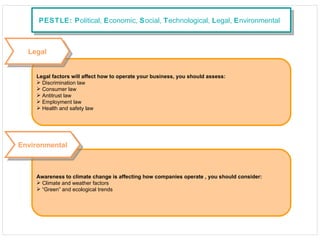
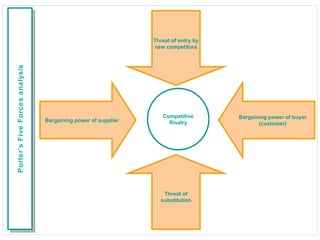
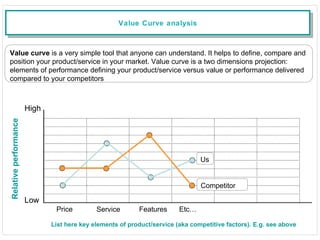
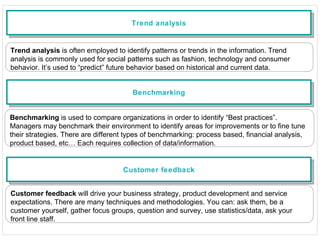
The document discusses various change management tools, including SWOT, PESTLE, Porter's Five Forces, value curve analysis, trend analysis, benchmarking, and customer feedback. It outlines each tool's purpose and applicability in assessing business environments and strategic planning. The overarching recommendation is to regularly monitor and evaluate the external environment using multiple methodologies for better decision-making.