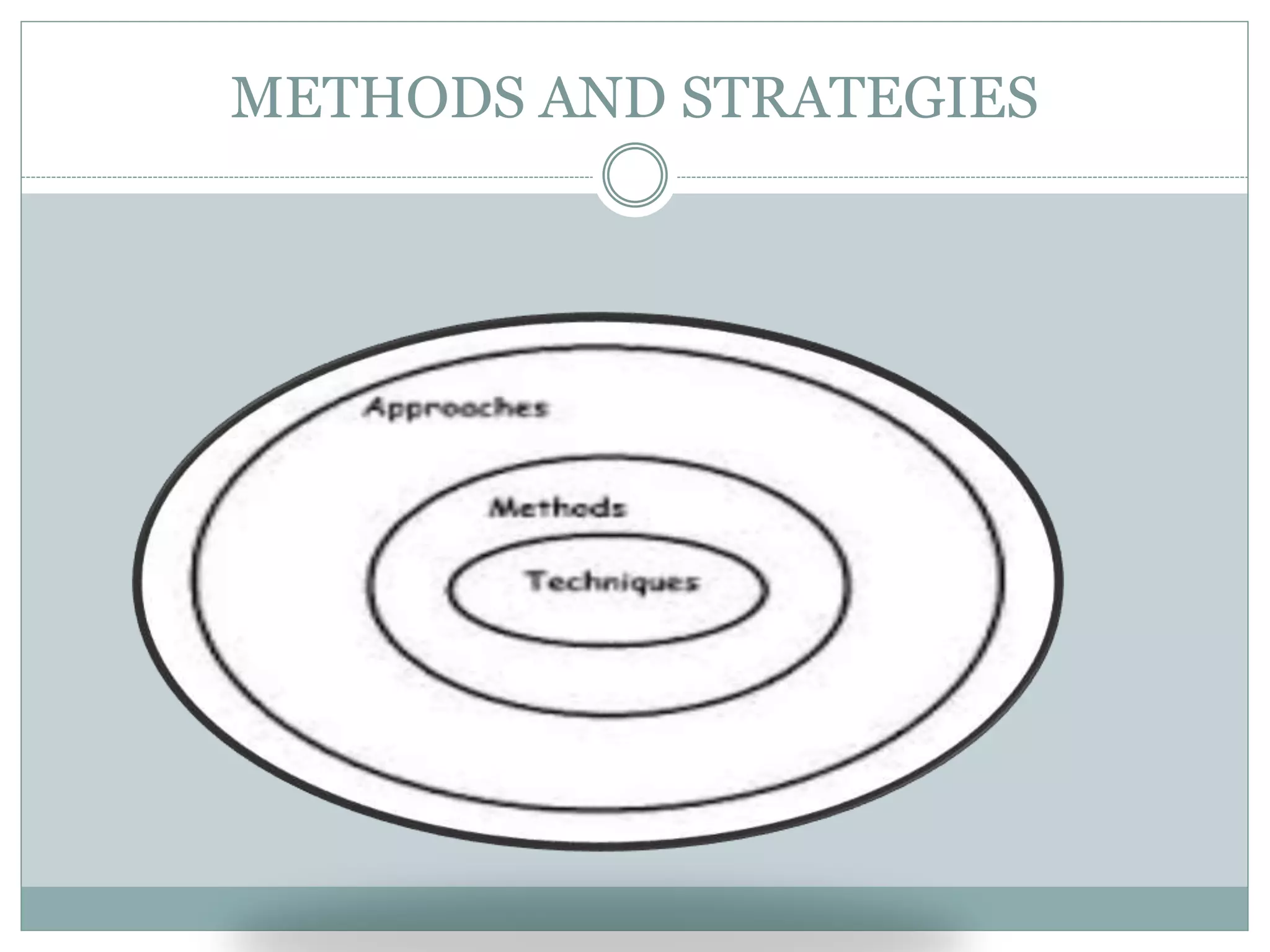
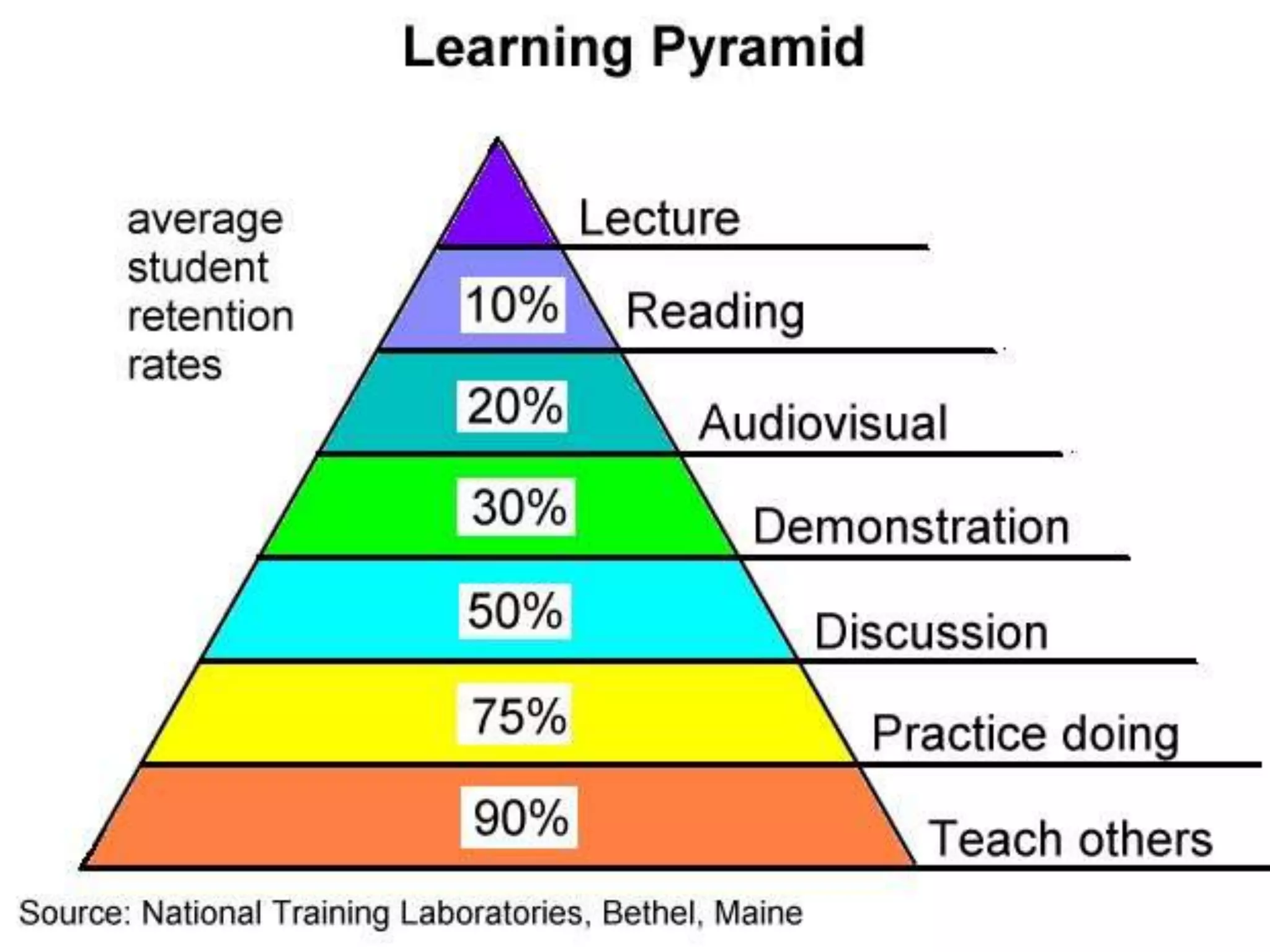
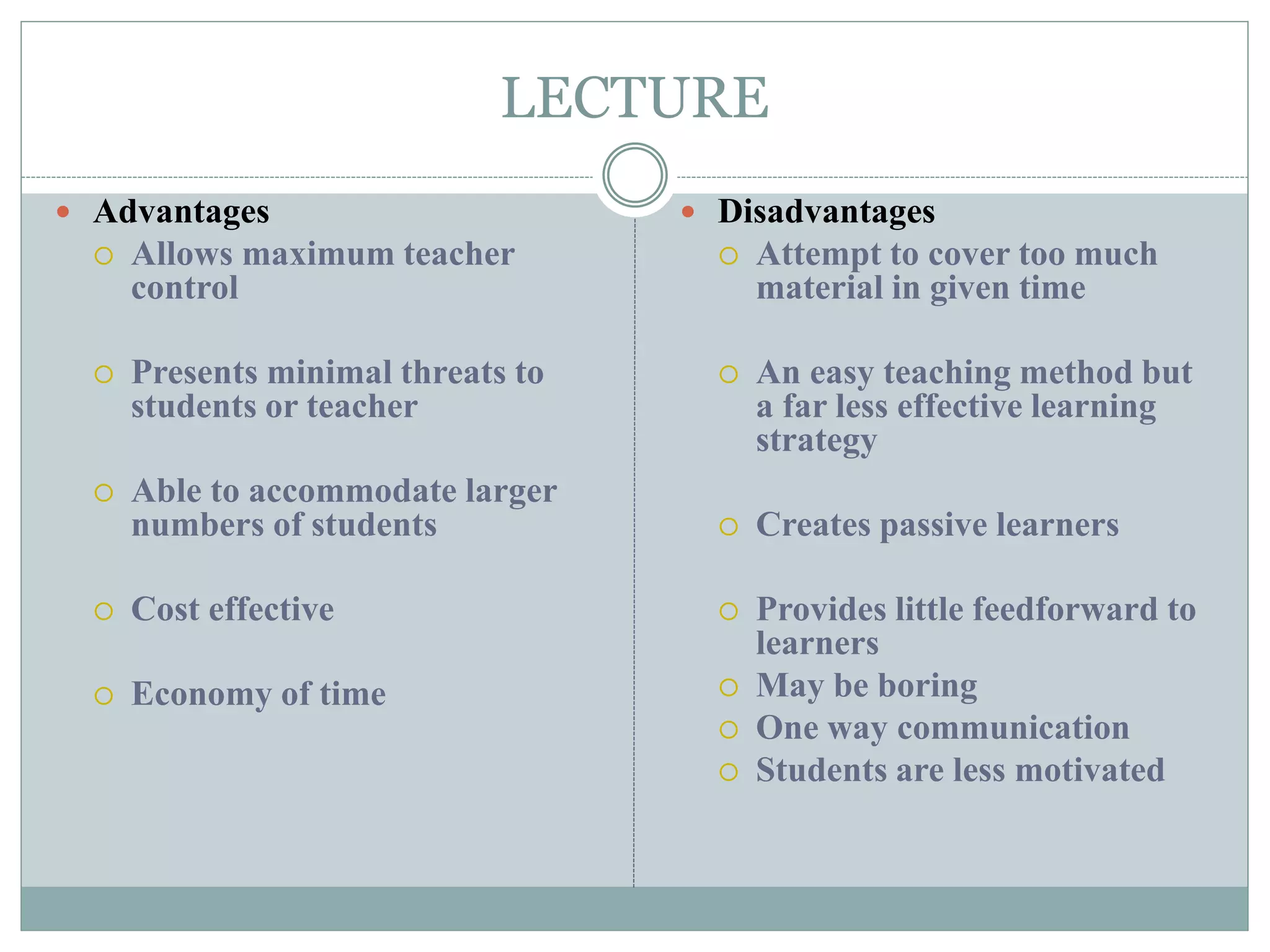
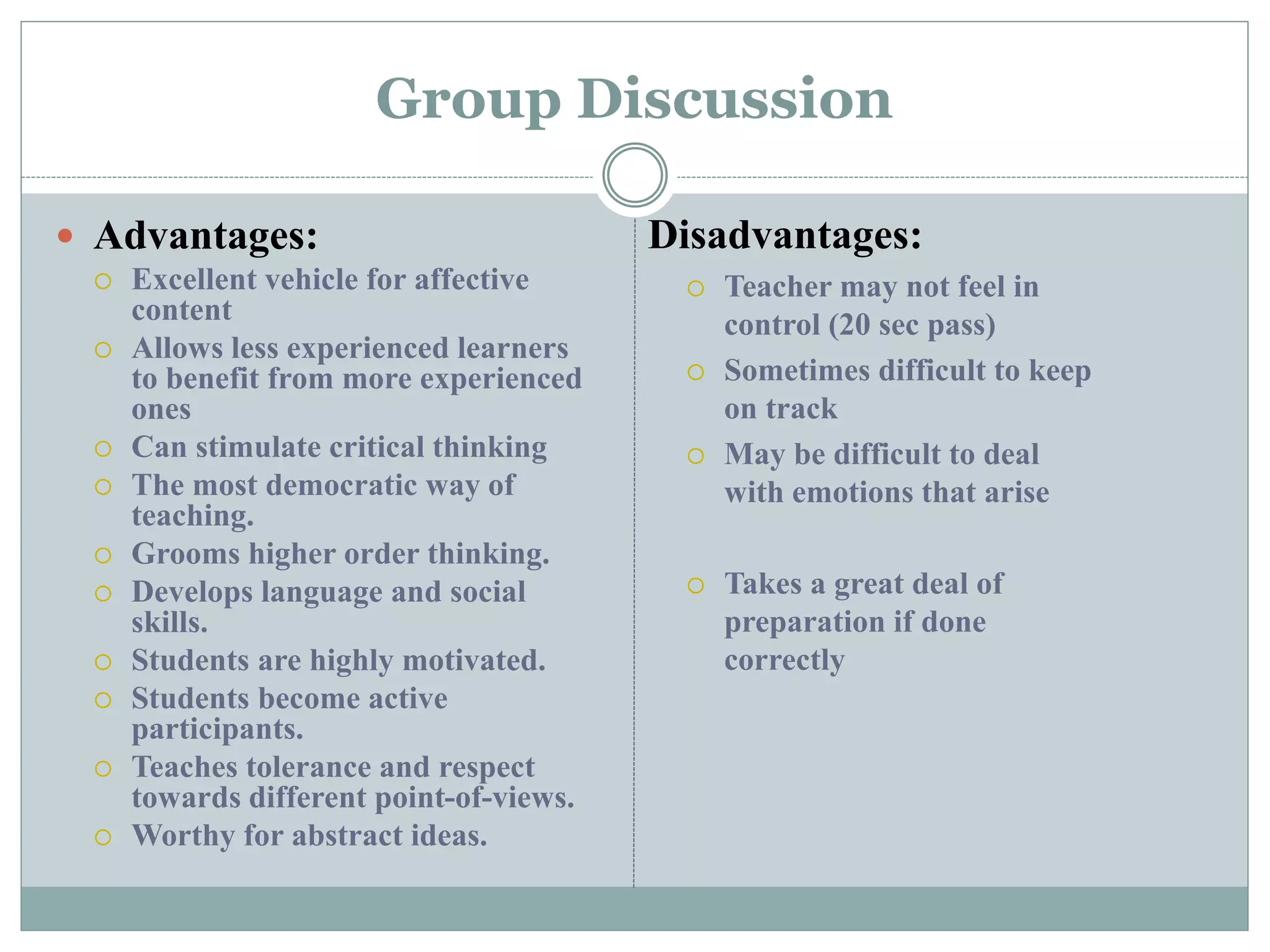
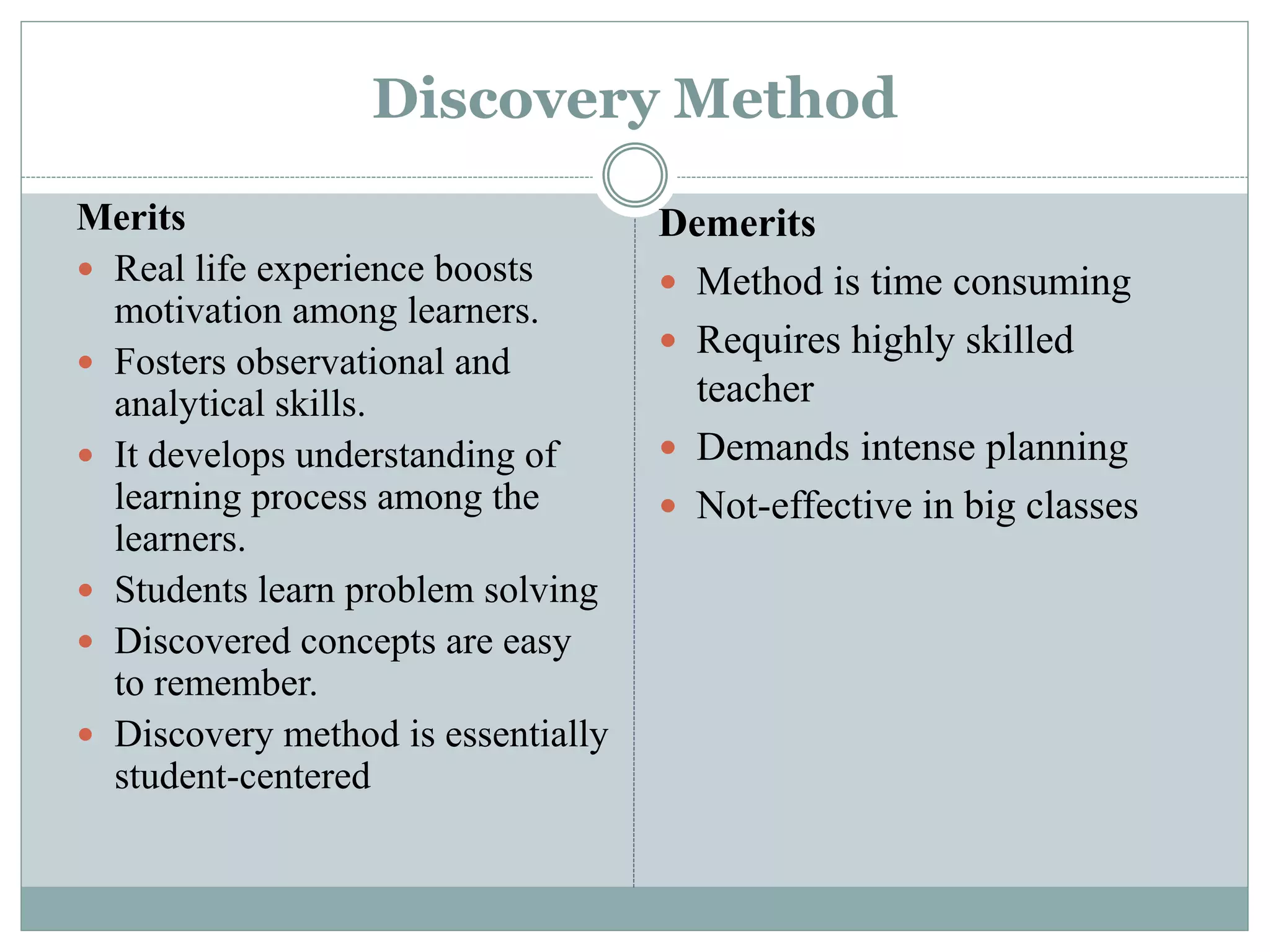
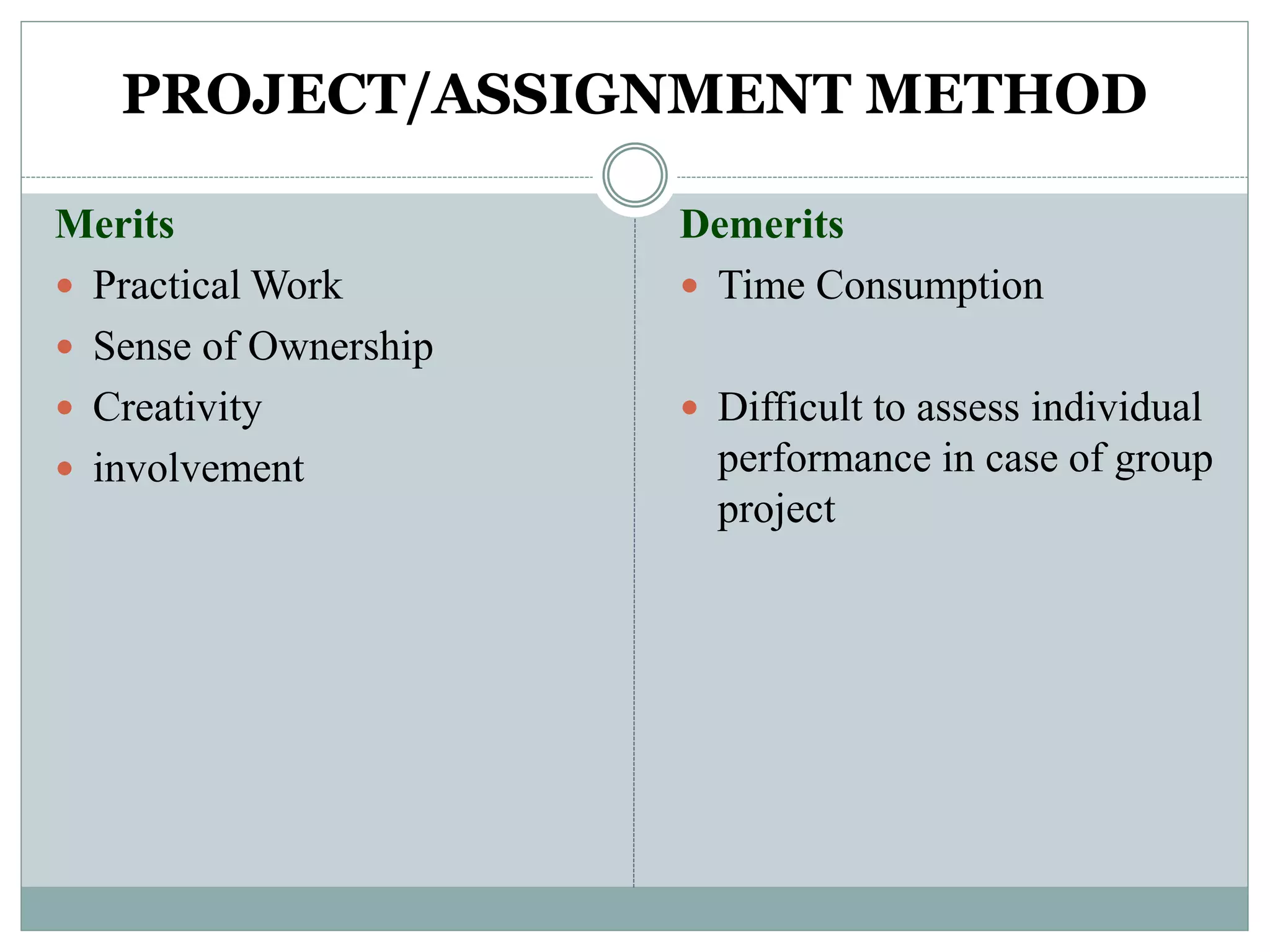
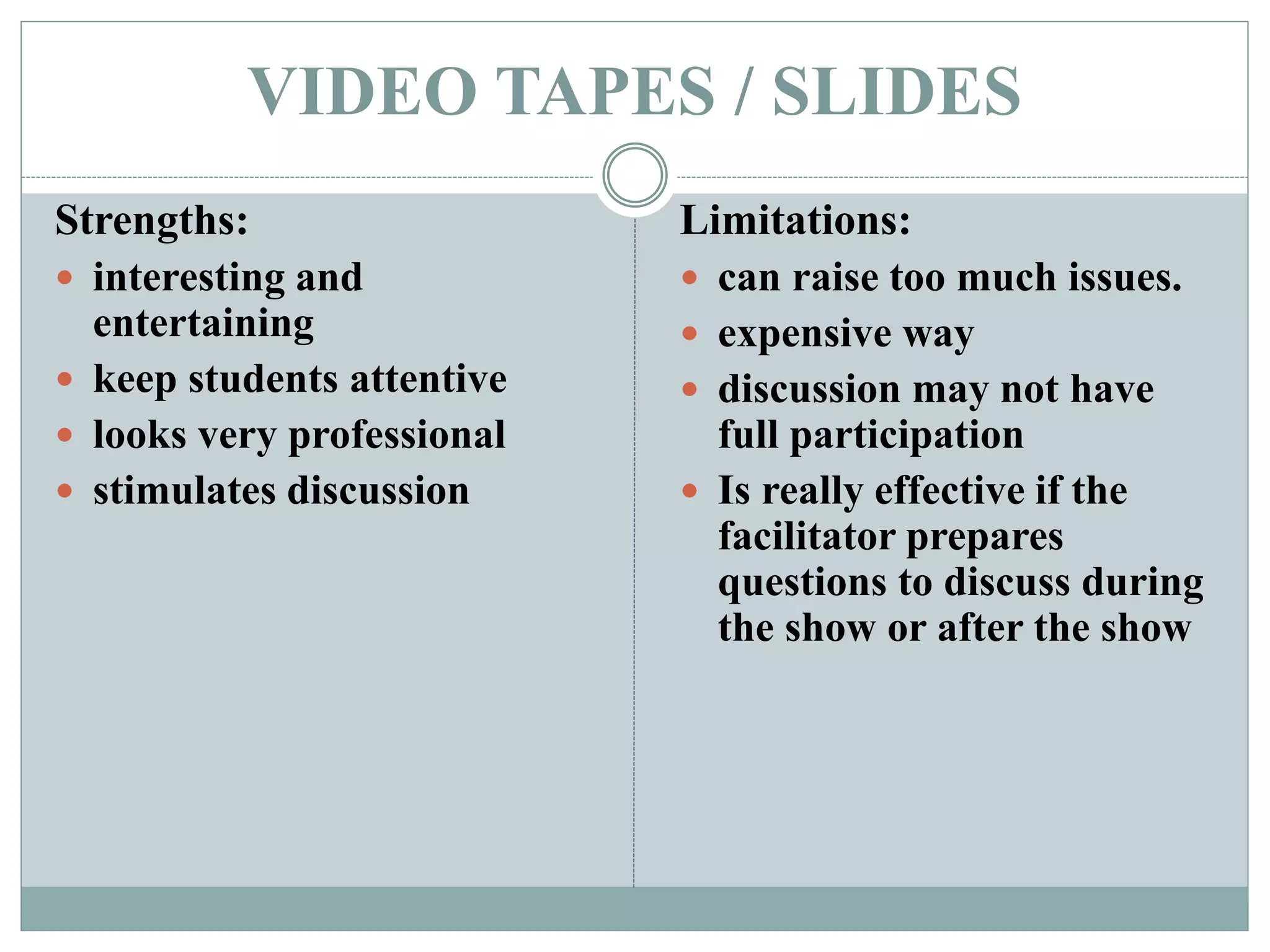
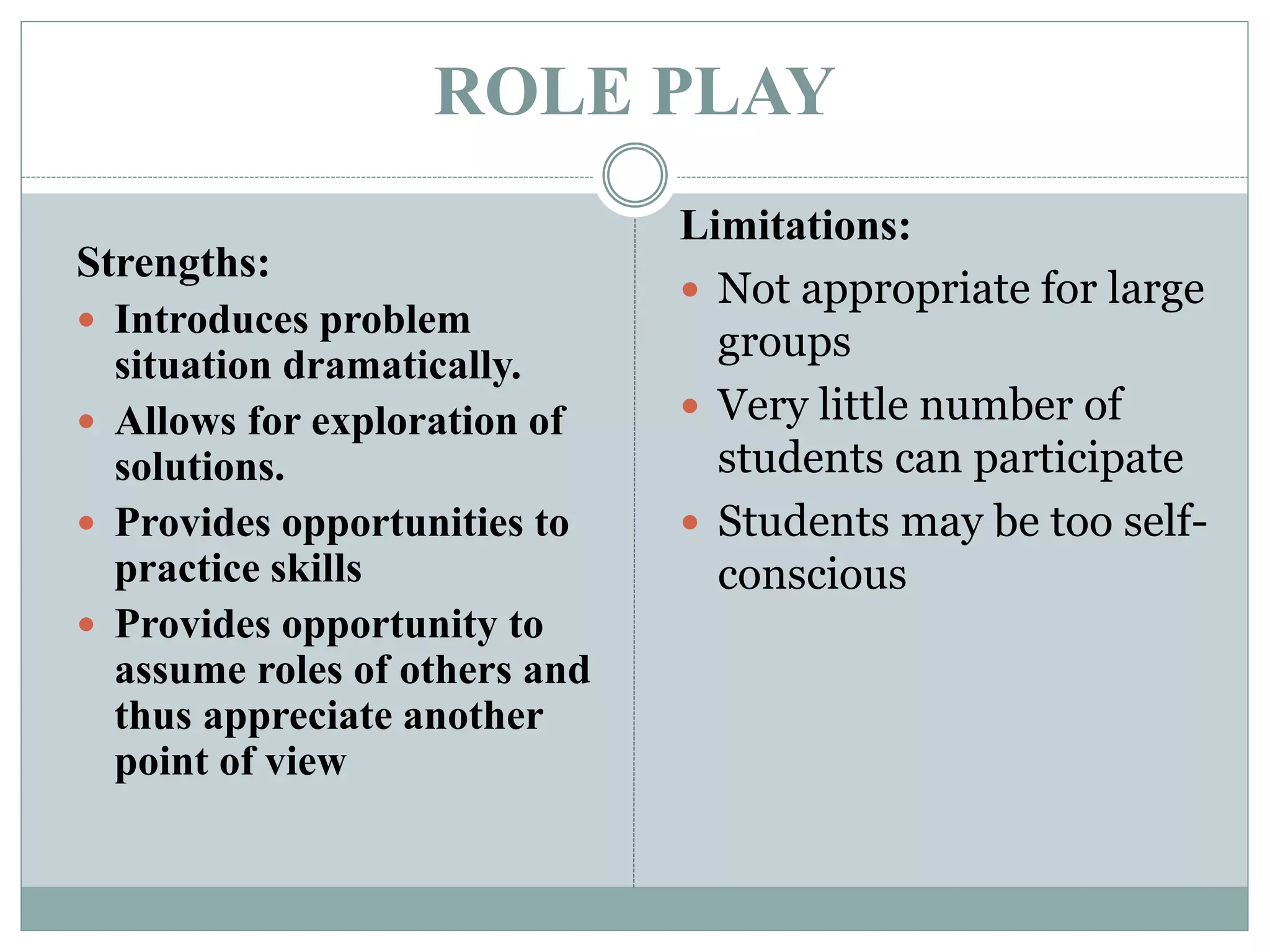
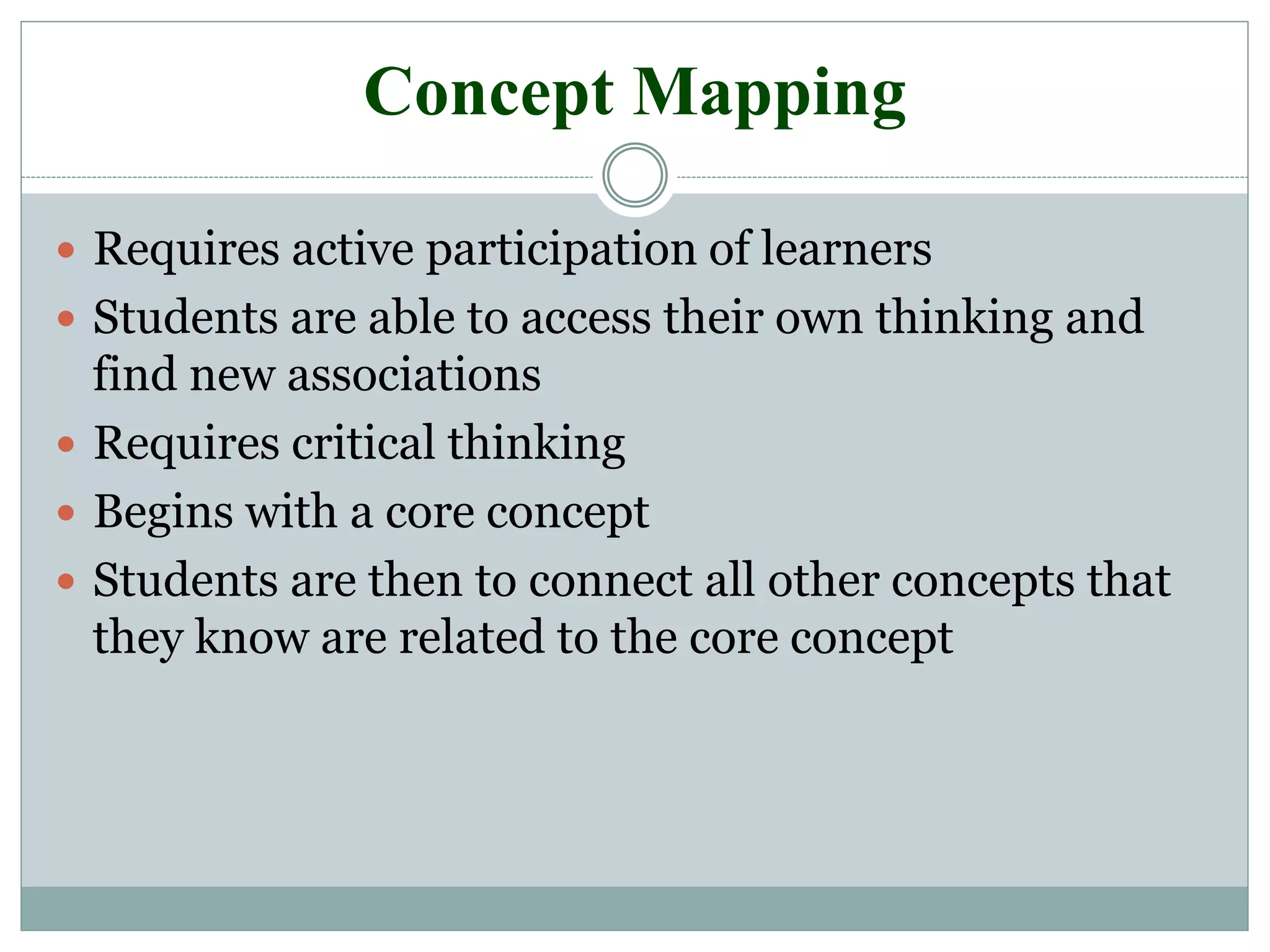
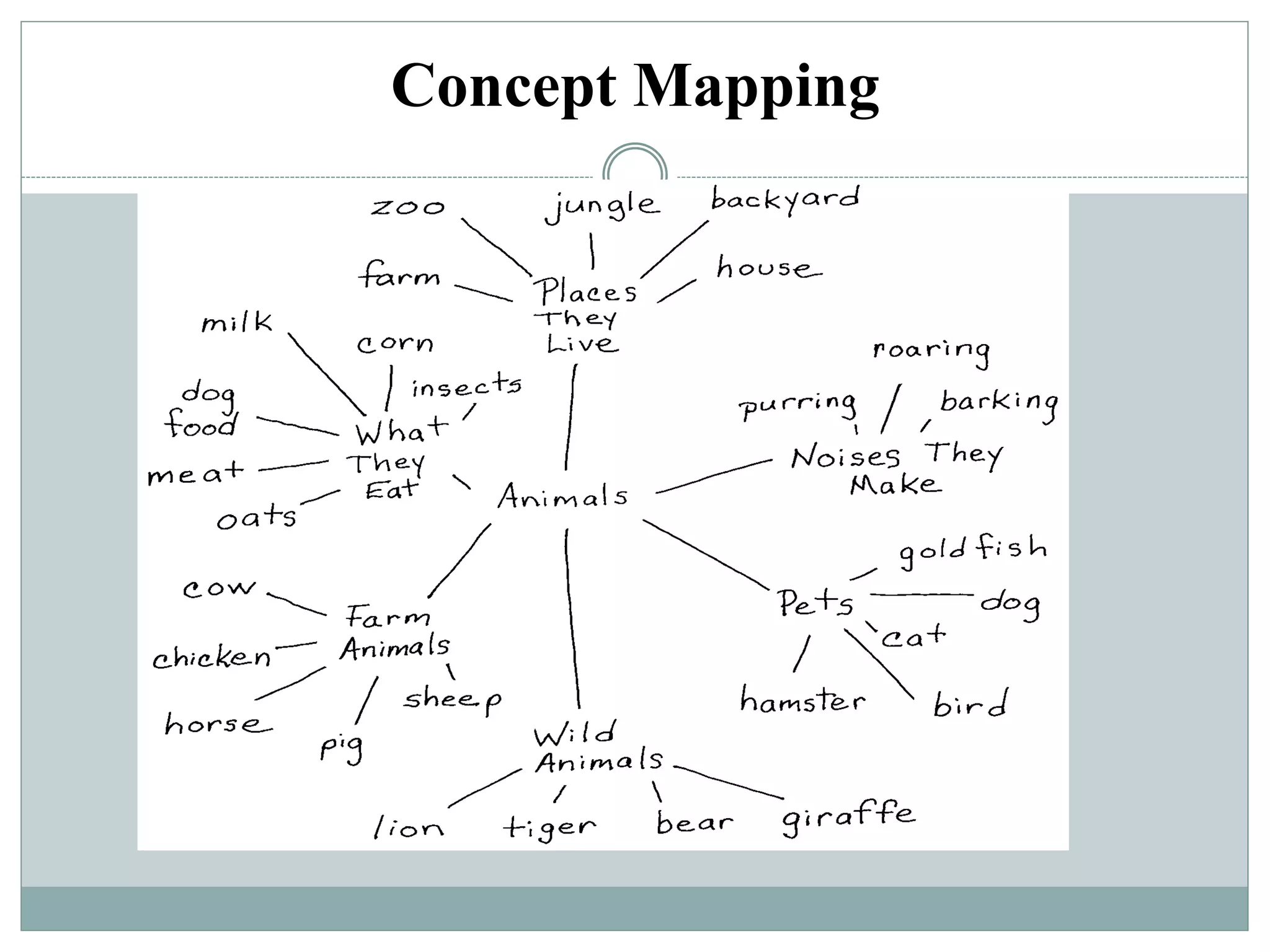
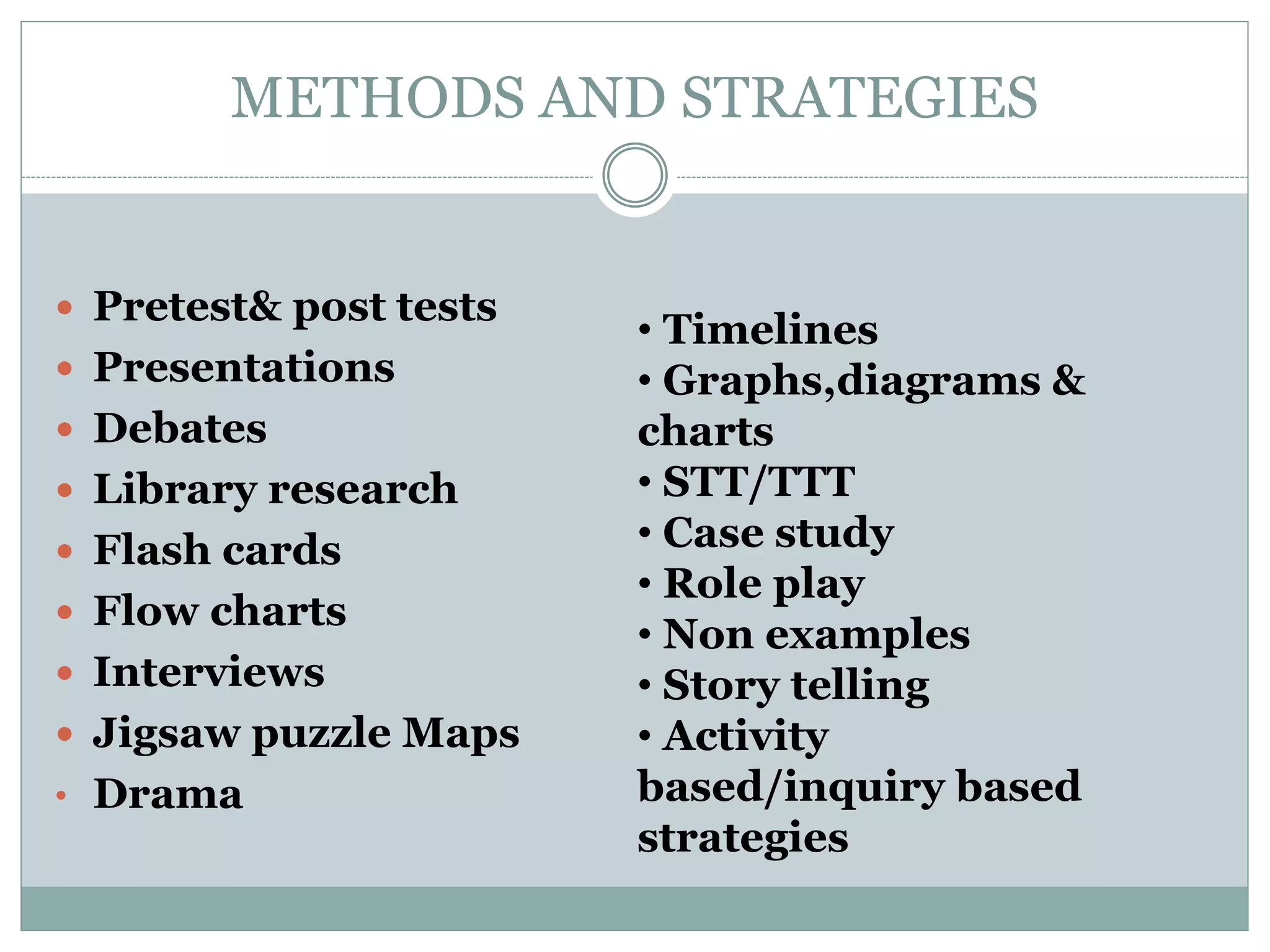
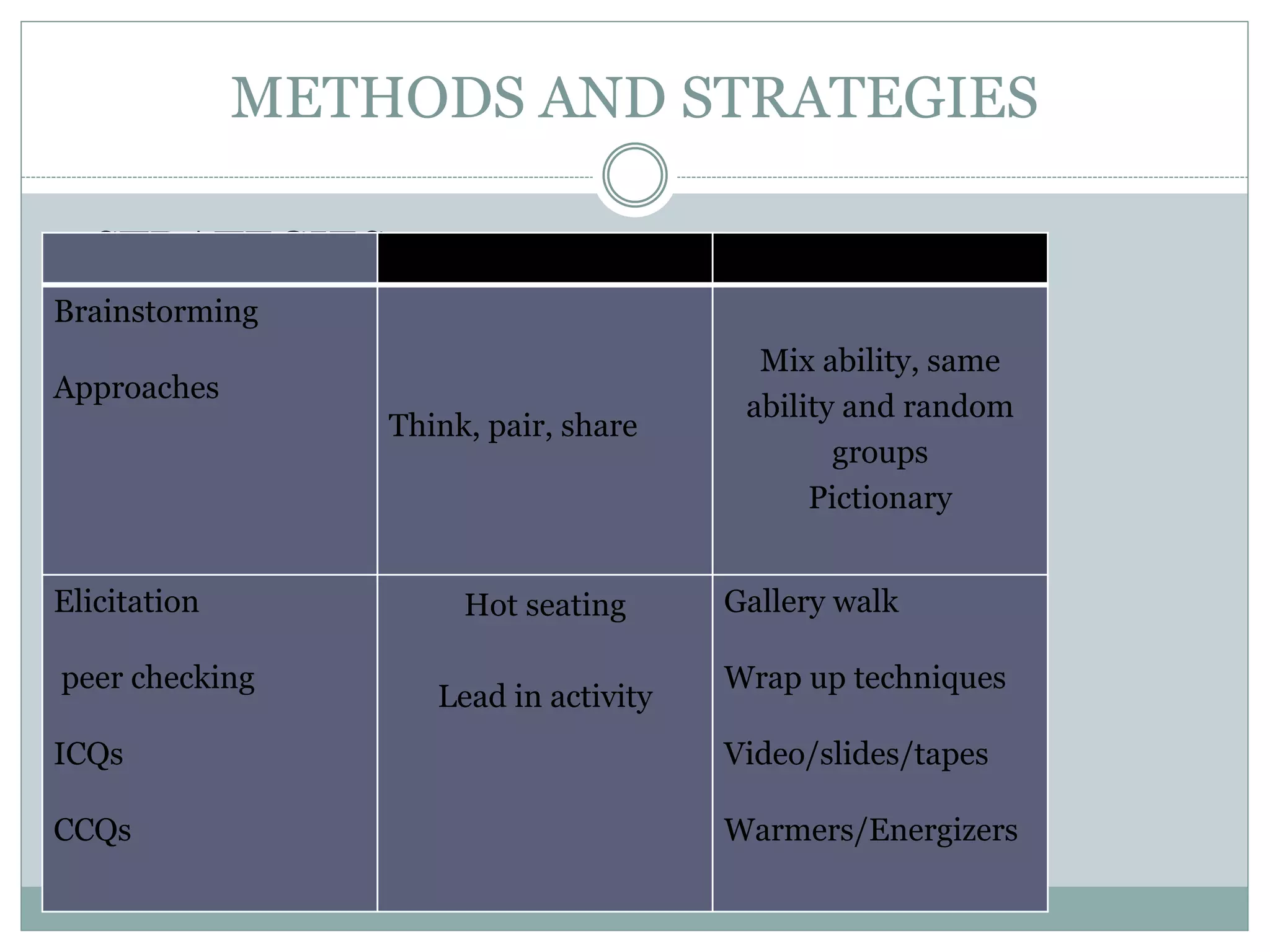
This document discusses various teaching methods and strategies. It begins by defining key concepts like approach, method, and strategy. It then provides tables listing the advantages and disadvantages of different common teaching methods like lectures, group discussions, discovery methods, and games. It also discusses strategies like questioning techniques, simulations, debates and more. The document provides examples of strategies used by the Prophet and ends by outlining tasks for participants to discuss teaching scenarios and plan lesson methodologies incorporating strategies.