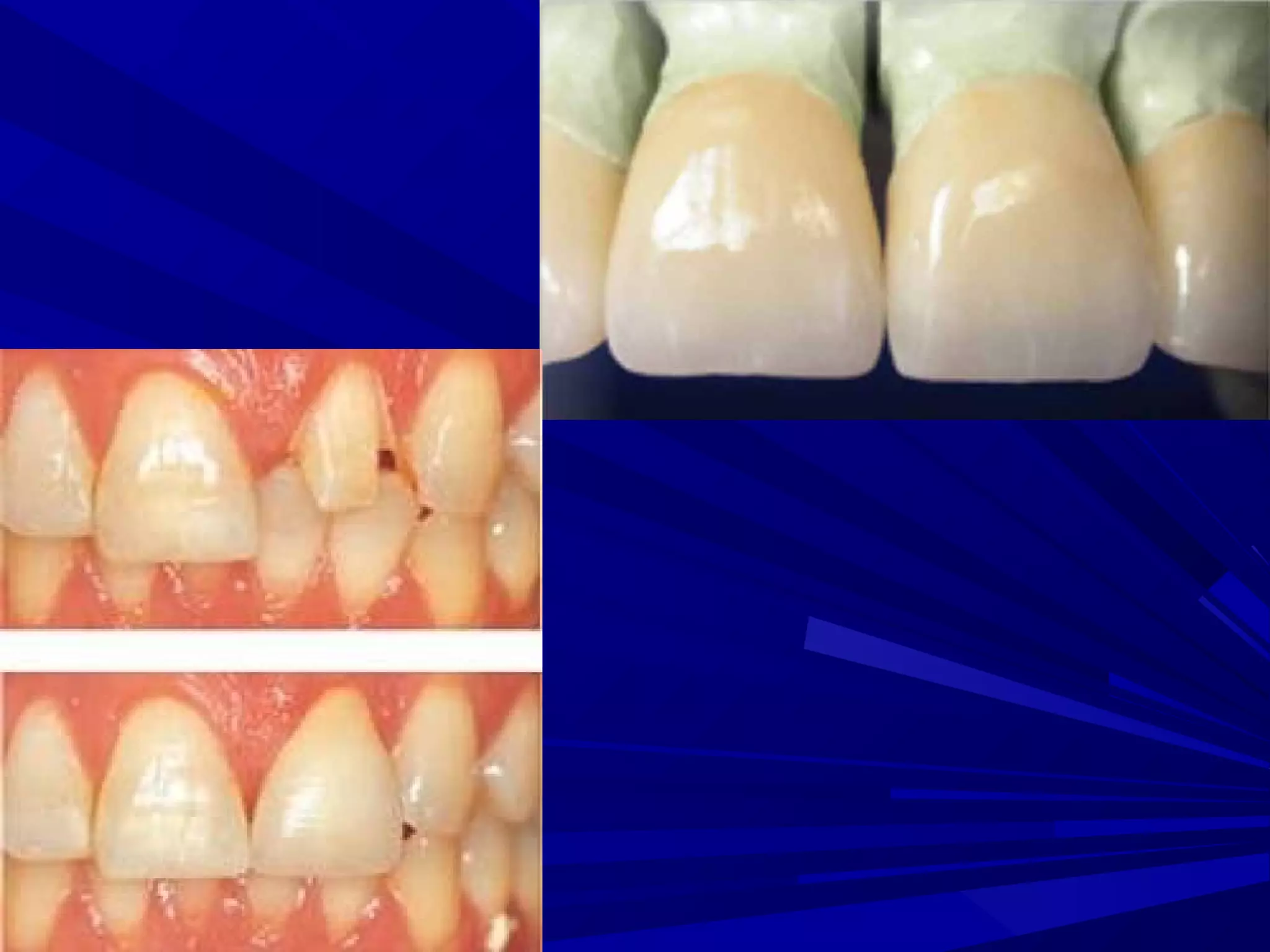
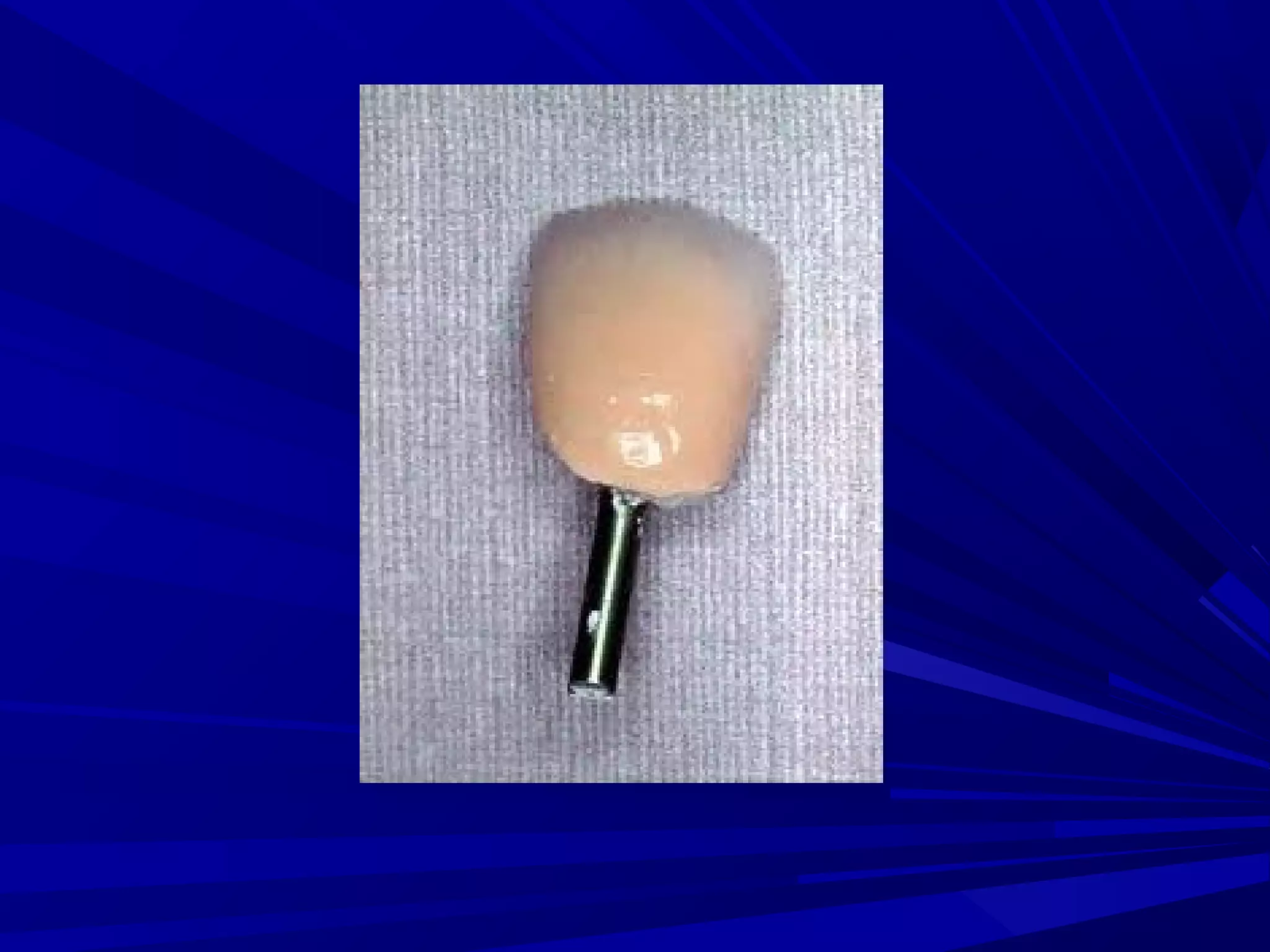
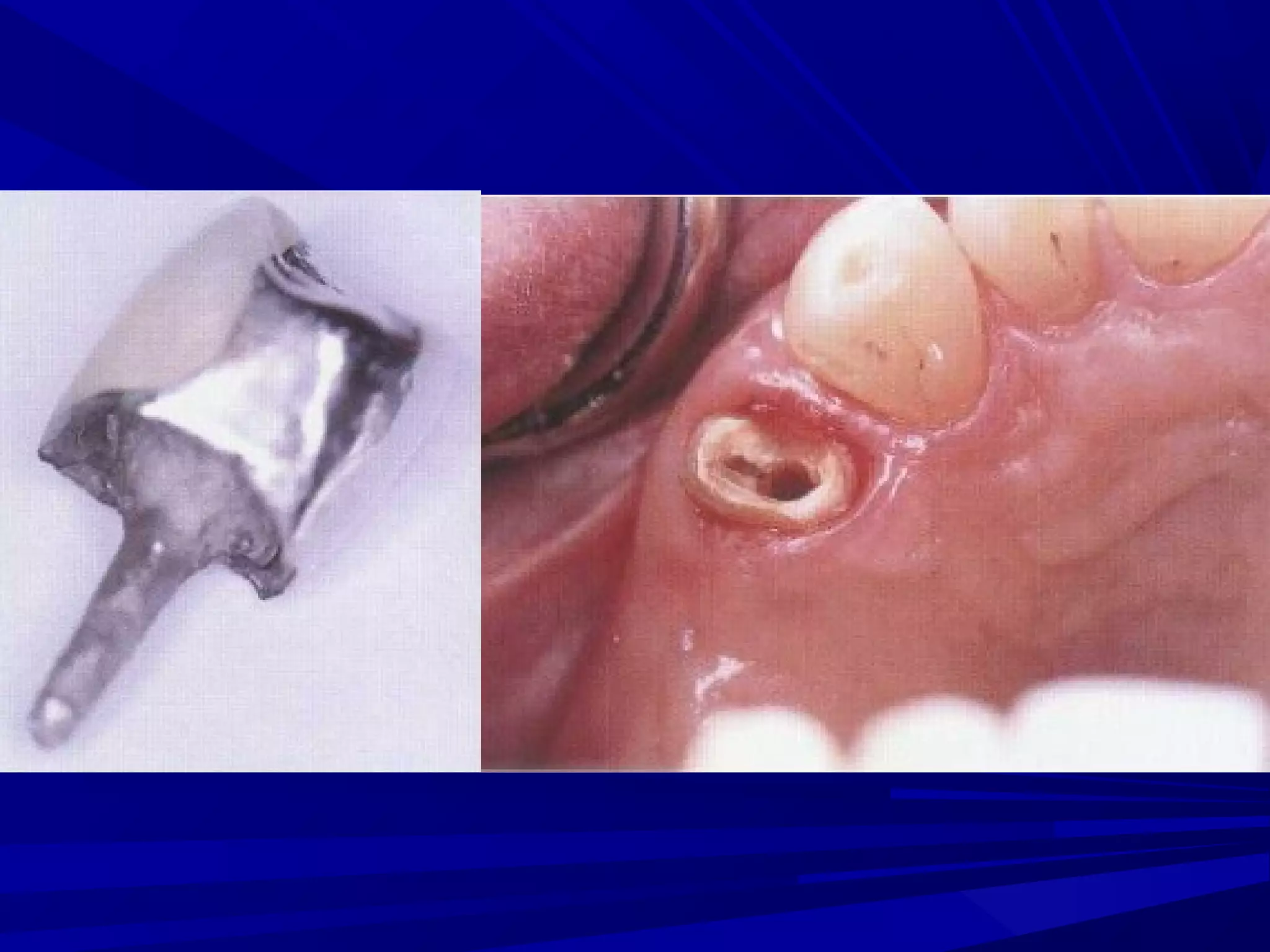
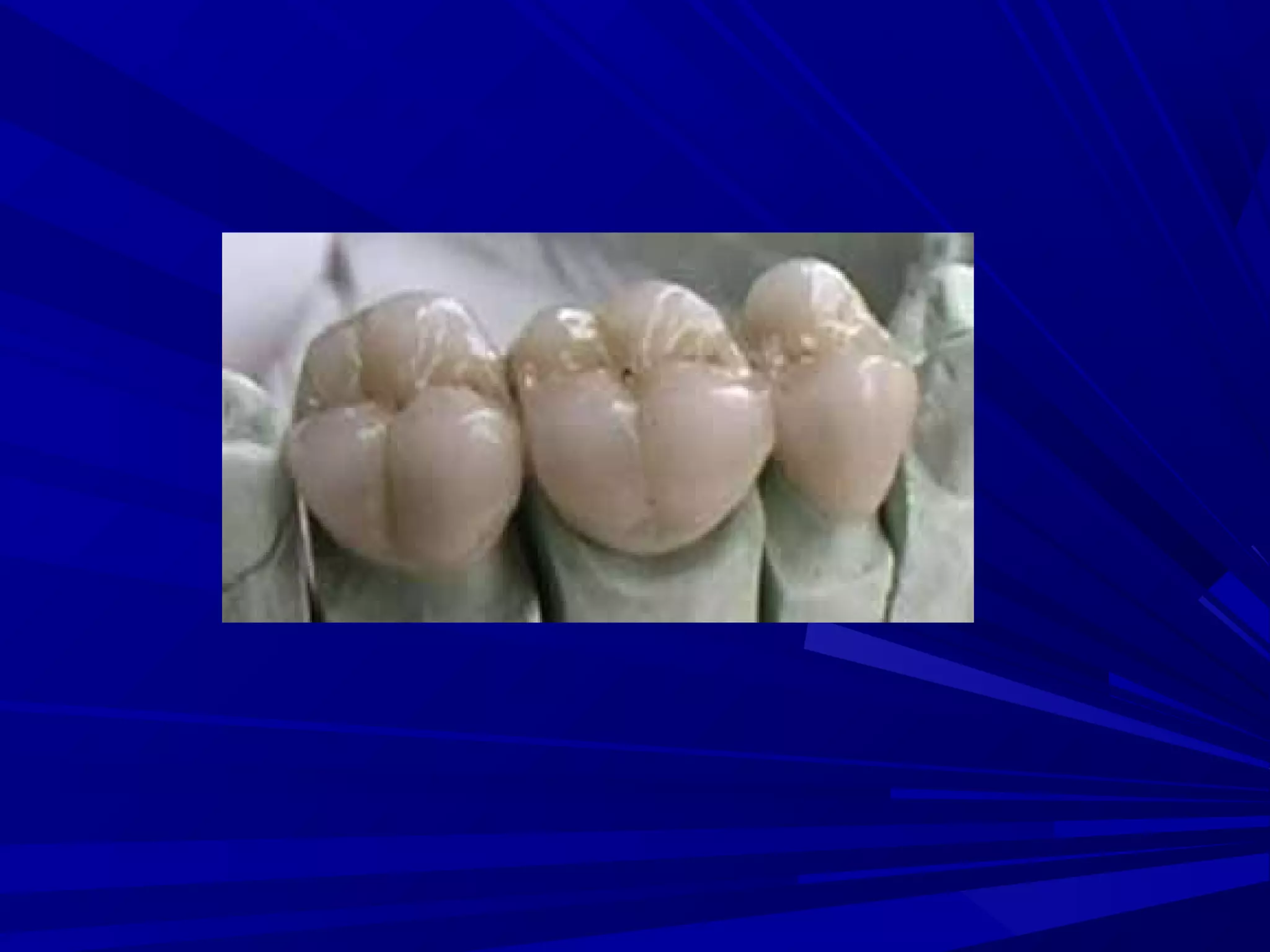
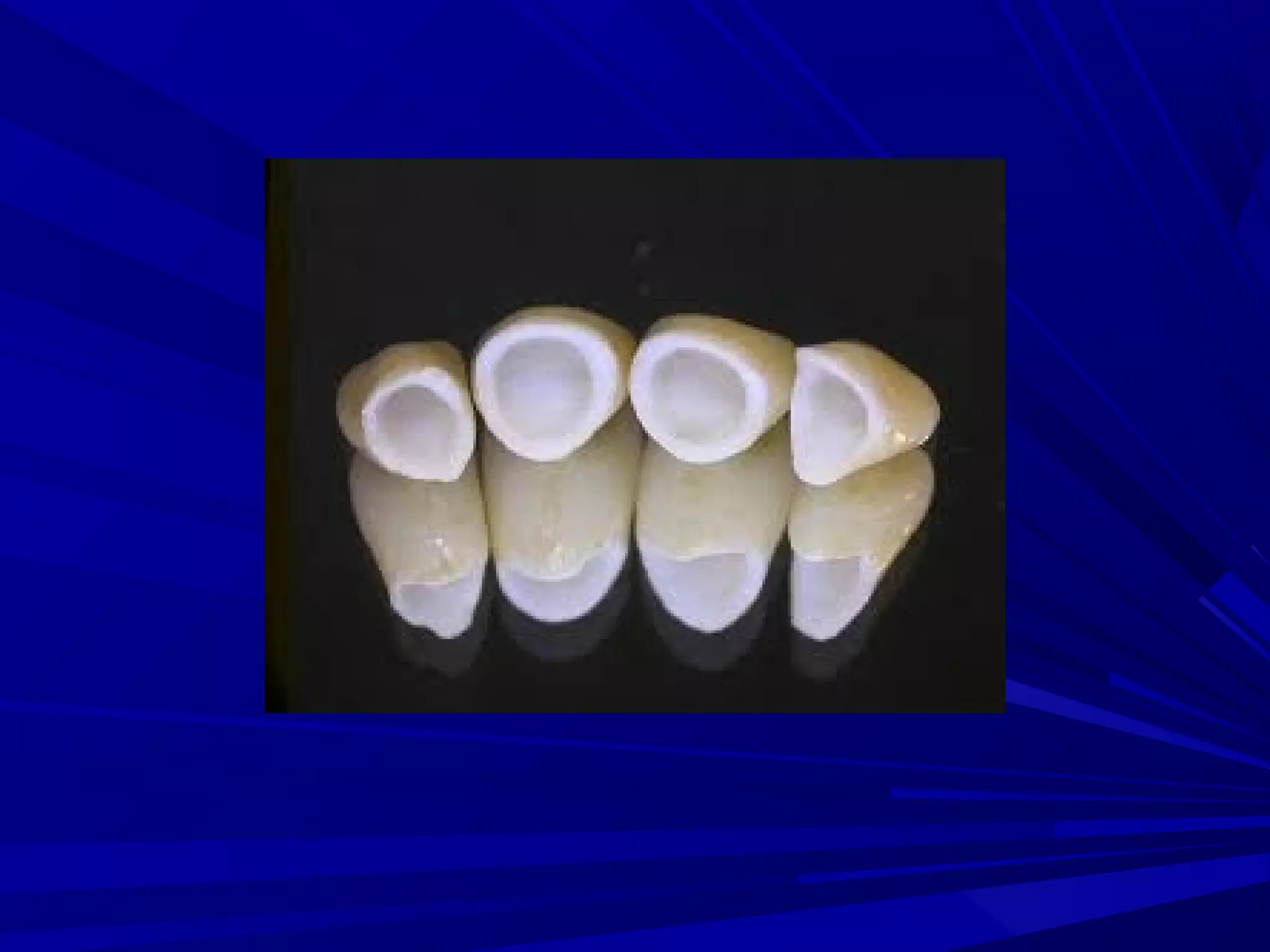
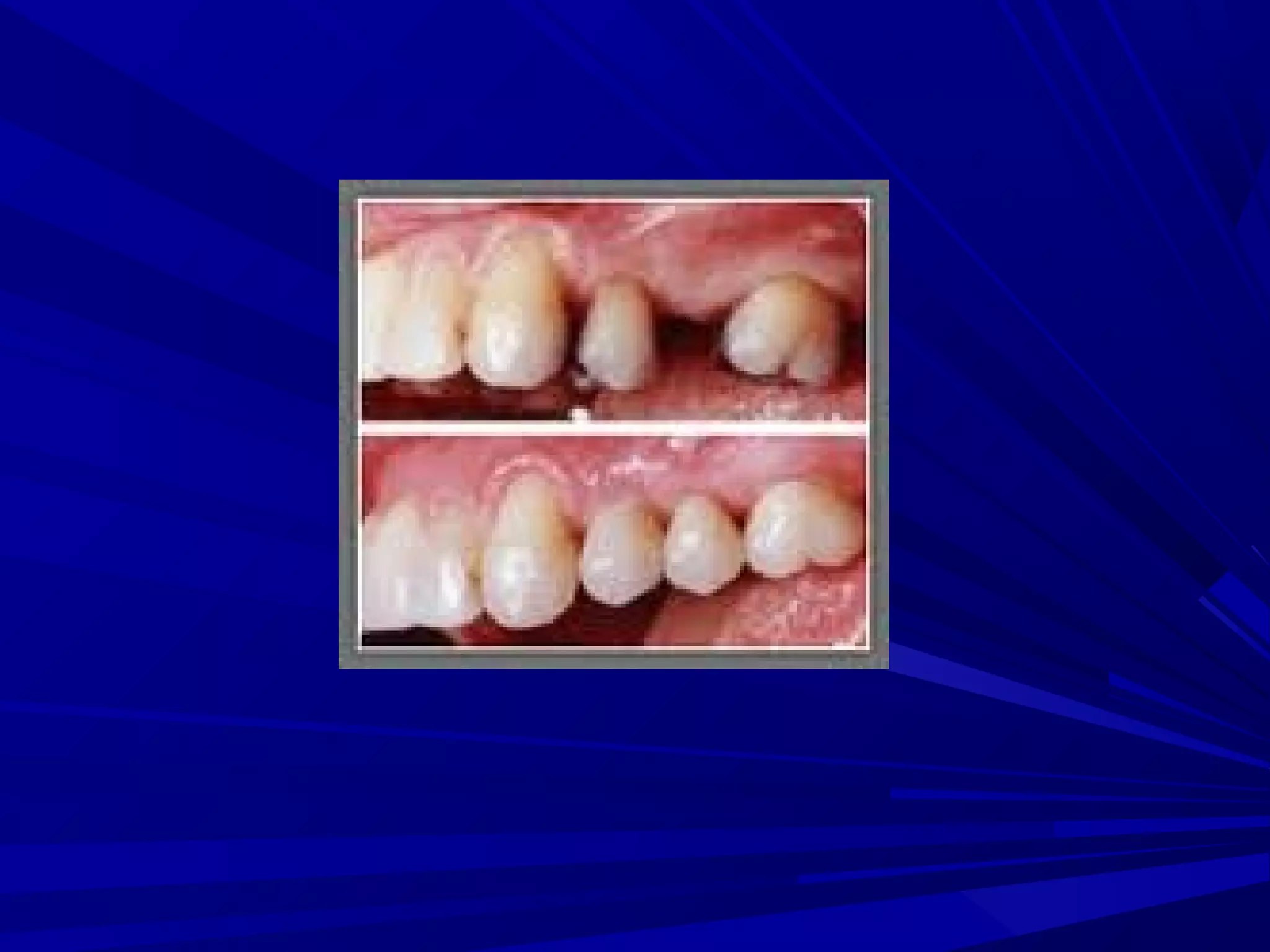
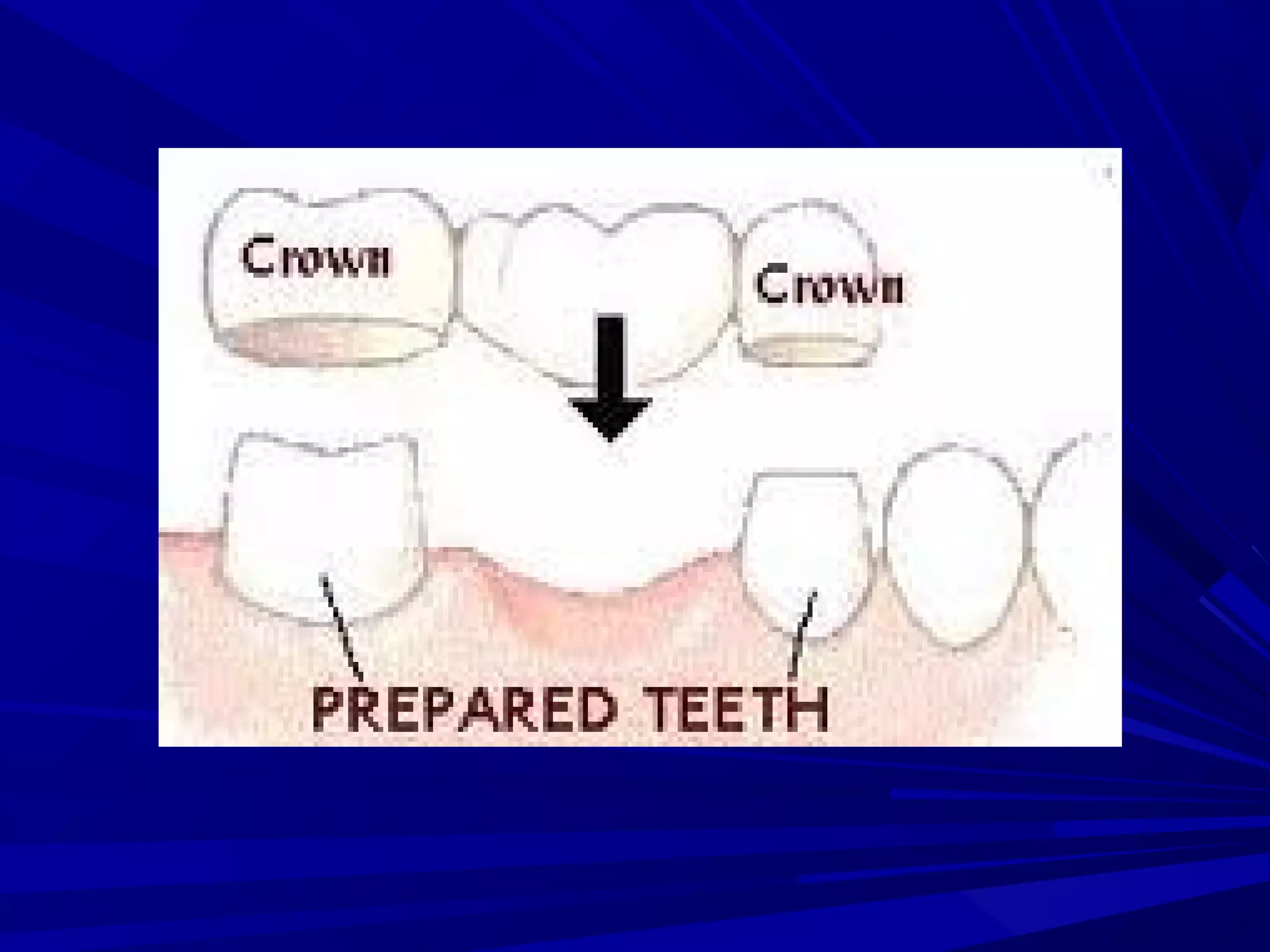
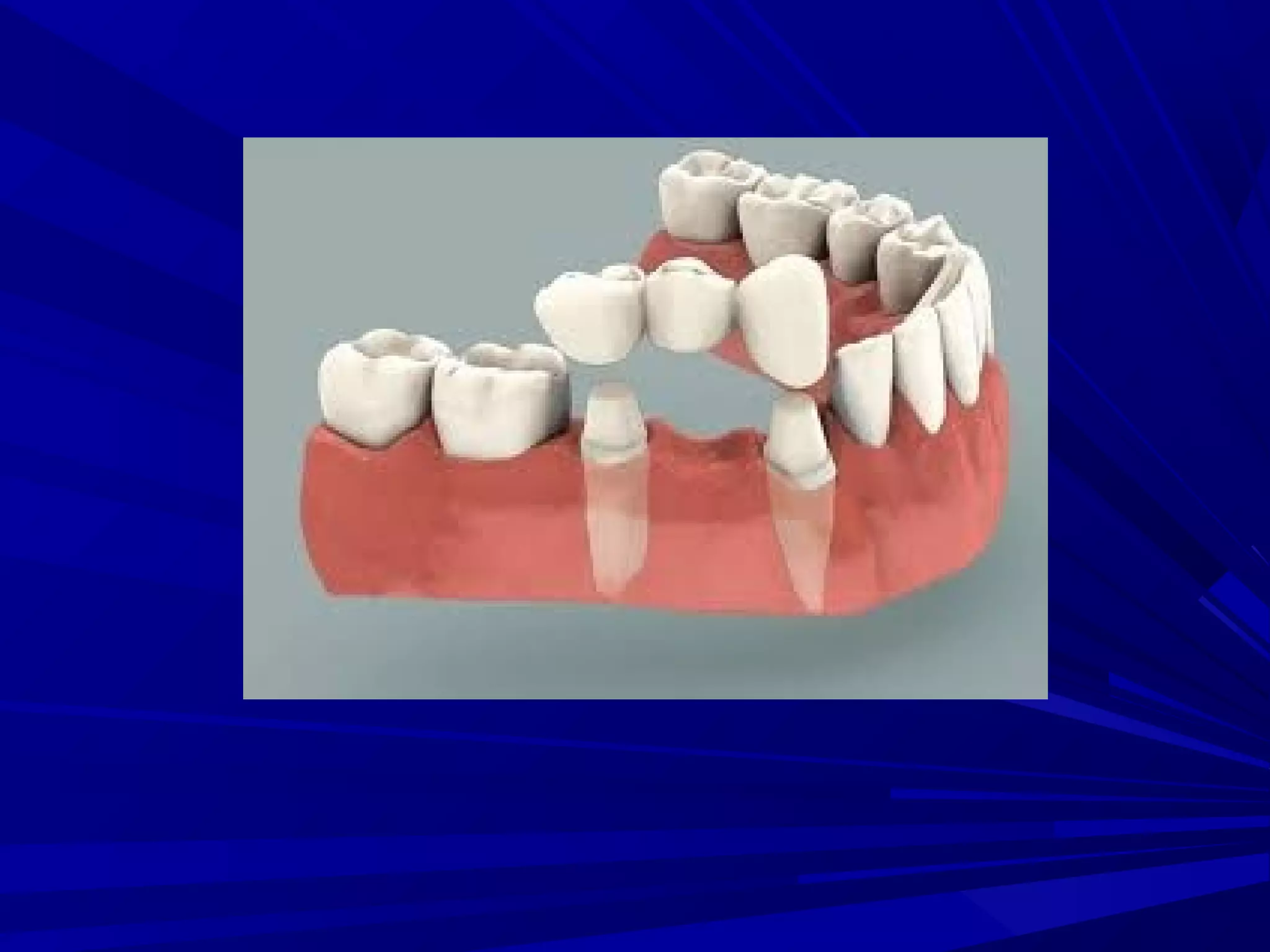
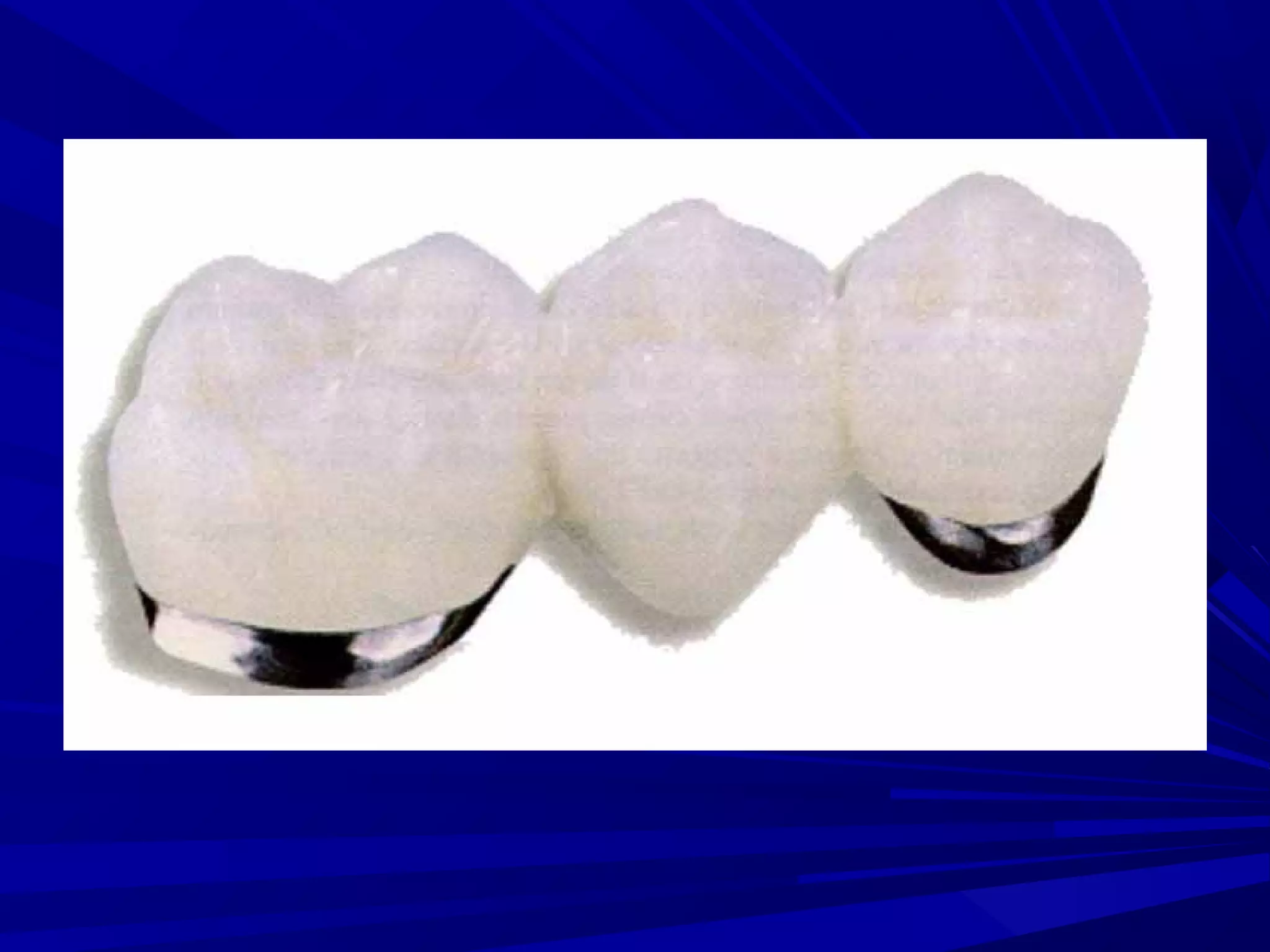
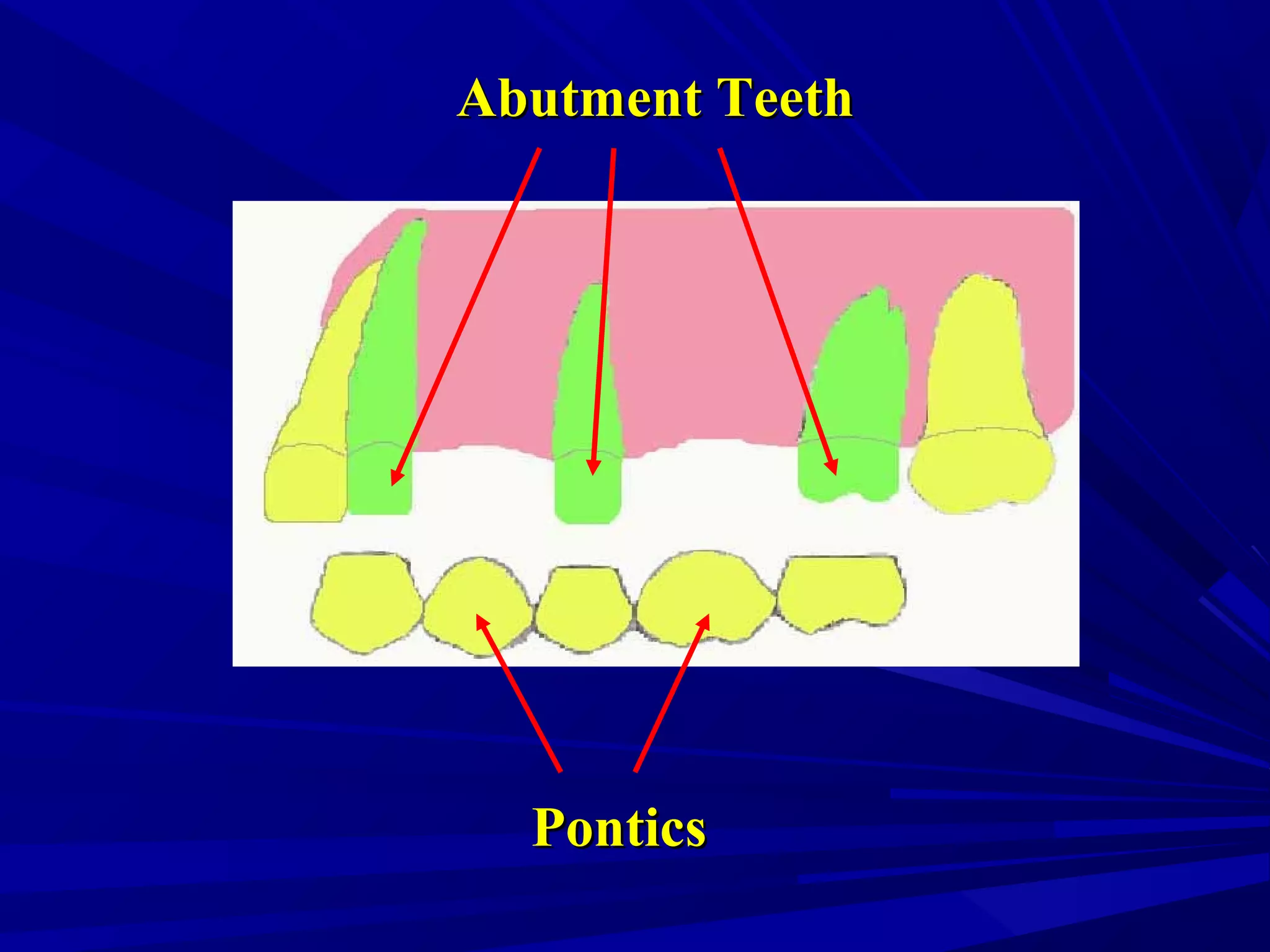
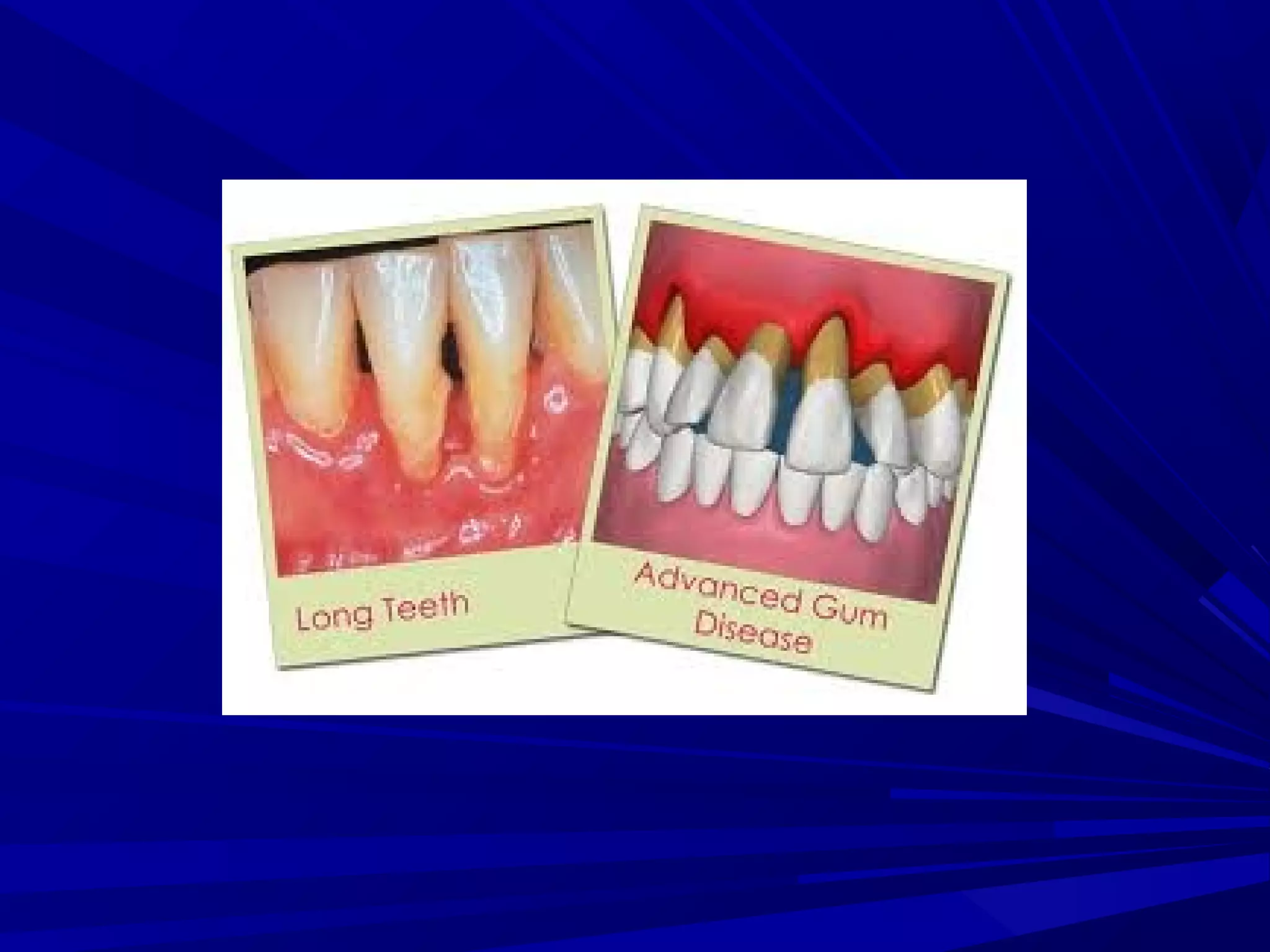
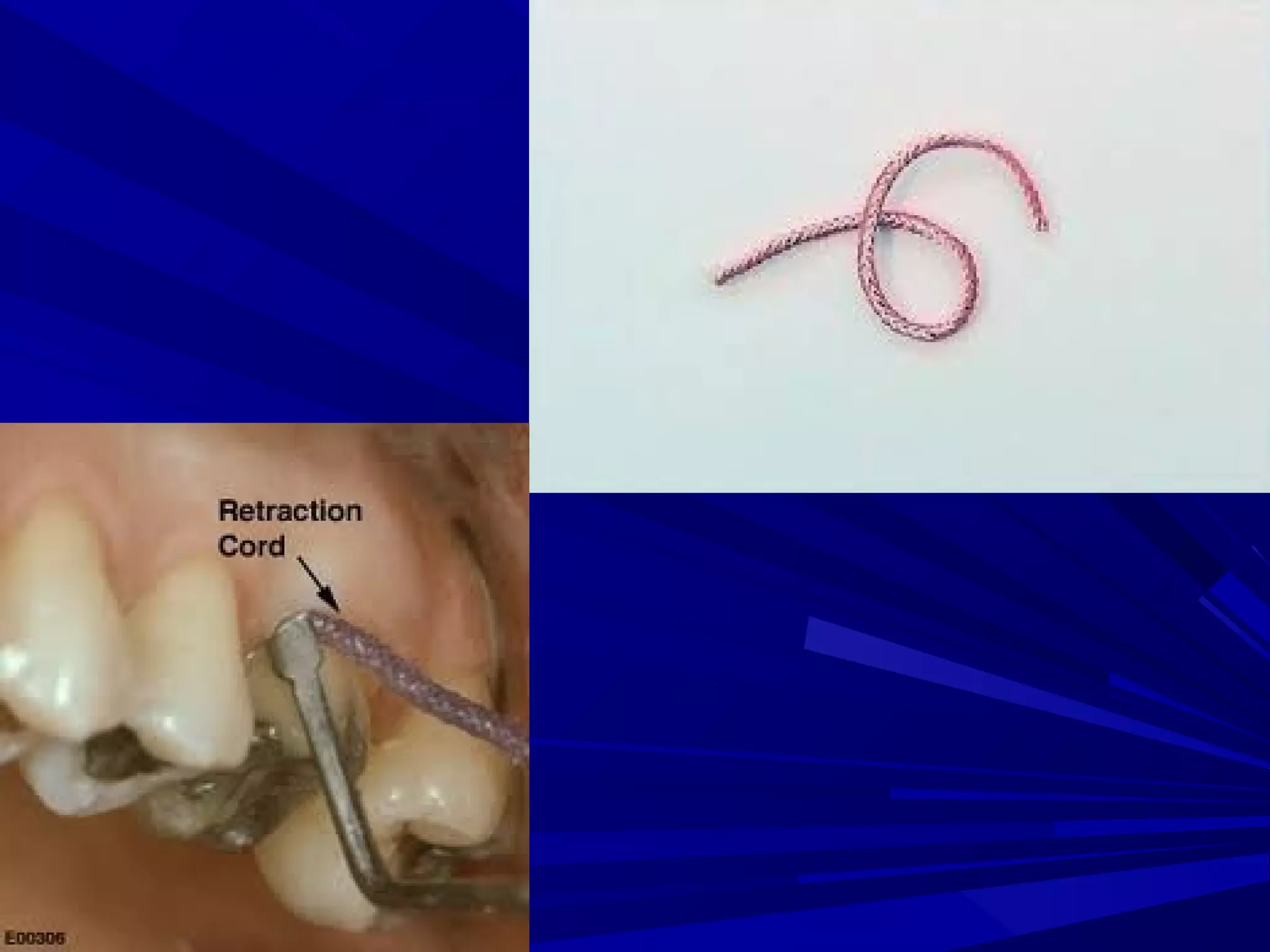
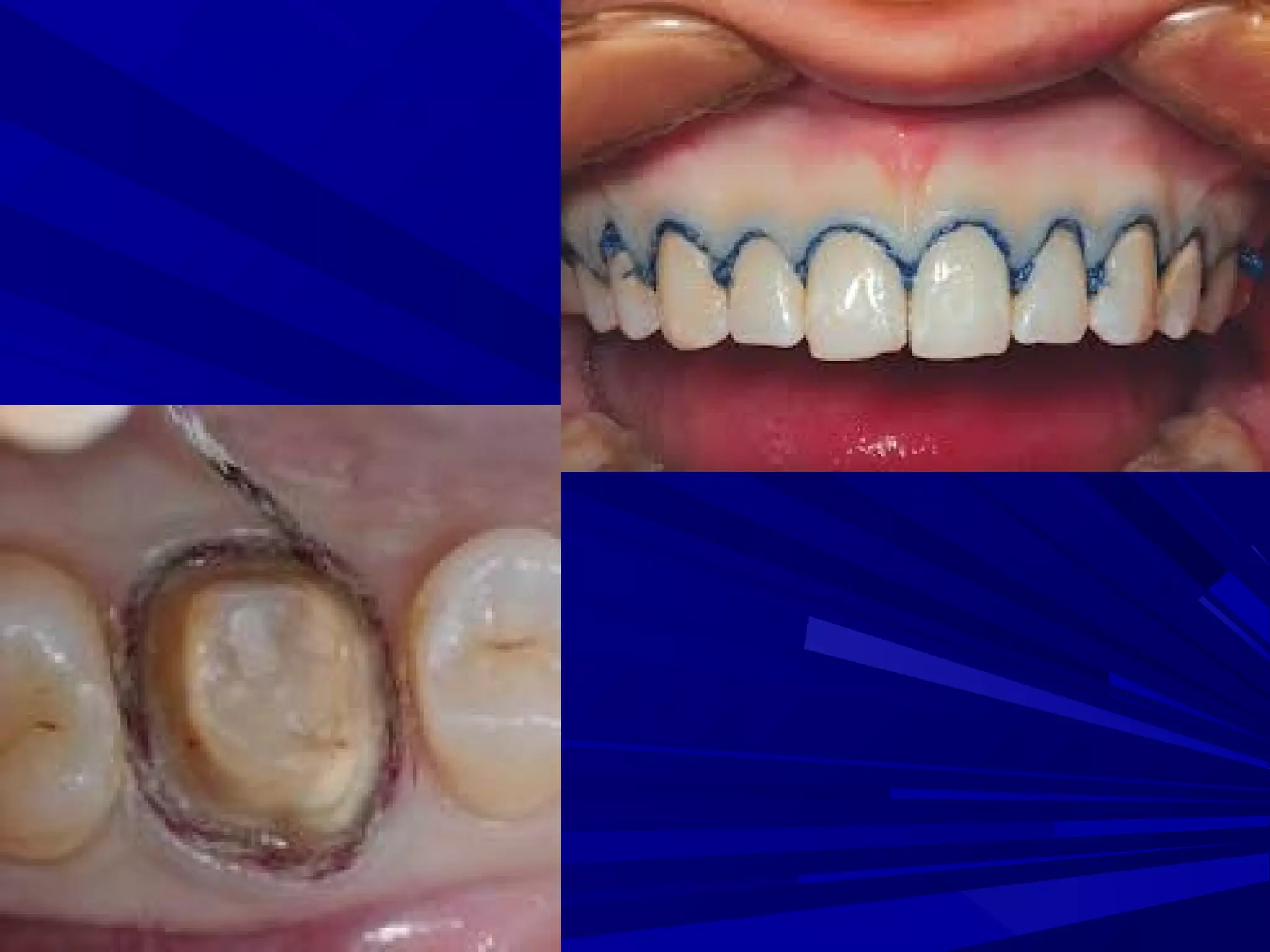
The document provides an overview of fixed prosthodontics, detailing its purpose of dental restoration for decayed or missing teeth with examples such as crowns, bridges, and veneers. It describes various types of crowns and bridges, their components, and the requirements for candidates considering fixed prosthodontics. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of proper oral hygiene and the process of creating these prosthetics in dental laboratories.