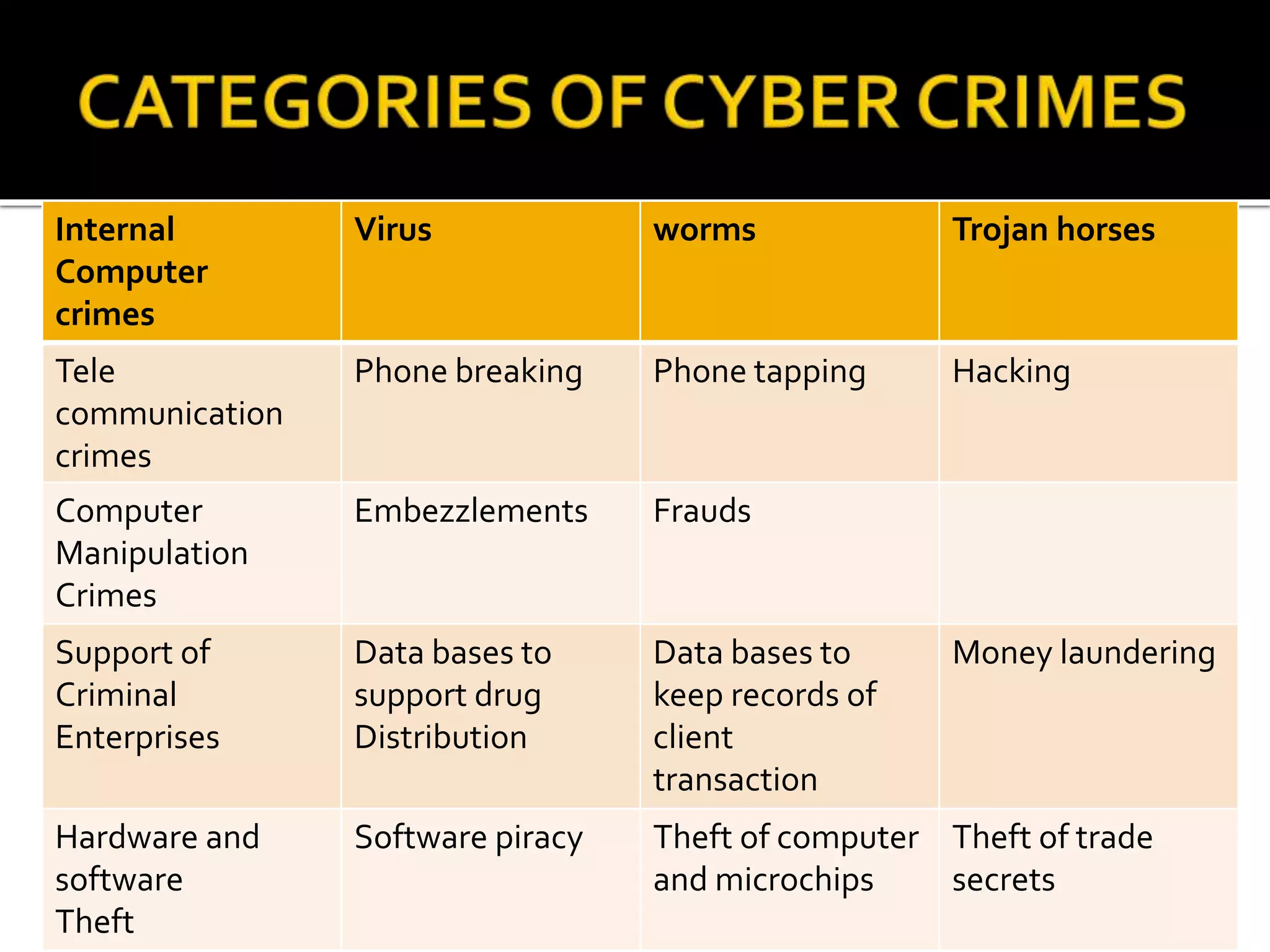
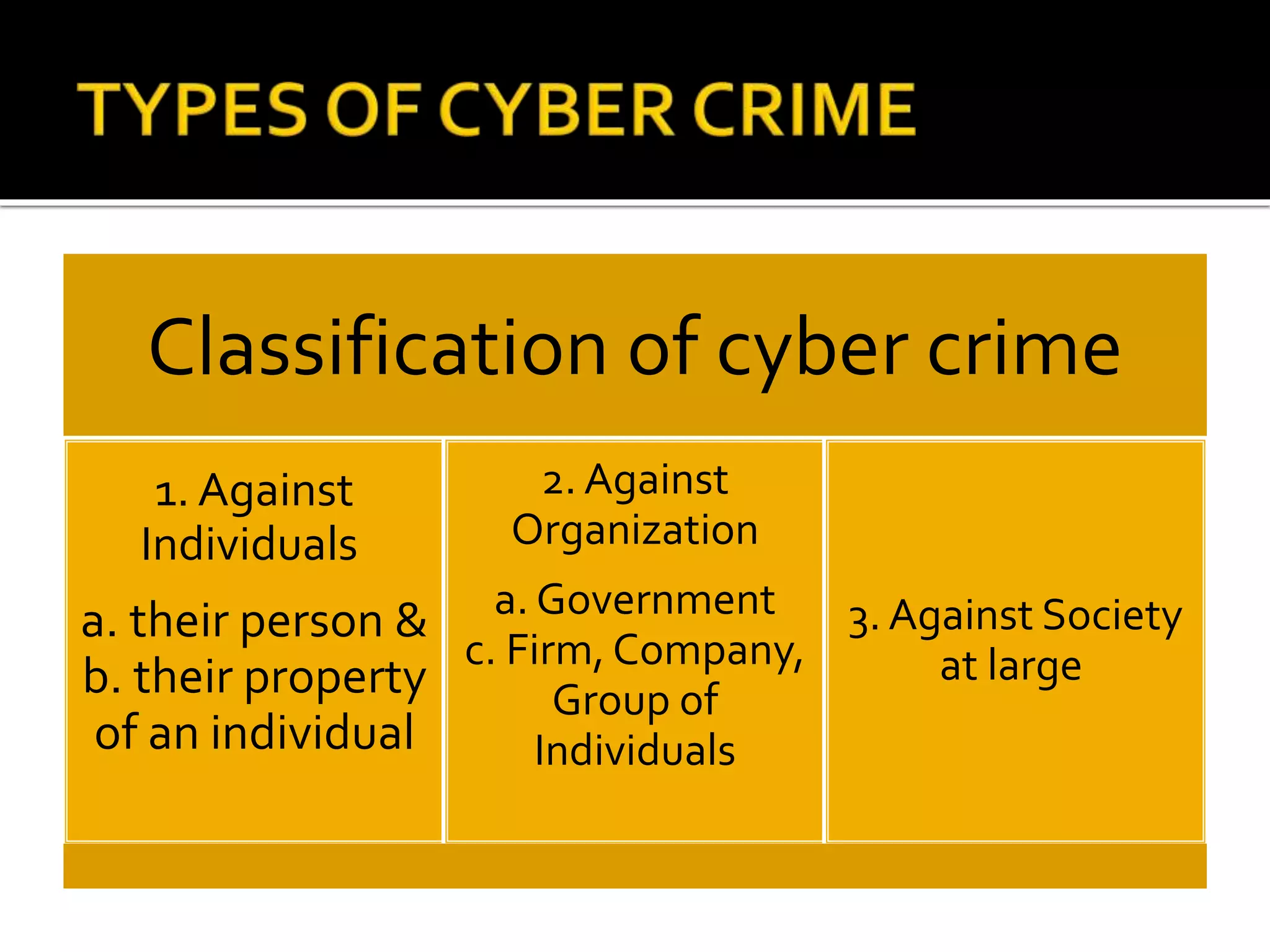
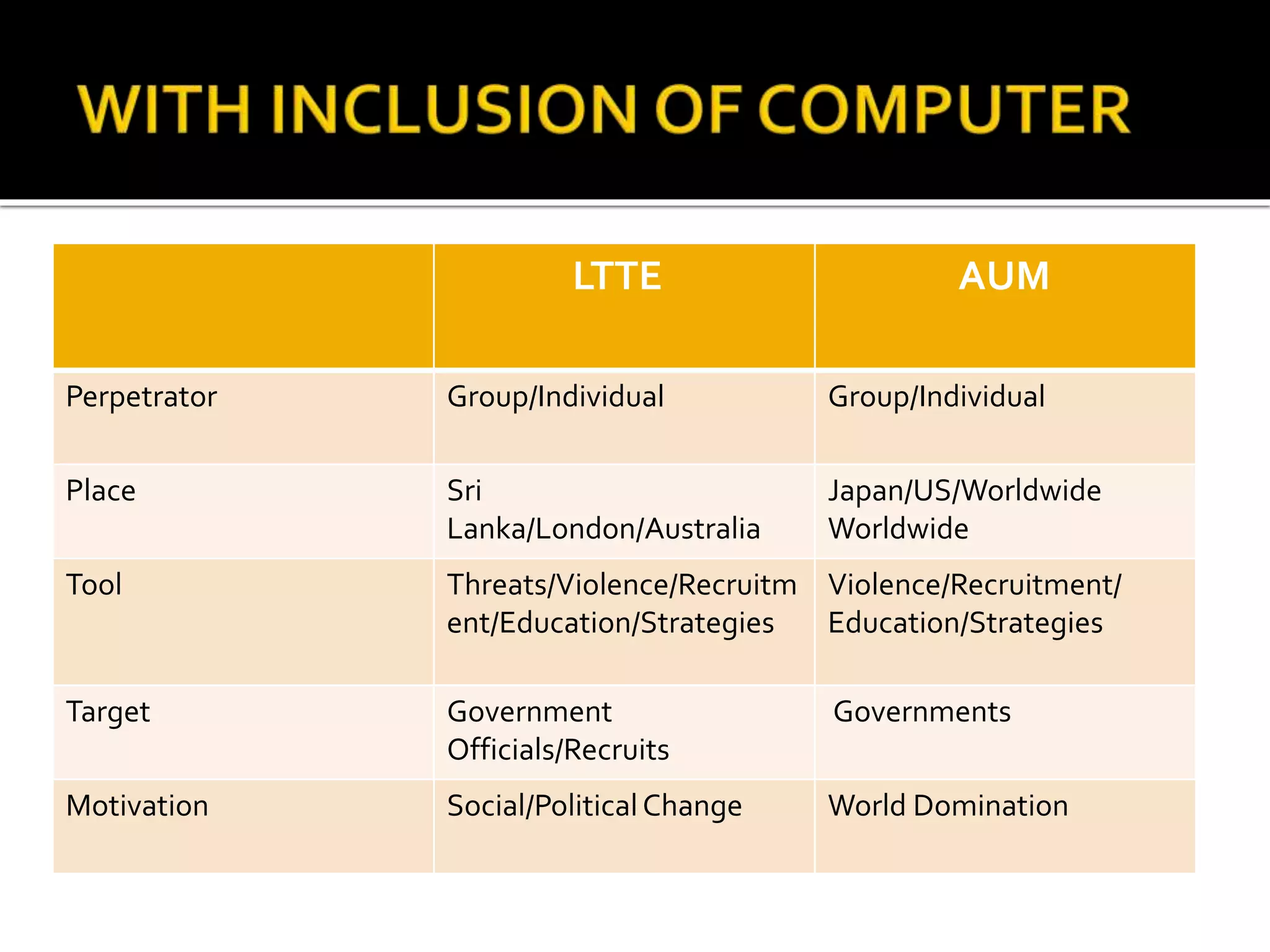
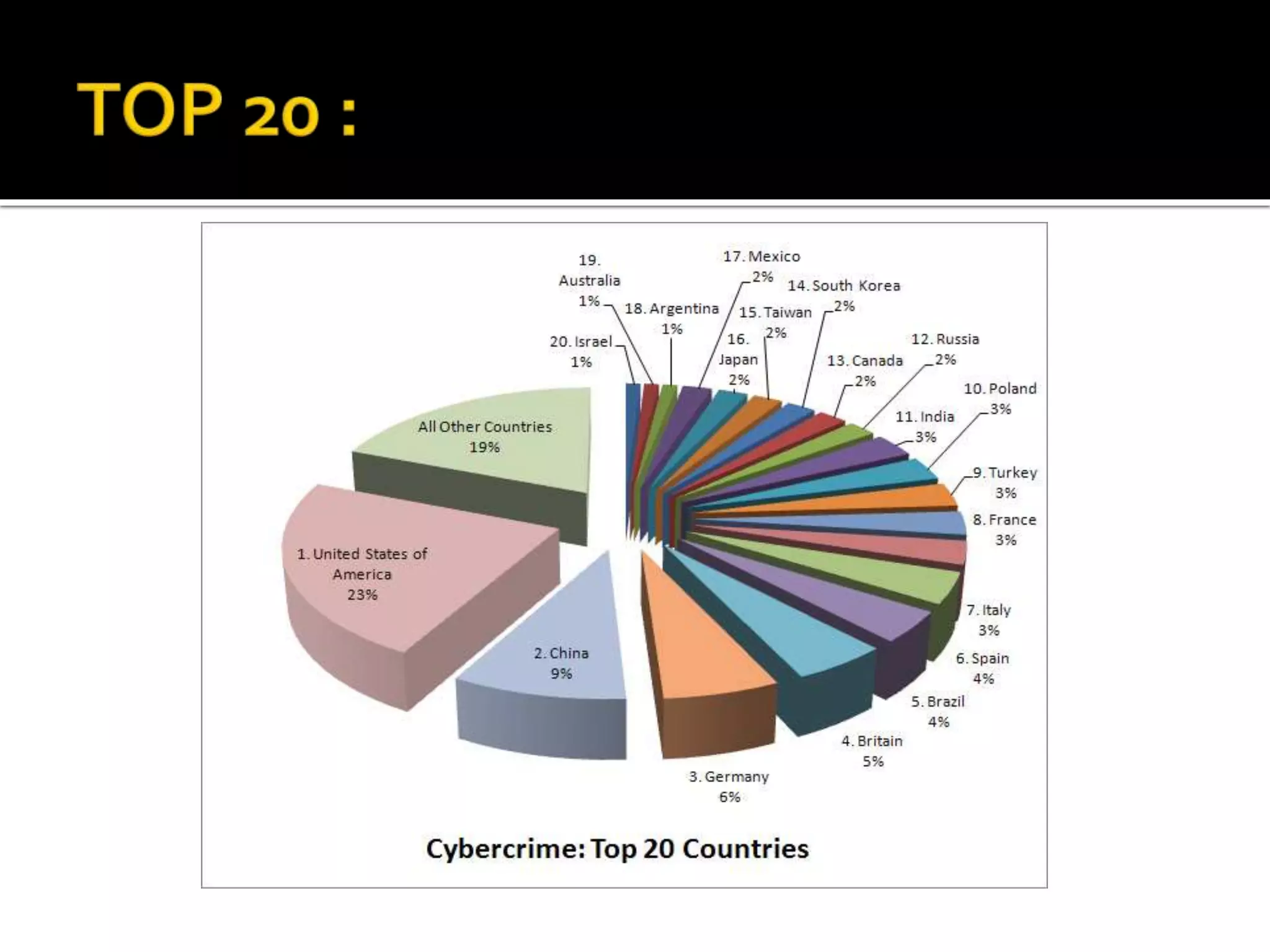
Cyber crime has increased with the growth of internet usage. While the internet initially aimed to improve communication and research, it now enables crimes to be committed remotely from a computer. Some criminals began exploiting the internet for illegal acts in the 1980s, termed "cyber crimes". These can include hacking, theft of information, computer viruses, and other online offenses. While laws have been implemented to address cyber crimes, legislation alone cannot eliminate all criminal acts. Continued education of legal rights and responsibilities, as well as stringent enforcement of laws, are needed to help control cyber crime.