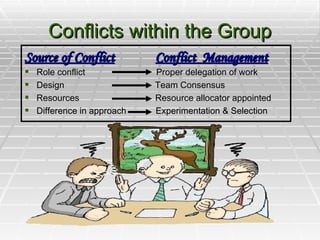
The document discusses the stages of group development including forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning. It emphasizes the importance of setting goals and analyzing tasks and strategies. Conflicts within groups can be functional or dysfunctional and proper delegation and leadership are important. Effective communication, motivation, and applying leadership theories can help groups achieve outcomes and goals.