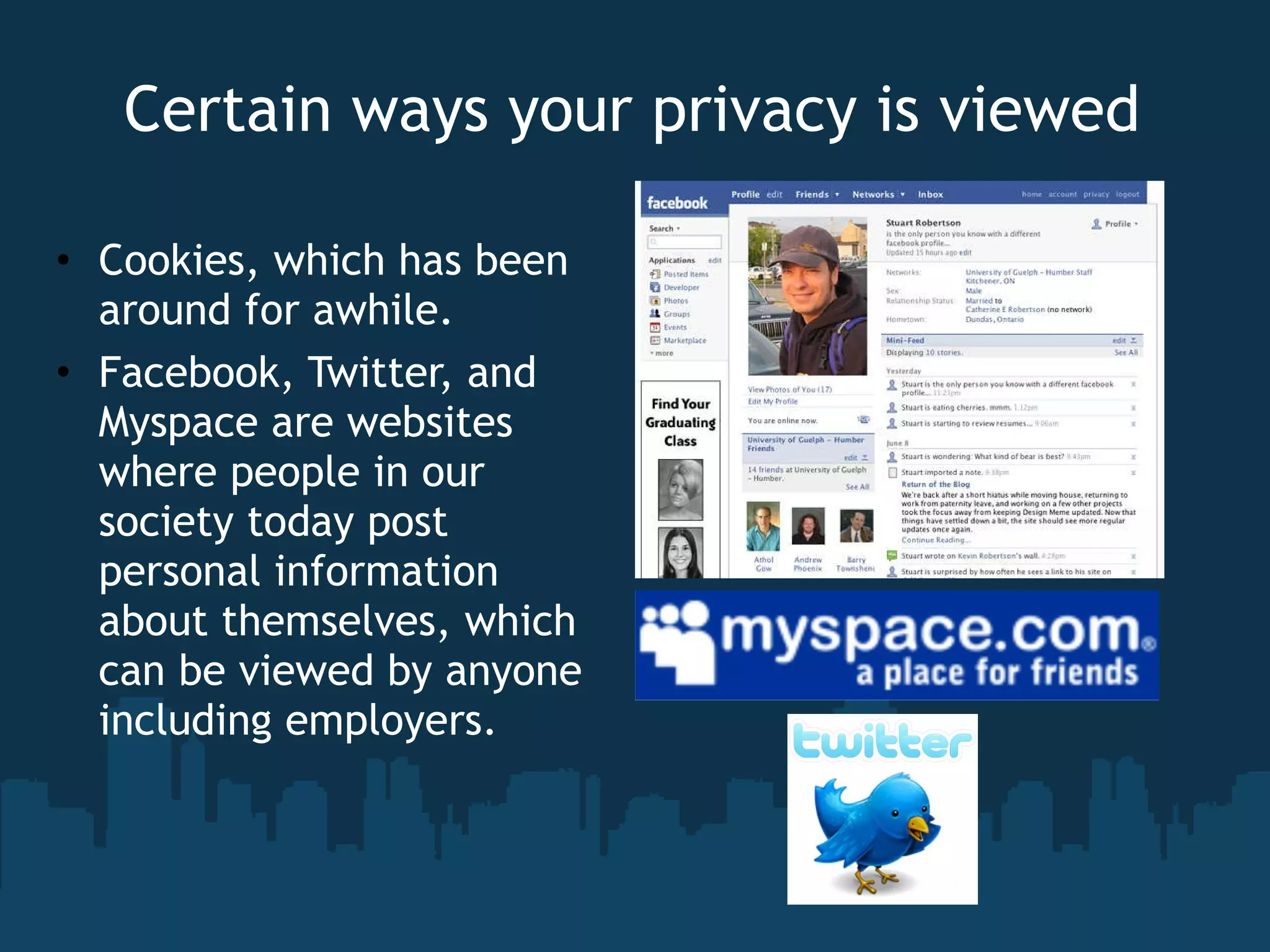
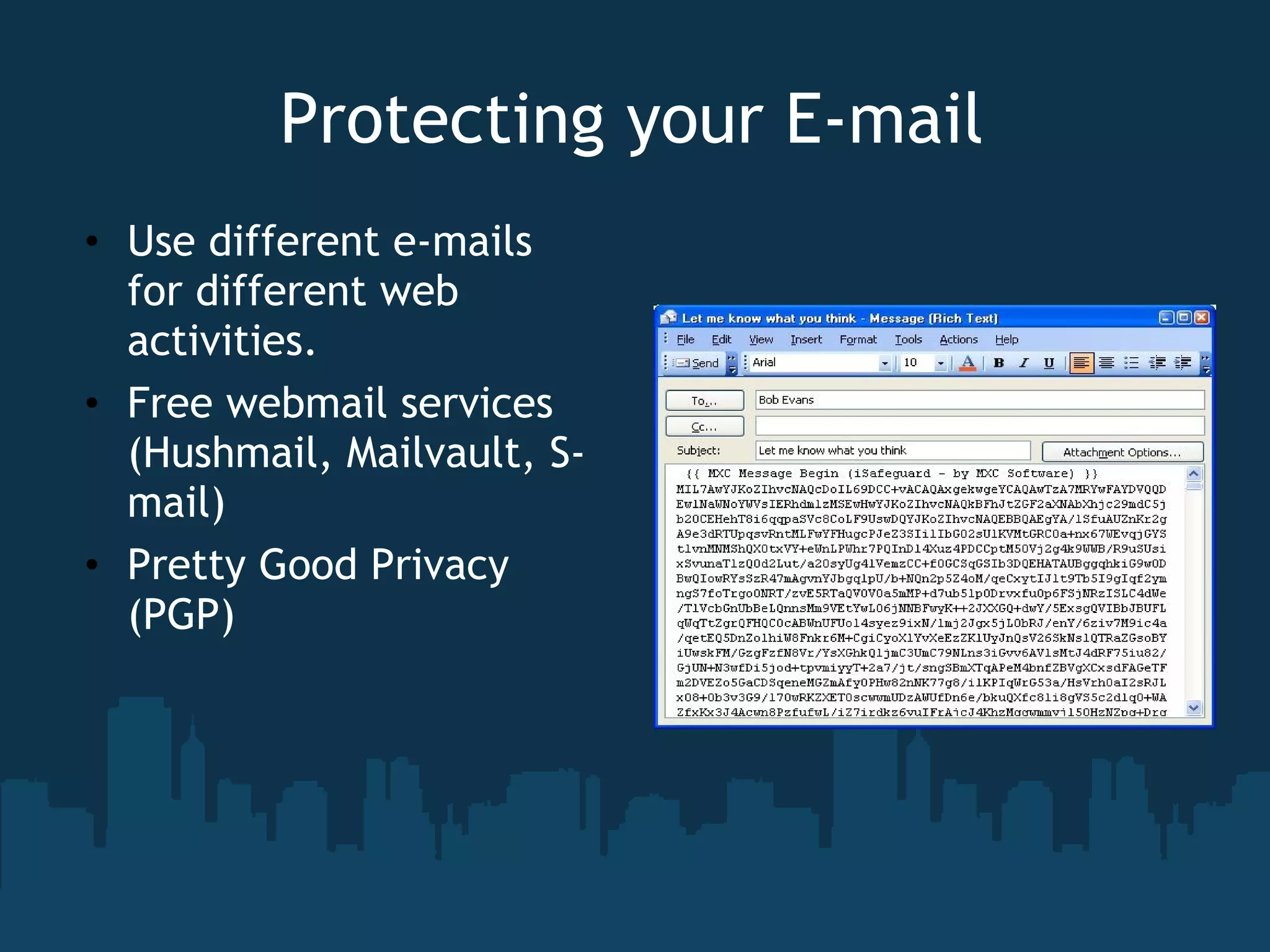
The document discusses the topic of computer privacy and provides information on its history, current legislation, and future concerns. It notes several data breaches that have exposed personal information of millions of individuals. Finally, it offers tips on protecting privacy such as using antivirus software, browser security add-ons, and anonymizing browsers.