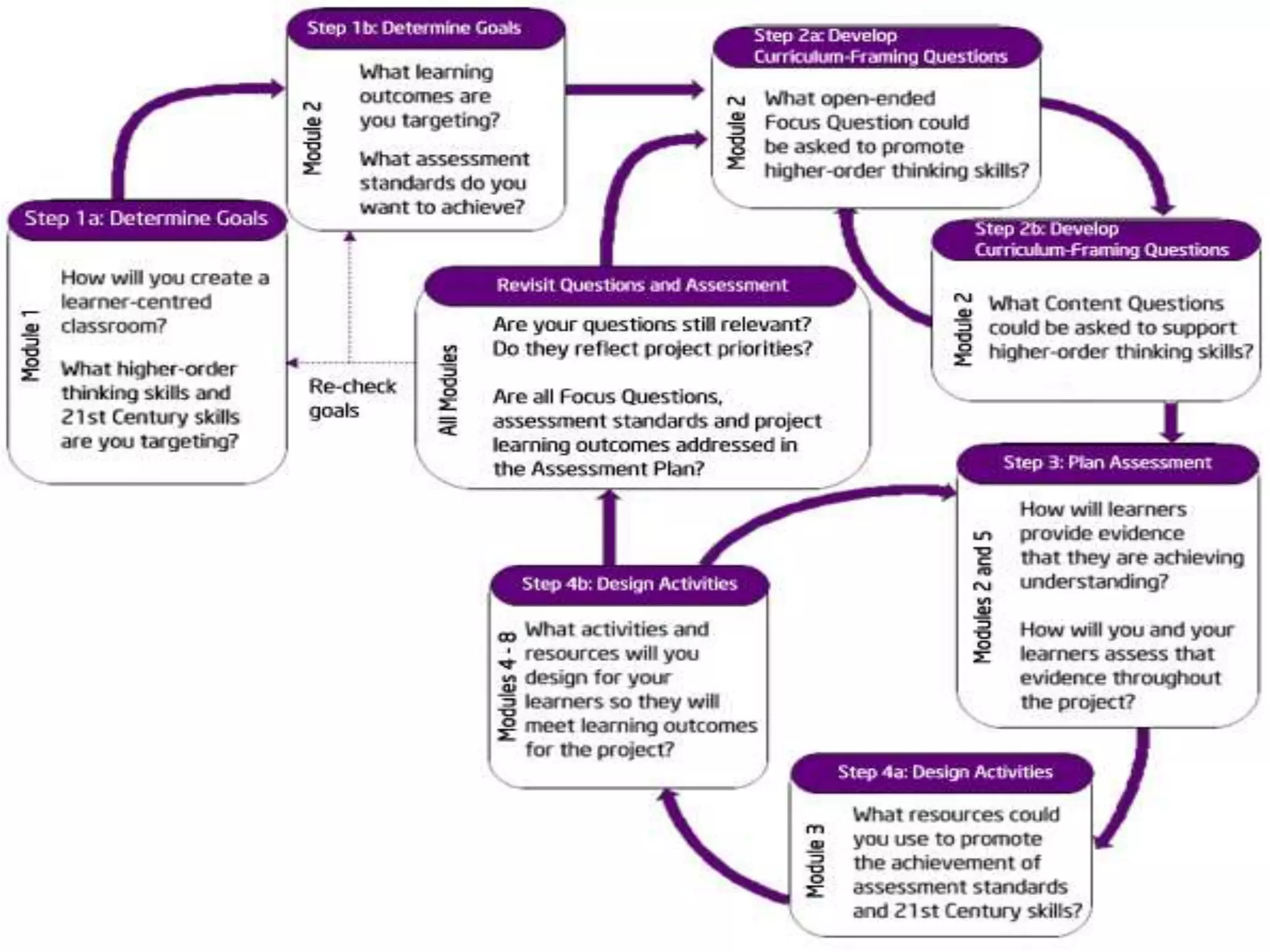
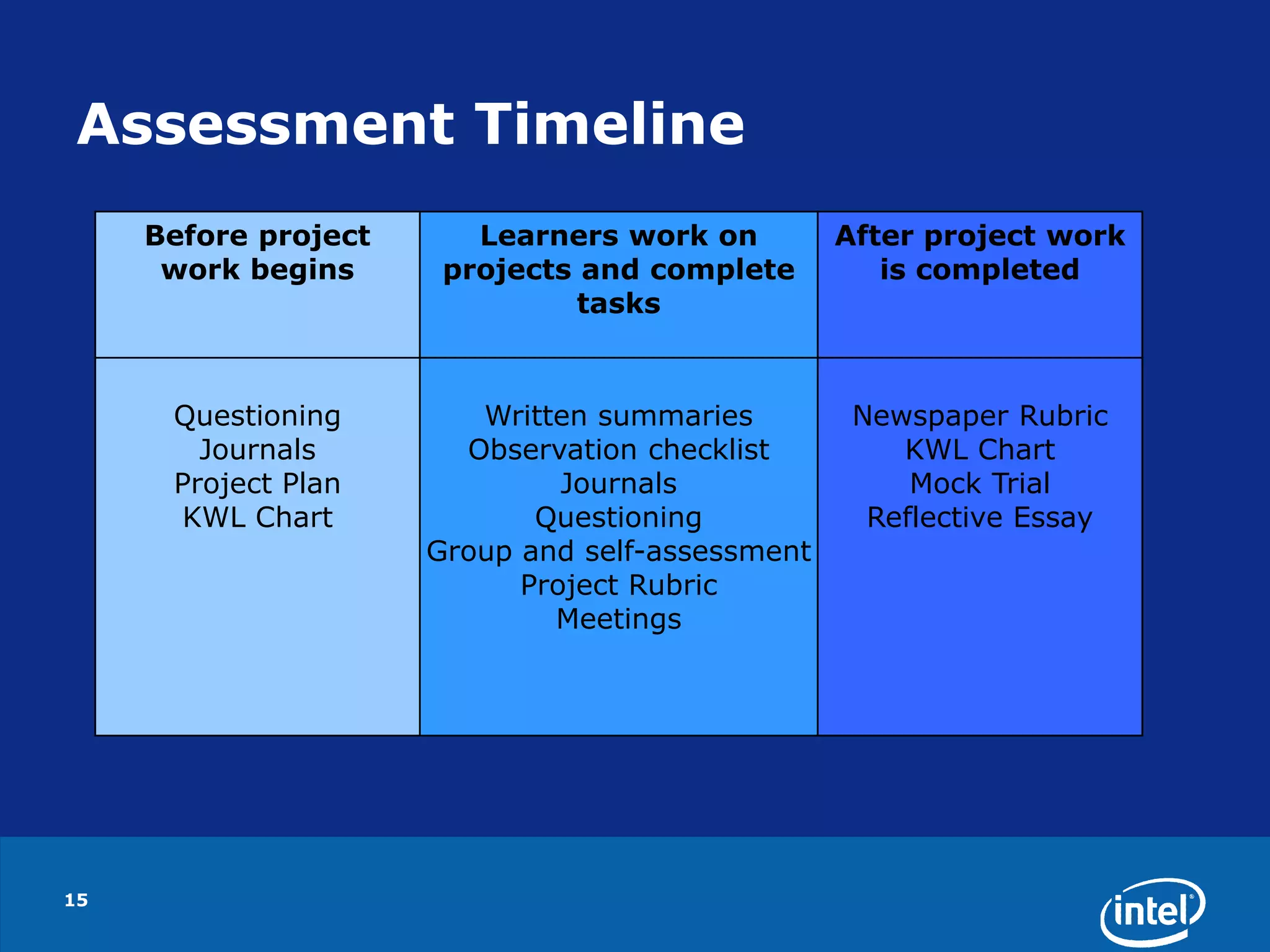
The document outlines a workshop on integrating ICT in education, part of the Intel® Teach Essentials program aimed at improving teaching and learning through technology. It covers project-based learning, assessment strategies, legal and ethical practices, and emphasizes the development of 21st-century skills. Participants are expected to possess intermediate computer skills and engage in hands-on activities to facilitate learner-centered classrooms.