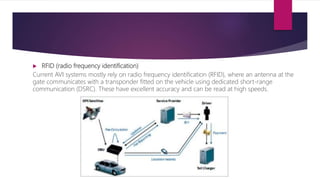
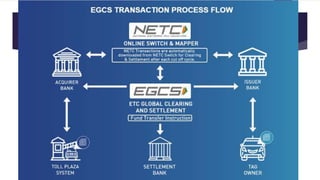
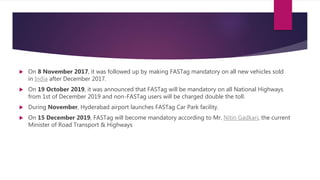
The document presents a comprehensive overview of Fastag, an electronic toll collection system in India that employs RFID technology to facilitate automatic toll payments while vehicles are in motion. It details the historical development of electronic tolling, the workings of Fastag, its advantages and disadvantages, as well as the timeline for its implementation across Indian highways. Additionally, it outlines the objectives of the National Electronic Toll Collection (NETC) program and provides information on how to obtain a Fastag.