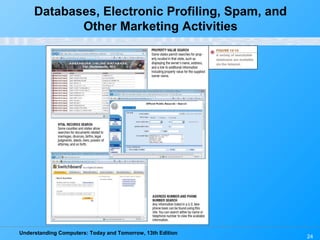
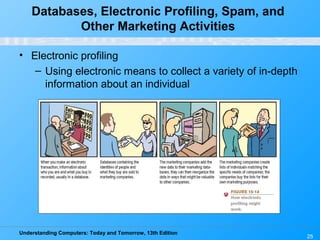
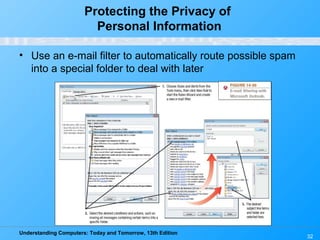
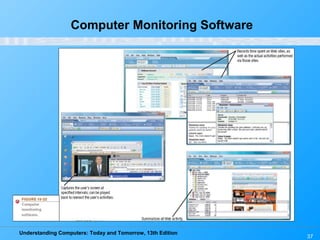
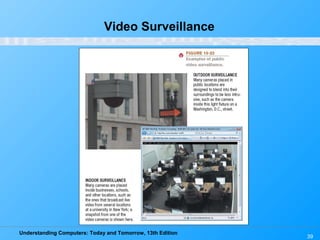
Chapter 15 of 'Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow' focuses on computer security and privacy, addressing issues such as hardware loss, software piracy, and personal information privacy. It discusses the importance of safeguarding against hardware theft and damage, protecting against software piracy, and the risks of electronic surveillance and data breaches. The chapter emphasizes the need for preventative measures, disaster recovery plans, and understanding privacy policies to protect personal information.