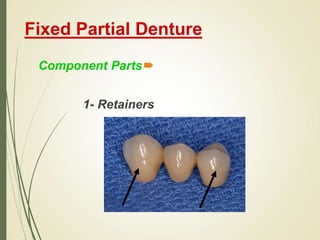
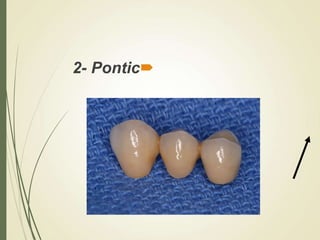
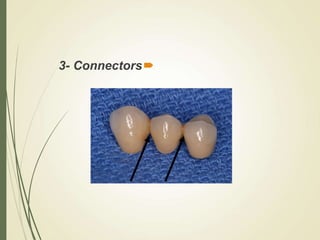
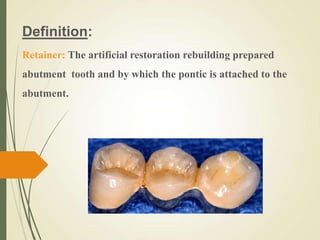
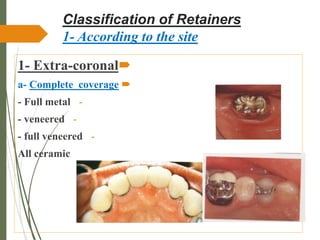
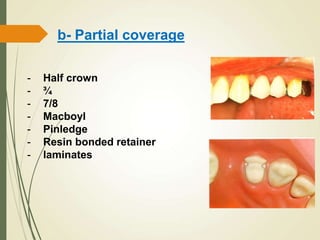
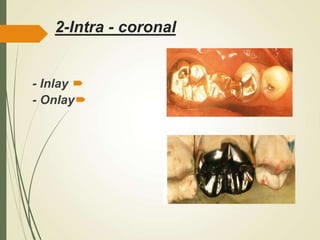
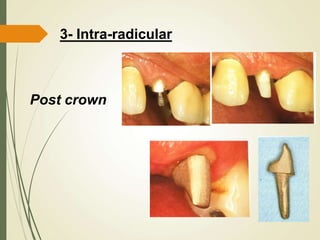
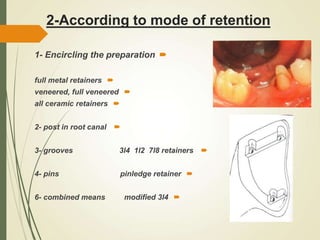
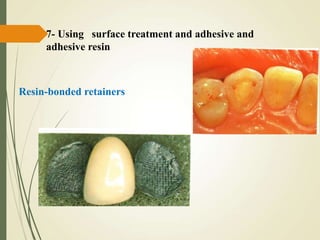
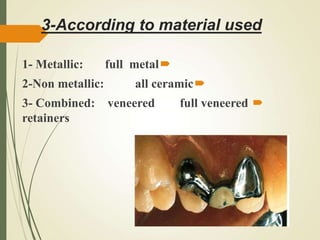
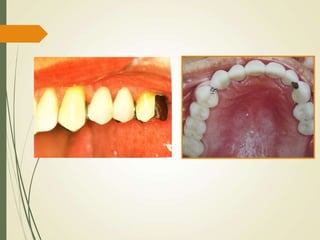
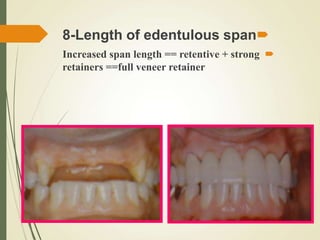
This document discusses fixed partial dentures and their components. It defines retainers as the artificial restorations that rebuild prepared abutment teeth and attach the pontic. There are different types of retainers classified by site (extra-coronal vs intra-coronal) and mode of retention. Complete coverage retainers provide more resistance but can endanger the pulp, while partial coverage retainers are more conservative but less retentive. The selection of retainers depends on factors like the abutment condition, esthetics, oral hygiene, patient age, occlusion, existing caries, and length of the edentulous span.